Greenland Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Greenland, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Greenland, Arctic Region (4 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Nuuk (Godthaab), and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Arctic state.
Quick links: Google Maps Greenland, Nuuk (Godthaab) Google maps, Driving Directions Greenland, Printable Road Map.

About Greenland in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Greenland
- The conventional long form of the name: none
- Local short form: Kalaallit Nunaat
- The legal system in Greenland: the laws of Denmark apply where applicable and Greenlandic law applies to other areas.
- Climate: Arctic to subarctic, cool summers, cold winters.
- The national symbols are polar bear; national colors: red, white.
- Internet TLD: .gl
Denmark’s autonomous overseas territory owes its name to Erik the Red: the red-bearded Viking leader’s “Green Land” stretches 24 degrees (!) from 60 degrees north latitude to the Arctic, the Realm of eternal snow and ice. However, the vast island, framed by mountain ranges of ancient rocks rising well above 3,000 meters, lacks the vegetation, the taiga, of this latitude; the thick ice cap in its Interior allows only tundra to be present. In the spring, Greenland is truly ‘greened’ – at least on its periphery – as its name suggests, with the typical tundra plants taking over the snow-covered coastline in winter. It is a time of festivities and Inuit cultural festivals that try to forget the long Arctic night. On the west coast of the island, 250 km north of the Arctic Circle, Greenland’s only World Heritage Site is located: in the 40,000 hectares of Ilulissat Fjord, one of the world’s fastest-moving and most active glaciers, the Sermeq Kujalleq glacier, which rises 19 m a day, reaches the waters of Disko Bay.
The glacier sheds 35 km3 of ice per year – one-tenth of the total volume of ice that Greenland sheds into the world’s oceans, more than any other glacier exchange in the northern hemisphere. Disko Bay and its surroundings are also a focal point for Greenlandic tourism, with kayaking, skiing, and dog sledding tours departing from IIIulissat to explore the area. Greenland’s biggest celebration is the Polar Night Farewell Festival, held in late January and early February. In the capital, Nuuk, a snow sculpture festival is held in March, and the Uummannaq Fjord is the site of a unique spectacle: the annual World Ice Golf Championships are held on its ice fields. The ‘island nation’ is accessible from Europe via Denmark and Iceland, with flights arriving at Kulusuk on the east coast and Kangerlussuaq on the west coast, welcoming visitors from Canada.
Background
Greenland, the world’s largest island, is about 80% ice-capped. Vikings reached the island in the 10th century from Iceland. Danish colonization began in the 18th century, and Greenland became an integral part of the Danish Realm in 1953. It joined the European Community (now the EU) with Denmark in 1973 but withdrew in 1985 over a dispute centered on stringent fishing quotas. Greenland remains a member of the Overseas Countries and Territories Association of the EU.
Greenland was granted self-government in 1979 by the Danish parliament. The law went into effect the following year. Greenland voted in favor of increased self-rule in November 2008 and acquired greater responsibility for internal affairs when the Act on Greenland Self-Government was signed into law in June 2009. Denmark, however, continues to exercise control over several policy areas on behalf of Greenland, including foreign affairs, security, and financial policy, in consultation with Greenlands Self-Rule Government.
Geography
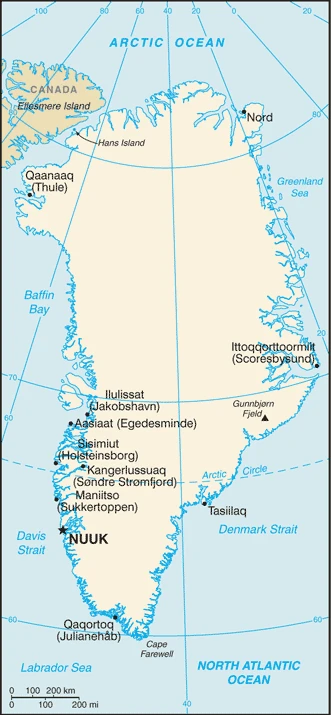
Greenland, known for its long and barren coastline and deep fjords, is a land of ice and snow. The island’s history has been marked by centuries of colonization by various European powers (Greenland became an independent country in 1979).
This state is located in Northern North America, an island between the Arctic Ocean and the North Atlantic Ocean, northeast of Canada, under the coordinates of 72 00 N, 40 00 W, covering an area of 2,166,086 sq km with a coastline of 44,087 km. Greenland is Slightly more than three times the size of Texas.
Greenland has 0 km of land boundaries.
