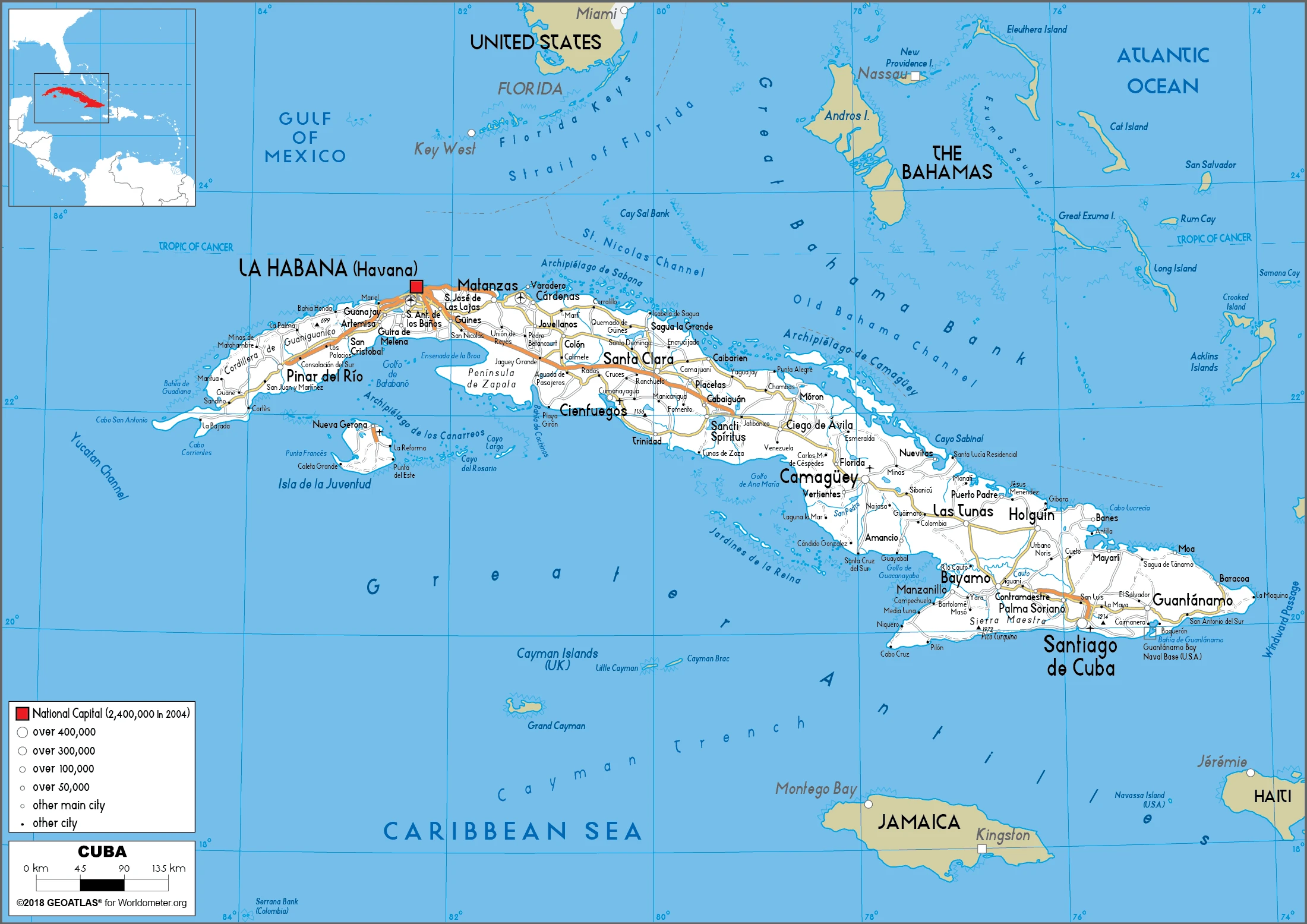
Cuba Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Cuba, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Cuba, Central America. The Caribbean (35 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Havana, bordering countries like the US Naval Base at Guantanamo Bay, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Central American and the Caribbean state.
Quick links: Google maps Cuba, Havana Google maps, Driving Directions Cuba, Printable Road Map.

About Cuba in a nutshell
- Fidel Castro had become the worlds longest-serving nonhereditary ruler before handing power to his brother Raúl in 2006.
- Conventional short form of the name: Cuba
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of Cuba
- Local long form: Republica de Cuba
- Local short form: Cuba
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: name derives from the Taino Indian designation for the island coabana meaning great place.
- The legal system in Cuba: civil law system based on Spanish civil code.
- Climate: Subtropical. Hot all year round, and very hot in summer. Heaviest rainfall in the mountains. Hurricanes can strike in the fall.
- The national symbols are royal palm; national colors: red, white, blue.
