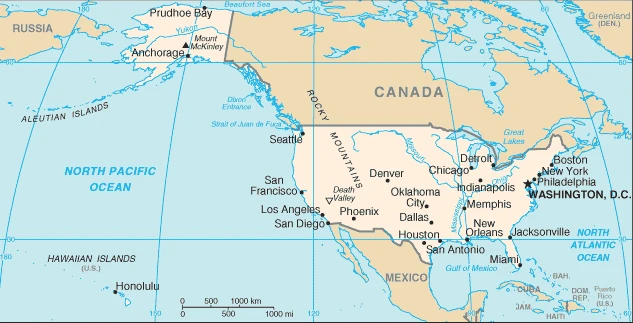
The United States Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like the United States, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to the United States, North America, showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Washington, DC, bordering countries like Canada, Mexico, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this North American state.
Quick links: Google Maps United States, Washington, DC Google maps, Driving Directions United States, Printable Road Map.

About the United States in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: USA
- The conventional long form of the name: none
- Etymology: self-descriptive name specifying the territories affiliation and location.
- The legal system in the United States: common law system based on English common law at the federal level; state legal systems based on common law, except Louisiana, where state law is based on the Napoleonic civil code.
- Climate: There are four main climatic zones. The north and east are continental and temperate, with heavy rainfall, warm summers, and cold winters. Florida and the Deep South are tropical and prone to hurricanes. The southwest is an arid desert with searing summer heat and low rainfall. Southern California is the Mediterranean, with hot summers and mild winters.
- The national symbols are the bald eagle; the national colors: are red, white, and blue.
- Internet TLD: .us
The United States is the third-largest country on Earth, but in terms of contiguous land area (excluding Alaska and Hawaii), it is ahead of China and Brazil. The “middle” between the Appalachian escarpment and the young chain of the Coastal Cordillera, which begins in Alaska, is filled by the vast basins and plateaus of the Rocky Mountains and their ranges in the west and the lowlands and valleys of the Mississippi River basin in the east. The Great Lakes to the northeast and the limestone plateau of the Florida peninsula to the southeast complete the range of contiguous highlands of the states. The Gulf Stream, born in the Gulf of Mexico, warms only the Florida coast, while the cold Labrador Current often carries icebergs as far north as New York, at the latitude of Madrid. In the west, the warm current from Asia splits as it reaches the continent: its northward branch “heats” the coast of Alaska, while its southward branch, turning into a cold current, “cools” the California coastline.
The first European to set foot on the land of the (then non-existent) United States was Juan Ponce de Léon of Spain, who landed in Florida 20 years after Columbus. The Dutch, British, and French followed the Spaniards, and due to the struggle for independence, the United States of America was formed in 1776 from 13 states created from the British colonies on the east coast. The first 13 states were followed by 37 more, with Hawaii joining in 1959 to become the 50th member state of the USA. In the Pacific and Caribbean, the United States has several foreign possessions.
The actual records collected in a United States census must remain confidential for 72 years by law.
Background
Britain’s American colonies broke with the mother country in 1776 and were recognized as the new nation of the United States of America following the Treaty of Paris in 1783. During the 19th and 20th centuries, 37 new states were added to the original 13 as the nation expanded across the North American continent and acquired several overseas possessions. The two most traumatic experiences in the nation’s history were the Civil War (1861-65), in which a northern Union of states defeated a secessionist Confederacy of 11 southern slave states, and the Great Depression of the 1930s, an economic downturn during which about a quarter of the labor force lost its jobs. Buoyed by World Wars I and II victories and the end of the Cold War in 1991, the US remains the world’s most powerful nation-state. Since World War II, the economy has achieved relatively steady growth, low unemployment and inflation, and rapid technological advances.
Geography
The US has a varied topography. Forested mountains stretch from New England in the far northeast, giving way to lowlands and swamps in the extreme south. The Mississippi, Missouri River, and the Great Lakes on the Canadian border dominate the central plains. The Rocky Mountains in the west contain active volcanoes and drop to the coast across the earthquake-prone San Andreas Fault. The southwest is an arid desert. Mountainous Alaska is mostly Arctic tundra.