Flat to gradually sloping icecap covers all but a narrow, mountainous, barren, rocky coast. Gunnbjorn fjeld 3,694 m as the highest point of Greenland, while Atlantic Ocean 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 1,792 m throughout the country. With a total of 2,166,086 sq km, Greenland has 2,166,086 sq km (approximately 1,710,000 sq km ice-covered) of land and N/A water surface area.
Dominates the North Atlantic Ocean between North America and Europe; sparse population confined to small settlements along the coast; close to one-quarter of the population lives in the capital, Nuuk; world’s second-largest ice sheet after that of Antarctica, covering an area of 1.71 million sq km (660,000 sq mi) or about 79% of the island, and containing 2.85 million cu km (684 thousand cu mi) of ice (this is almost 7% of all of the worlds freshwater); if all this ice were converted to liquid water, one estimate is that it would be sufficient to raise the height of the world’s oceans by 7.2 m (24 ft).
The climate in Greenland is as follows: Arctic to subarctic, cool summers, cold winters.
When you visit Greenland, the natural hazards shall be considered: Continuous permafrost over the northern two-thirds of the island.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Greenland: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Greenlandic people: especially vulnerable to climate change and disruption of the Arctic environment; preservation of the Inuit traditional way of life, including whaling and seal hunting.
Google Maps Greenland
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Nuuk (Godthaab) found under the coordinates 64 11 N, 51 45 W, applying the time zone UTC-3 (2 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October.
Nuuk lies on the large Uummannaq Fjord in western Greenland. This town is the largest city in that country and is home to around 18,000 people. Nuuk had many names in its early days, including Nuummuseat and Godthaab.
Greenland became independent on none (extensive self-rule as part of the Kingdom of Denmark; foreign affairs is the responsibility of Denmark, but Greenland actively participates in international agreements relating to Greenland), and its national holiday is National Day, June 21.
Administrative divisions: 5 municipalities (kommuner, singular kommune); Avannaata, Kujalleq, Qeqertalik, Qeqqata, Sermersooq note: Northeast Greenland National Park (Kalaallit Nunaanni Nuna Eqqissisimatitaq) and the Thule Air Base in Pituffik (in northwest Greenland) are two unincorporated areas; the national parks 972,000 sq km – about 46% of the island – makes it the largest national park in the world and also the most northern.
People and society
The population in Greenland is 57,799 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of -0.01% (2021 estimate) change. That means Greenland is the No. 205 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 34.3 years median age (35.1 years for males and 35.1 years for women), Greenland ranks No. 92 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Greenlander(s) (noun) or Greenlandic (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Greenlandic 89.5%, Danish 7.5%, other Nordic peoples 1.1%, and other 1.9% (2020 estimate). Note: data represent population by country of birth.
They speak Greenlandic (West Greenlandic or Kalaallisut is the official language), Danish, English languages, and practice the following religions: Evangelical Lutheran traditional Inuit spiritual beliefs.
We can conclude the following about the population in Greenland: Settlement concentrated on the southwest shoreline, with limited settlements scattered along the remaining coast. The Interior is uninhabited. In Greenland, we are talking about 87.5% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 18,000 Nuuk (capital city) (2018).
Industry
Greenland’s economy depends on exports of shrimp and fish and a substantial subsidy from the Danish Government. Fish account for over 90% of its exports, subjecting to price fluctuations. The subsidy from the Danish Government is budgeted to be about $535 million in 2017, more than 50% of government revenues and 25% of GDP. The economy is expanding after a period of decline. Between 2012 and 2014, the economy contracted grew by 1.7% in 2015 and by 7.7%in 2016. The expansion has been driven by larger quotas for shrimp, the predominant Greenlandic export, and increased activity in the construction sector, especially in Nuuk, the capital. Private consumption and tourism also contribute to GDP growth more than in previous years. Tourism in Greenland grew annually by around 20% in 2015 and 2016, mainly due to increasing numbers of cruise lines now operating in Greenland’s western and southern waters during the peak summer tourism season. The public sector, including publicly owned enterprises and municipalities, plays a dominant role in Greenland’s economy.
The Greenland Self Rule Government pursued conservative fiscal and monetary policies during the last decade, but public pressure has increased for better schools, health care, and retirement systems. The budget was in deficit in 2014 and 2016, but public debt remains low at about 5% of GDP. Significant challenges face the island, including low levels of qualified labor, geographic dispersion, lack of industry diversification, the long-term sustainability of the public budget, and a declining population due to emigration. Hydrocarbon exploration has ceased with declining oil prices. The island has potential for natural resource exploitation with proposed rare-earth, uranium, and iron ore mineral projects, but a lack of infrastructure hinders development.
