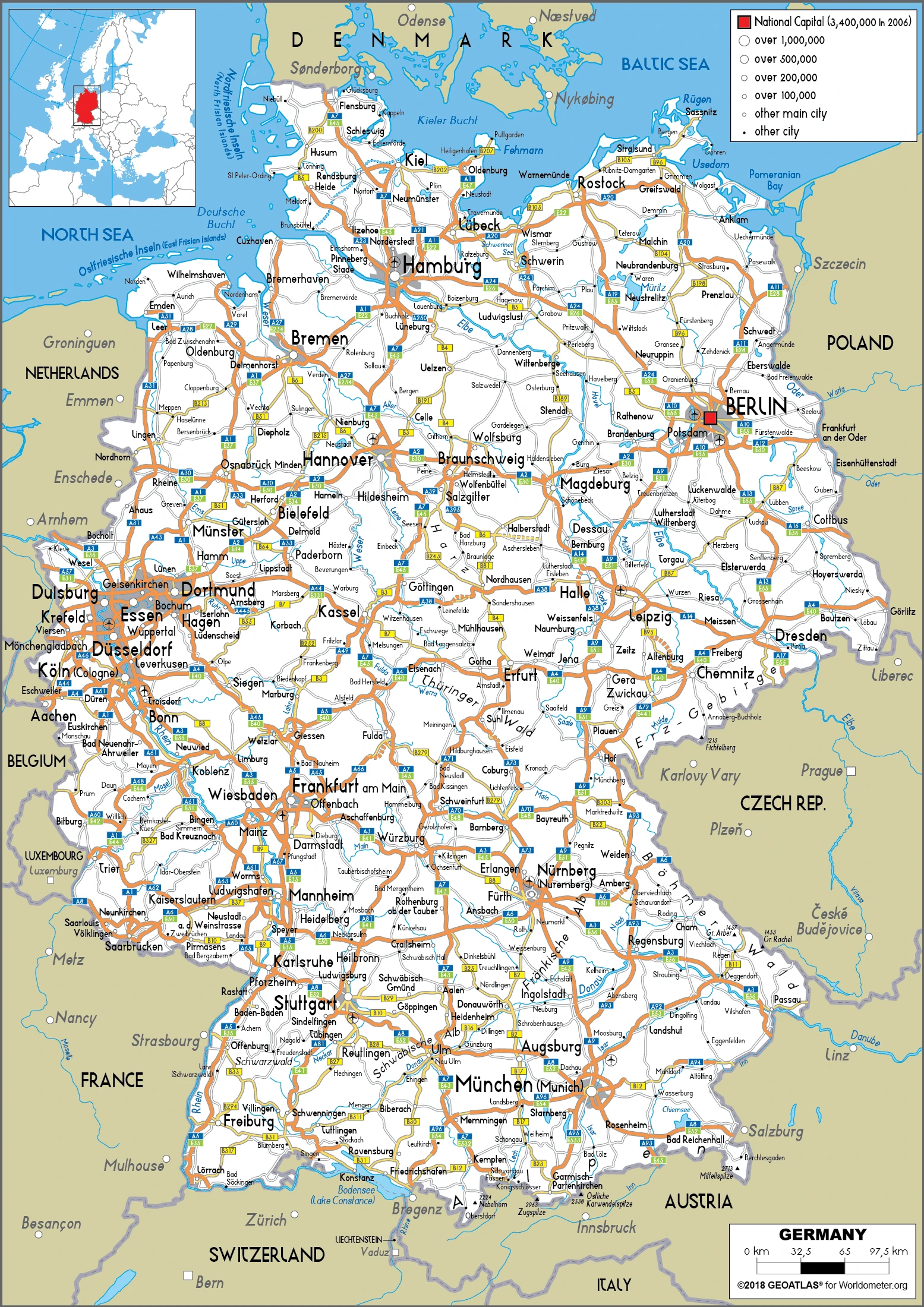
Germany Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Germany, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Germany, Europe (47 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Berlin, and bordering countries like Austria, Belgium, Czechia, Denmark, France, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Poland, Switzerland, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this European state.