The country known as the United States is a land of citizens, immigrants, and rebels. It was founded with help from an agreement among thirteen colonies, which eventually became states. It has been a leader in many fields – its ideas have led to industrial revolutions, policy reforms, and constitutional changes. The US has faced many challenges: slavery, immigration rights, civil rights movements, and international conflicts.
This state is located in North America, bordering both the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Pacific Ocean, between Canada and Mexico, under the coordinates of 38 00 N, 97 00 W, covering an area of 9,833,517 sq a coastline of 19,924 km.
The United States is About half the size of Russia, about three-tenths the size of Africa, about half the size of South America (or slightly larger than Brazil), slightly larger than China, and more than twice the size of the European Union.
The United States borders 5 nations: Canada, 8,891 km (including 2,475 km with Alaska), and Mexico, 3,111 km.
The vast central plain, mountains in the west, hills and low mountains in the east, rugged mountains, broad river valleys in Alaska, and rugged, volcanic topography in Hawaii. With 9,833,517 sq km, the United States has 9,147,593 sq km of land and 685,924 sq km of water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Michigan 57,750 sq km; Superior 53,348 sq km; Huron 23,597 sq km; Erie 12,890 sq km; Ontario 9,220 sq km; Lake of the Woods 4,350 sq km; Iliamna 2,590 sq km; Okeechobee 1,810 sq km; Belcharof 1,190 sq km; Red 1,170 sq km; Saint Clair 1,113 sq km; Champlain 1,100 sq km (a freshwater lake), Great Salt 4,360 sq km; Pontchartrain 1,620 sq km; Selawik 1,400 sq km; Salton Sea 950 sq km (saltwater lake) while the major rivers are: Missouri – 3,768 km, Mississippi (shared with Canada) – 3,544 km, Yukon (shared with Canada) – 3,190 km, Saint Lawrence (shared with Canada) – 3,058 km, Rio Grande (shared with Mexico) – 3,057 km, Colorado (shared with Mexico) – 2,333 km, Arkansas – 2,348 km, Columbia (shared with Canada) – 2,250 km, Red – 2,188 km Ohio – 2,102 km, Snake – 1,670 km. The significant watersheds for the United States are Atlantic Ocean drainage: (Gulf of Mexico) Mississippi (3,202,185 sq km), Rio Grande (607,965 sq km), (Gulf of Saint Lawrence) Saint Lawrence (1,049,636 sq km total, US only 505,000 sq km) Pacific Ocean drainage: Yukon (847,620 sq km, US only 23,820 sq km); Colorado (703,148 sq km), Columbia (657,501 sq km, US only 554,501 sq km).
The climate in the United States is as follows: Mostly temperate but tropical in Hawaii and Florida, arctic in Alaska, semiarid in the great plains west of the Mississippi River, and arid in the great basin of the southwest, low winter temperatures in the northwest are ameliorated occasionally in January and February by warm chinook winds from the eastern slopes of the rocky mountains. Many consider Denali, the highest peak in the US, to be the world’s coldest mountain because it combines high elevation and its subarctic location at 63 degrees north latitude, permanent snow and ice cover over 75 percent of the mountain, and enormous glaciers, up to 45 miles long and 3,700 feet thick, spider out from its base in every direction. It is home to some of the world’s oldest and most violent weather, where winds of over 150 miles per hour and temperatures of -93F have been recorded.
When you visit the United States, the natural hazards shall be considered: Tsunamis; volcanoes; earthquake activity around the Pacific Basin; hurricanes along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coasts; tornadoes in the midwest and southeast; mudslides in California; forest fires in the west; flooding; permafrost in northern Alaska.