Greenland is rich in natural resources: Coal, iron ore, lead, zinc, molybdenum, diamonds, gold, platinum, niobium, tantalite, uranium, fish, seals, whales, hydropower, possible oil and gas.
The main industrial sectors are typically fish processing (mainly shrimp and Greenland halibut), anorthosite and ruby mining, handicrafts, hides and skins, small shipyards.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in fish, crustaceans, fishing ships (2019), partnering with these nations: Denmark 55%, China 22%, Japan 6% (2019). The export trade resulted in $407.1 million. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2015 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Greenland’s position of 195.
Land use in Greenland: 0% (2018 estimate) forest, 99.4% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 0% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 0.6% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 0.6% (2018 estimate).
The main agro-industrial products of Greenland are sheep, cattle, reindeer, fish, shellfish.
The country typically needs to import: fishing ships, refined petroleum, construction vehicles, crustaceans, delivery trucks (2019), partnering with the following nations: Denmark 51%, Spain 23%, Sweden 12%, Iceland 7% (2019) in a sum value of $783.5 million (2015 estimate) $866.1 million (2014 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Greenland 196.
Greenland Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Greenland, Northern North America, an island between the Arctic Ocean and the North Atlantic Ocean, northeast of Canada. We published some basic information about its capital Nuuk (Godthaab), and the Greenlandic nation.
Are you interested in visiting Greenland and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Greenland below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Greenland
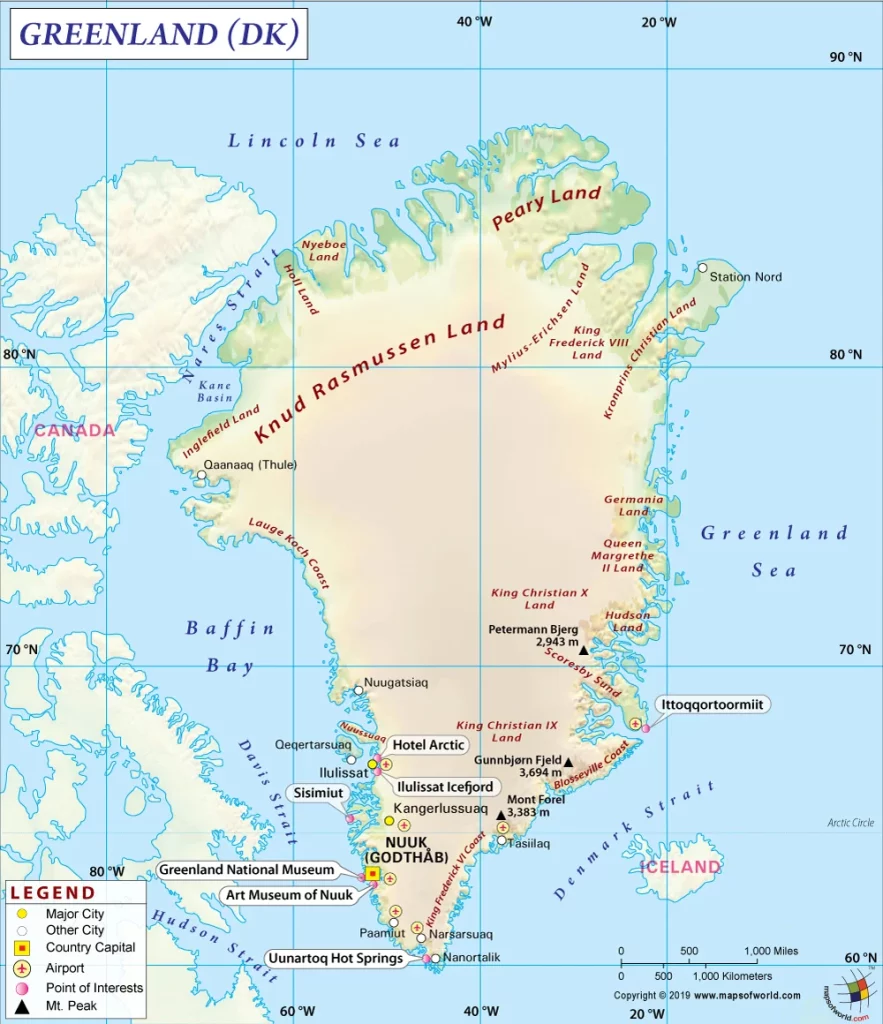
Did you know about Greenland?
Greenland is the world’s largest island. It is also considered one of the most isolated places globally, with no roads or highways leading to it and a very harsh climate. The country has been entirely uninhabited for over 700 years.
After virtually visiting Greenland, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Canada, Denmark, or the United States of America.
If you liked our Google map and Greenland information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.