- Internet TLD: .cu
Background
The native Amerindian population of Cuba began to decline after the European discovery of the island by Christopher COLUMBUS in 1492 and following its development as a Spanish colony during the next several centuries. Large numbers of enslaved Africans were imported to work the coffee and sugar plantations, and Havana became the launching point for the annual treasure fleets from Mexico and Peru bound for Spain. Spanish rule eventually provoked an independence movement and harshly suppressed occasional rebellions. US intervention during the Spanish-American War in 1898 assisted the Cubans in overthrowing Spanish rule. The Treaty of Paris established Cuban independence from Spain in 1898. Following three-and-a-half years of subsequent US military rule, Cuba became an independent republic in 1902. The island experienced a string of governments mostly dominated by corrupt military politicians. Fidel CASTRO led a rebel army to victory in 1959. His authoritarian rule held the subsequent regime together for nearly five decades. He stepped down as president in February 2008 in favor of his younger brother Raul CASTRO.
Cubas communist revolution, with Soviet support, was exported throughout Latin America and Africa during the 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s. Miguel DIAZ-CANEL Bermudez, hand-picked by Raul CASTRO to succeed him, was approved as president by the National Assembly and took office on 19 April 2018. DIAZ-CANEL was appointed First Secretary of the Communist Party on 19 April 2021 following the resignation of Raul CASTRO., The country faced a severe economic downturn in 1990 following the withdrawal of former Soviet subsidies worth $4-6 billion annually. Cuba traditionally and consistently portrays the US embargo in place since 1961 as the source of its difficulties. As a result of efforts begun in December 2014 to re-establish diplomatic relations with the Cuban government, which were severed in January 1961, the US and Cuba reopened embassies in their respective countries in July 2015.
The embargo remains in place, and the relationship between the US and Cuba remains tense. Illicit migration of Cuban nationals to the US via maritime and overland routes has been a longstanding challenge. On 12 January 2017, the US and Cuba signed a Joint Statement ending the so-called wet-foot, dry-foot policy by which Cuban nationals who reached US soil were permitted to stay. Illicit Cuban migration by sea has dropped significantly, but land border crossings continue. In FY 2018, the US Coast Guard interdicted 312 Cuban nationals at sea. Also, in FY 2018, 7,249 Cuban migrants presented themselves at various land border ports of entry throughout the US.
Geography
Mostly fertile plains and basins. Three mountainous areas. Forests of pine and mahogany cover one-quarter of the country.
A former Spanish colony, Cuba is the largest island in the Caribbean. It became the only communist country in the Americas after Fidel Castro seized power in 1959.
This state is located in the Caribbean, an island between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, 150 km south of Key West, Florida, under the coordinates of 21 30 N, 80 00 W, covering an area of 110,860 sq km with a coastline of 3,735 km. Cuba is Slightly smaller than Pennsylvania.
Cuba has 28.5 km of land boundaries in total, and bordering with (1 nation): US Naval Base at Guantanamo Bay 28.5 km.
Mostly flat to rolling plains, with rugged hills and mountains in the southeast, with Pico Turquino 1,974 m as the highest point of Cuba, while the Caribbean Sea 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 108 m throughout the country. With 110,860 sq km, Cuba has 109,820 sq km of land and 1,040 sq km water surface area.
The largest country in the Caribbean and westernmost island of the Greater Antilles.
The climate in Cuba is as follows: Tropical, moderated by trade winds, dry season (November to April), rainy season (May to October).
When you visit Cuba, the natural hazards shall be considered: The east coast is subject to hurricanes from August to November (in general, the country averages about one hurricane every other year); droughts are common.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Cuba: degree of risk: intermediate (2020), bacterial diarrhea and hepatitis A, dengue fever.
Current environmental issues affecting the Cuban people: soil degradation and desertification (brought on by poor farming techniques and natural disasters) are the main environmental problems; biodiversity loss, deforestation; air and water pollution.
Google maps Cuba
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Havana found under the coordinates 23 07 N, 82 21 W, applying the time zone UTC-5 (same time as Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr begins second Sunday in March; ends first Sunday in November.
The home of the Cuban Revolution, Havana has been a destination for people seeking an escape from the fast-paced world. On this trip, you’ll find Havana’s streets lined with colonial mansions, cobblestone alleyways with colorful shutters, and oceanfront squares where the city’s iconic skyline is framed.
Cuba became independent on 20 May 1902 (from Spain 10 December 1898; administered by the US from 1898 to 1902); not acknowledged by the Cuban government as a day of independence, and its national holiday is Triumph of the Revolution (Liberation Day), 1 January (1959).
Administrative divisions: 15 provinces (provincias, singular – provincia) and 1 special municipality (municipio especial); Artemisa, Camaguey, Ciego de Avila, Cienfuegos, Granma, Guantanamo, Holguin, Isla de la Juventud, La Habana, Las Tunas, Matanzas, Mayabeque, Pinar del Rio, Sancti Spiritus, Santiago de Cuba, Villa Clara.
People and society
The Castro regime has reduced formerly extreme wealth disparities, given education a high priority, and established an efficient health service. Political dissent, however, is not tolerated. A dramatic fall in living standards since the late 1980s has led thousands of Cubans to flee to the US to seek asylum. About 70% of Cubans are of Spanish descent. There is little ethnic tension.