Volcanic activity in the Hawaiian islands, western Alaska, the pacific northwest, and the Northern Mariana islands; both Mauna Loa (4,170 m) in Hawaii and Mount Rainier (4,392 m) in Washington have been deemed decade volcanoes by the international association of volcanology and chemistry of the interior of the Earth, worthy of study due to their tumultuous history and proximity to human populations. Pavlov (2,519 m) is the most active volcano in Alaska’s Aleutian arc and poses a significant threat to air travel since the area constitutes the main flight path between North America and East Asia; st. Helens (2,549 m), famous for the devastating 1980 eruption, remains active today; numerous other historically active volcanoes exist, mainly concentrated in the Aleutian arc and Hawaii; they include Alaska: Aniakchak, Augustine, Chiginagak, Fourpeaked, Iliamna, Katmai, Kupreanof, Martin, Novarupta, Redoubt, Spurr, Wrangell, Trident, Ugashik-Peulik, Ukinrek Maars, Veniaminof; in Hawaii: Haleakala, Kilauea, Loihi; in the Northern Mariana Islands: Anatahan; and the pacific northwest: Mount Baker, Mount hood.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting the United States: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the American people: air pollution; large emitter of carbon dioxide from the burning of fossil fuels; water pollution from runoff of pesticides and fertilizers; limited natural freshwater resources in much of the western part of the country require careful management; deforestation; mining; desertification; species conservation; invasive species (the Hawaiian Islands are particularly vulnerable).
Google Maps the United States
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Washington, DC, found under the coordinates 38 53 N, 77 02 W, applying the time zone UTC-5 (during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr, begins second Sunday in March; ends first Sunday in November.
Washington, DC, is the capital of the United States and the second-largest city in the country. It is home to many world-renowned landmarks like the White House, Smithsonian Institution, and National Mall. The nation’s capital has been built for over 200 years and hosts many cultural and educational events yearly. The Washington Monument is one of its most famous monuments.
The United States became independent on July 4, 1776 (declared independence from Great Britain); September 3, 1783 (recognized by Great Britain), and its national holiday is Independence Day, July 4 (1776).
Administrative divisions: 50 states and 1 district; Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, District of Columbia, Florida, Georgia, Hawaii, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, North Carolina, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Carolina, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Vermont, Virginia, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin, Wyoming.
People and society
Although the demographic, economic, and cultural dominance of White Americans is firmly entrenched after over 400 years of settlement, the ethnic balance of the country is shifting. Barack Obama, whose father was African, became the first non-White US president in 2009. Originally uprooted by the slave trade, the African-American community had a strong consciousness. Less well-organized socially but more numerous and faster-growing, the Hispanic community is predicted to surpass 30% of the population by 2050. Native Americans, dispossessed in the 19th century, are now among the poorest people. Constitutionally, state and religion are separated. Conservative Christianity, however, is increasingly dominant politically. Living standards are high, but bad diet and insufficient exercise have left over a third of Americans obese.
The population of the United States is 334,998,398 (July 2021 estimate). Note: the US Census Bureaus’ 2020 census results show the US population as 331,449,281 as of April 1, 2020. That means the United States is the No. 3 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 38.5 years median age (37.2 years for males and 37.2 years for women), the United States ranks No. 61 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the American(s) (noun) or American (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: White 72.4%, Black 12.6%, Asian 4.8%, Amerindian and Alaska Native 0.9%, Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander 0.2%, other 6.2%, two or more races 2.9% (2010 estimate). Note: a separate listing for Hispanics is not included because the US Census Bureau considers Hispanic to mean persons of Spanish/Hispanic/Latino origin, including those of Mexican, Cuban, Puerto Rican, Dominican Republic, Spanish, and Central or South American origin living in the US who may be of any race or ethnic group (White, Black, Asian, etc.); an estimated 16.3% of the total US population is Hispanic as of 2010.
They speak English only at 78.2%, Spanish at 13.4%, Chinese at 1.1%, and others at 7.3% (2017 estimate). Note: data represent the language spoken at home; the US has no official national language, but English has acquired official status in 32 of the 50 states; Hawaiian is an official language in the state of Hawaii, and 20 indigenous languages are official in Alaska languages and practice the following religions: Protestant 46.5%, Roman Catholic 20.8%, Jewish 1.9%, Church of Jesus Christ 1.6%, other Christian 0.9%, Muslim 0.9%, Jehovahs Witness 0.8%, Buddhist 0.7%, Hindu 0.7%, other 1.8%, unaffiliated 22.8%, don’t know/refused 0.6% (2014 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in the United States: Large urban clusters are spread throughout the eastern half of the US (particularly the great lakes area, northeast, east, and southeast) and the western tier states. Mountainous areas, principally the rocky mountains and Appalachian chain, deserts in the southwest, the dense boreal forests in the extreme north, and less densely populated central prairie states. Alaska’s population is concentrated along its southern coast – particularly in the city of Anchorage – and Hawaii is centered on the island of Oahu. In the United States, we are talking about 82.9% (2021) of the total population lives in cities. Most of them reside in the following municipalities: 18.823 million, New York-Newark, 12.459 million, Los Angeles-Long Beach-Santa Ana, 8.877 million, Chicago, 6.491 million, Houston, 6.397 million, Dallas-Fort Worth, 5.378 million, Washington, DC (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Worlds largest economy: huge resource base; well-established high-tech, engineering, and entertainment industries; global spread of US culture. The decline of manufacturing as jobs are lost to low-wage economies. The combination of the “war on terrorism” launched after 9/11, military involvement in Afghanistan and Iraq, and a drive to cut taxes sent the government debt spiral. Hurricane Katrina hit oil production in 2005. Then a “bubble” of excessive risky mortgage lending burst, and the financial and stock market crisis went global after the Lehman Brothers bank crashed in 2008. Combining tax cuts with more public spending, an economic incentive program helped lift out of recession but widened the gaping budget deficit. Obama’s government has struggled with this ever since. Pressures to cut spending hurt its social agenda, while conservative opponents denounce tax increases as a threat to growth.
The US has the most technologically robust economy globally, with a per capita GDP of $59,500. US firms are at or near the forefront of technological advances, especially in computers, pharmaceuticals, medical, aerospace, and military equipment; however, their advantage has narrowed since World War II. Based on a comparison of GDP measured at purchasing power parity conversion rates, the US economy in 2014, having stood as the largest in the world for more than a century, slipped into second place behind China, which has more than tripled the US growth rate for each year of the past four decades. In the US, private individuals and business firms make most of the decisions, and the federal and state governments predominantly buy needed goods and services in the private marketplace. US business firms enjoy greater flexibility than their counterparts in Western Europe and Japan in decisions to expand capital plants, lay off surplus workers, and develop new products. At the same time, businesses face higher barriers to entering their rival’s home markets than foreign firms face entering US markets.
Long-term problems for the US include stagnation of wages for lower-income families, inadequate investment in deteriorating infrastructure, rapidly rising medical and pension costs of an aging population, energy shortages, and sizable current account and budget deficits. The surge of technology has been a driving factor in the gradual development of a two-tier labor market in which those at the bottom lack the education and the professional/technical skills of those at the top and, more and more, fail to get comparable pay raises, health insurance coverage, and other benefits. But the globalization of trade, and especially the rise of low-wage producers such as China, has put additional downward pressure on wages and upward pressure on the return to capital. Since 1975, practically all the gains in household income have gone to the top 20% of households. Since 1996, dividends and capital gains have grown faster than wages or any other category of after-tax income. Imported oil accounts for more than 50% of US consumption, significantly impacting the economy’s overall health.
Crude oil prices doubled between 2001 and 2006, the year home prices peaked, higher gasoline prices ate into consumers’ budgets, and many individuals fell behind in their mortgage payments. Oil prices climbed another 50% between 2006 and 2008, and bank foreclosures more than doubled in the same period. Besides dampening the housing market, soaring oil prices caused a drop in the value of the dollar and a deterioration in the US merchandise trade deficit, which peaked at $840 billion in 2008. Because the US economy is energy-intensive, falling oil prices since 2013 have alleviated many problems the earlier increases had created. The sub-prime mortgage crisis, falling home prices, investment bank failures, tight credit, and the global economic downturn pushed the US into a recession by mid-2008. GDP contracted until the third quarter of 2009, the deepest and longest downturn since the Great Depression.