The population in Cuba is 11,032,343 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of -0.23% (2021 estimate) change. That means Cuba is the No. 83 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 42.1 years median age (40.2 years for males and 40.2 years for women), Cuba ranks No. 37 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Cuban(s) (noun) or Cuban (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: White 64.1%, Mulatto or mixed 26.6%, Black 9.3% (2012 estimate). Note: data represent racial self-identification from Cubas 2012 national census.
They speak Spanish (official language) languages and practice the following religions: Christian 58.9%, folk religion 17.6%, Buddhist <1%, Hindu <1%, Jewish <1%, Muslim <1%, other <1%, none 23.2% (2020 estimate) note: folk religions include religions of African origin, spiritualism, and others intermingled with Catholicism or Protestantism; data is estimative because no authoritative source on religious affiliation exists in Cuba. We can conclude the following about the population in Cuba: Large population clusters are found throughout the country, the more significant ones being in, the larger towns and cities, particularly the capital of Havana. In Cuba, we are talking about 77.3% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 2.143 million, Havana (capital city) (2021).
Industry
The sugar industry is now superseded by tourism and nickel. US trade embargo, since 1961. Shortages drive the black market. Parallel use of the US dollar (1993-2004), and the convertible peso, boosted investment but created a “dollarized” elite: dual peso system to be scrapped.
The government continues to balance the need for loosening its socialist economic system against a desire for firm political control. In April 2011, the government held the first Cuban Communist Party Congress in almost 13 years, during which leaders approved a plan for wide-ranging economic changes. Since then, the government has slowly and incrementally implemented limited economic reforms, including allowing Cubans to buy electronic appliances and cell phones, stay in hotels, and buy and sell used cars. The government has cut state sector jobs as part of the reform process, and it has opened up some retail services to self-employment, leading to the rise of so-called cuentapropistas or entrepreneurs.
More than 500,000 Cuban workers are currently registered as self-employed. The Cuban regime has updated its economic model to include permitting the private ownership and sale of real estate and new vehicles, allowing private farmers to sell agricultural goods directly to hotels, allowing the creation of non-agricultural cooperatives, adopting a new foreign investment law, and launching a Special Development Zone around the Mariel port. Since 2016, Cuba has attributed slowed economic growth to problems with petroleum product deliveries from Venezuela. Since late 2000, Venezuela provided petroleum products to Cuba on preferential terms, supplying nearly 100,000 barrels per day. In part, Cuba paid for the oil with the services of Cuban personnel in Venezuela, including some 30,000 medical professionals.
Cuba is rich in the following natural resources: Cobalt, nickel, iron ore, chromium, copper, salt, timber, silica, petroleum, arable land.
The main industrial sectors are typically petroleum, nickel, cobalt, pharmaceuticals, tobacco, construction, steel, cement, agricultural machinery, sugar.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in cigars, raw sugar, nickel products, rum, zinc (2019), partnering with these nations: China 38%, Spain 11%, Netherlands 5%, Germany 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $2.63 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2017 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Cuba’s position of 147.
Land use in Cuba: 27.3% (2018 estimate) forest, 12.4% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 33.8% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 60.3% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 3.6% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 22.9% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 8,700 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Cuba are sugar cane, cassava, vegetables, plantains, sweet potatoes, tomatoes, milk, pumpkins, mangoes/guavas, rice.
The country typically needs to import: poultry meat, wheat, soybean products, corn, concentrated milk (2019), partnering with the following nations: Spain 19%, China 15%, Italy 6%, Canada 5%, Russia 5%, United States 5%, Brazil 5% (2019) in a sum value of $11.06 billion (2017 estimate) $10.28 billion (2016 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Cuba 101.
Cuba Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Cuba, the Caribbean, the island between the Caribbean Sea, and the North Atlantic Ocean, 150 km south of Key West, Florida. We published some basic information about its capital Havana, and the Cuban nation.
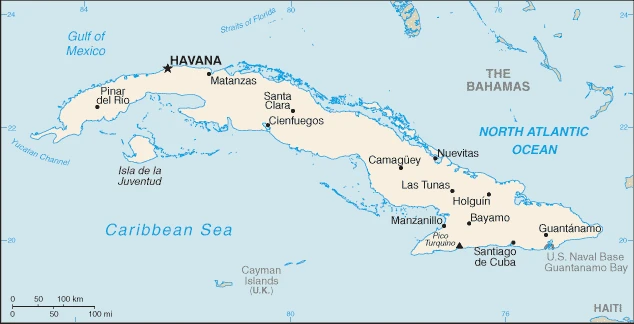
Are you interested in visiting Cuba and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Cuba below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Cuba
Did you know about Cuba?
Cuba is a beautiful country with a fascinating history and culture. It is situated in the Caribbean and is famous for its cigars, rum, and music. The culture of Cuba is influenced by many different cultures, including Spanish, French, African, Caribbean, and Native American. When you think of Cuban food, don’t forget to think about rice and beans!
After virtually visiting Cuba, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: US Naval Base at Guantanamo Bay.
If you liked our Google map and Cuba information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.