To help stabilize financial markets, the US Congress established a $700 billion Troubled Asset Relief Program in October 2008. The government used some of these funds to purchase equity in US banks and industrial corporations, much of which had been returned to the government by early 2011. In January 2009, Congress passed. Former President Barack OBAMA signed a bill providing an additional $787 billion fiscal stimulus over 10 years – two-thirds on additional spending and one-third on tax cuts – to create jobs and help the economy recover. In 2010 and 2011, the federal budget deficit reached nearly 9% of GDP. In 2012, the Federal Government reduced spending growth, and the deficit shrank to 7.6% of GDP. US revenues from taxes and other sources are lower as a percentage of GDP than most other countries. Wars in Iraq and Afghanistan required major shifts in national resources from civilian to military purposes and contributed to the budget deficit and public debt growth. Through FY 2018, the direct costs of the wars will have totaled more than $1.9 trillion, according to US Government figures. In March 2010, former President OBAMA signed the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA). This health insurance reform was designed to extend coverage to an additional 32 million Americans by 2016 through private health insurance for the general population and Medicaid for the impoverished. Total spending on healthcare – public plus private – rose from 9.0% of GDP in 1980 to 17.9% in 2010. In July 2010, the former president signed the DODD-FRANK Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, a law designed to promote financial stability by protecting consumers from financial abuses, ending taxpayer bailouts of financial firms, dealing with troubled banks that are too big to fail, and improving accountability and transparency in the financial system – in particular, by requiring certain financial derivatives to be traded in markets that are subject to government regulation and oversight.
The Federal Reserve Board (Fed) announced plans in December 2012 to purchase $85 billion per month of mortgage-backed and Treasury securities to hold down long-term interest rates and keep short-term rates near zero until unemployment dropped below 6.5% or inflation rose above 2.5%. The Fed ended its purchases during the summer of 2014 after the unemployment rate dropped to 6.2%, inflation stood at 1.7%, and public debt fell below 74% of GDP. In December 2015, the Fed raised its benchmark federal funds rate target by 0.25%, the first increase since the recession began. With continued low growth, the Fed opted to raise rates several times since then, and in December 2017, the target rate stood at 1.5%. In December 2017, Congress passed and former President Donald TRUMP signed the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which, among its various provisions, reduces the corporate tax rate from 35% to 21%; lowers the individual tax rate for those with the highest incomes from 39.6% to 37%, and by lesser percentages for those at lower income levels; changes many deductions and credits used to calculate taxable income; and eliminates in 2019 the penalty imposed on taxpayers who do not obtain the minimum amount of health insurance required under the ACA. The new taxes took effect on January 1, 2018; the tax cut for corporations is permanent, but those for individuals are scheduled to expire after 2025. The Joint Committee on Taxation (JCT) under the Congressional Budget Office estimates that the new law will reduce tax revenues and increase the federal deficit by about $1.45 trillion over the 2018-2027 period. This amount would decline if economic growth exceeded the JCT’s estimate.
The United States is rich in the following natural resources: Coal, copper, lead, molybdenum, phosphates, rare earth elements, uranium, bauxite, gold, iron, mercury, nickel, potash, silver, tungsten, zinc, petroleum, natural gas, timber, arable land. The US has the world’s largest coal reserves, with 491 billion short tons accounting for 27% of the world’s total. The US relies on imports for 100% of its needs for the following strategic resources – arsenic, cesium, fluorspar, gallium, graphite, indium, manganese, niobium, rare Earth, rubidium, scandium, tantalum, yttrium.
The main industrial sectors are highly diversified, world-leading, high-technology innovators, and the second-largest industrial output globally; petroleum, steel, motor vehicles, aerospace, telecommunications, chemicals, electronics, food processing, consumer goods, lumber, etc., mining.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in refined petroleum, crude petroleum, cars, and vehicle parts, integrated circuits, and aircraft (2019), partnering with these nations: Canada 17%, Mexico 16%, China 7%, Japan 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $2,127,250,000,000. In a global rank of the export, values resulted in the United States’s position of 2.
Land use in the United States: 33.3% (2018 estimate) forest, 100% (2018 estimate) other. The arable land area is 16.8% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 44.5% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops is 0.3% (2018 estimate), and permanent pasture is 27.4% (2018 estimate). The summed area of the irrigated land is 264,000 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of the United States are maize, milk, soybeans, wheat, sugar cane, sugar beet, poultry, potatoes, cotton, and pork.
The country typically needs to import: cars, crude petroleum, computers, broadcasting equipment, and packaged medicines (2019), partnering with the following nations: China 18%, Mexico 15%, Canada 13%, Japan 6%, Germany 5% (2019) in a sum value of $2,808,960,000,000. This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in the United States 1.
The United States Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about the United States and North America, bordering the North Atlantic and the North Pacific oceans, and between Canada and Mexico. We published basic information about its capital Washington, DC, and the American nation.
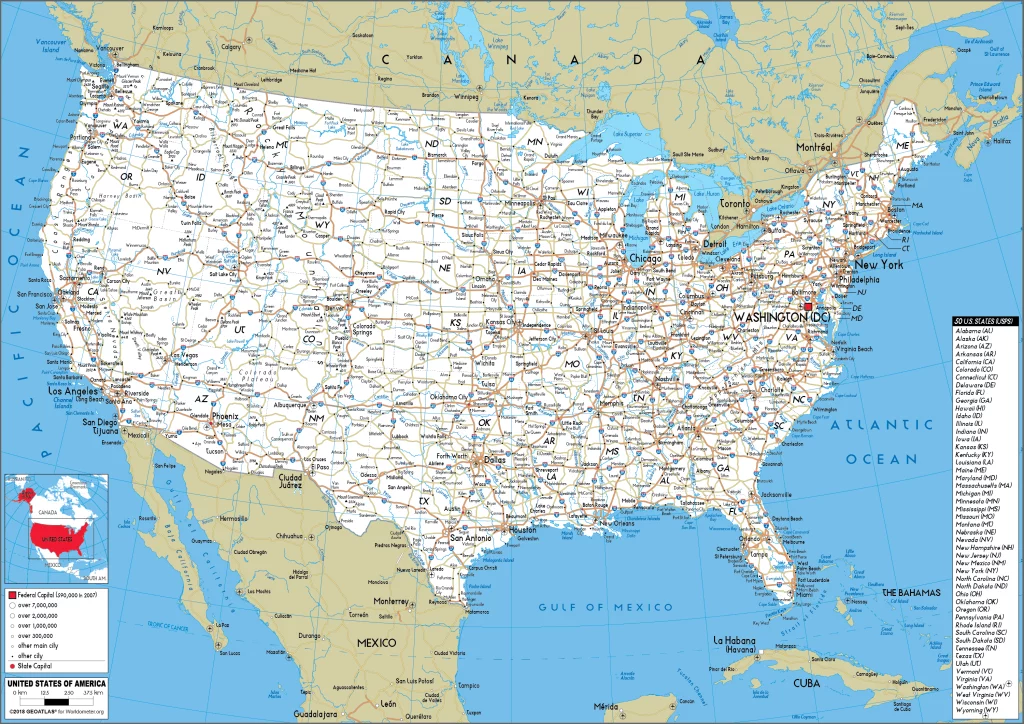
Are you interested in visiting the United States and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of the United States below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of the United States
Did you know about the United States?
The United States is the largest economy in the world. It has an area of 9,826,675 sq km and a population of 335 million, and they speak over 300 different languages as of 2021. The American Declaration of Independence was signed on July 4, 1776, and it became the first independent nation in history to govern itself.
There are 50 states in the United States. The states are divided into the Northern, Southern, Eastern, and Western geographical regions. The United States is the world’s third-largest country in both area and population. It also has a diverse landscape. There are deserts, snow-capped mountains, and fertile valleys. The climate varies based on the region. In the northeast, it’s humid and relaxed, while in the southwest, it’s dry and warm.
Here are some surprising facts about the United States:
- The Great Salt Lake in Utah is saltier than the Dead Sea, making it one of the saltiest bodies of water in the world.
- The first ever McDonald’s restaurant was opened in San Bernardino, California, in 1940 and served hot dogs, not hamburgers.
- The United States is home to the world’s largest hot air balloon festival, the Albuquerque International Balloon Fiesta, which takes place every October in New Mexico.
- Mount McKinley in Alaska, now known as Denali, is the highest peak in North America, standing at 20,310 feet tall.
- The Liberty Bell, one of America’s most iconic symbols of freedom, has a crack and is not rung anymore.
- The United States is home to the world’s largest indoor theme park, the Mall of America, in Bloomington, Minnesota.
- The Grand Canyon in Arizona, one of the Seven Natural Wonders of the World, is 277 miles long, up to 18 miles wide, and over a mile deep.
- The world’s first national park, Yellowstone, was established in the United States in 1872.
- The United States has the largest economy in the world and is home to numerous Fortune 500 companies.
- The United States is a country of immigrants, with over 40 million foreign-born residents, representing about 13% of the total population.
After virtually visiting the United States, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Canada and Mexico.
If you liked our Google map and the United States information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.