Quick links: Google Maps Germany, Berlin Google maps, Driving Directions Germany, Printable Road Map.

About Germany in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Germany
- The conventional long form of the name: Federal Republic of Germany
- Local long form: Bundesrepublik Deutschland
- Local short form: Deutschland
- Former name(s): German Reich
- Etymology: the Gauls (Celts) of Western Europe may have referred to the newly arriving Germanic tribes who settled in neighboring areas east of the Rhine during the first centuries B.C. as Germani, a term the Romans adopted as Germania; the native designation Deutsch comes from the Old High German diuretic meaning of the people.
- The legal system in Germany: civil law system.
- Climate: Damp, temperate in northern and central regions. Continental extremes in mountainous south.
- The national symbols are the eagle, while the national colors are black, red, and yellow.
- Internet TLD: .de
Berlin’s changing as they move into the 21st century, rebuilding especially in East Berlin where there’s lots of work. Meanwhile, they’ve now established themselves as the capital of Germany though the Berlin Wall is now a bike path. If you want to explore medieval Germany, the Romantic Road is your place. This pristine route will transport you back in time to new towns with beautiful architecture and natural beauty. Or, visit Neuschwanstein Castle, one of King Ludwig II’s best pieces of work.
Excluding Russia, Europe’s most populous country has favorable natural conditions: the ice-covered German plain on either side of the Elbe in the north is bounded in the south by old, mineral-rich rugged mountains, which continue south from the Danube to the northern slopes of the Alps, with glacial valleys and picturesque lakes. Among the universal treasures of humankind, the Messel mining pit, a 50 million-year-old archaeological site from the Tertiary period, is the most important natural heritage. The cultural heritage is much more diverse. The oldest are the Roman monuments: the German section of the Limes and the Roman monuments of Trier.
The cathedrals of Aachen, Speyer, Cologne, Hildesheim, Trier, Lorsch Abbey, Maulbronn and Reichenau, the pilgrimage church of Wies, the archbishop’s residence of Würzburg, and the Luther monuments are religious heritage. At the same time, the palaces of Brühl, Potsdam, and Berlin, the town hall of Bremen, and the Wartburg castle are secular masterpieces of German architecture. The Old Towns and Bauhaus buildings of Goslar, Bamberg, Wismar, Stralsund, Lübeck, Regensburg, Quedlinburg and Weimar. The Berlin Museum Island represents a German town and city planning from the Middle Ages to the 20th century. The Rhine belongs to Germany and is also the “artery” of the continent. Europe’s waterway links the continent’s first and most important industrial regions.
The industrial monuments of the ironworks at Völklingen in the Saar and the Zollverein coal mine in Essen are testimony to the industrialization of the last century and a half. The upper Rhine valley, richly decorated with castles, the Dresden stretch of the Elbe, the parks of Dessau and Wörlitz, and the cultural gardens of Muskauer Park on the Polish border are among Europe’s most picturesque World Heritage sites.
Germanys rivers and canals carry as much freight as its busy highways.
Background
As Europe’s largest economy and second most populous nation (after Russia), Germany is a vital member of the continent’s economic, political, and defense organizations. European power struggles immersed Germany in two devastating world wars in the first half of the 20th century and left the country occupied by the victorious Allied powers of the US, UK, France, and the Soviet Union in 1945. With the advent of the Cold War, two German states were formed in 1949: the western Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) and the eastern German Democratic Republic (GDR).
The democratic FRG embedded itself in key Western economic and security organizations, the EC (now the EU) and NATO, while the communist GDR was on the front line of the Soviet-led Warsaw Pact. The decline of the USSR and the end of the Cold War allowed for German reunification in 1990. Since then, Germany has expended considerable funds to bring Eastern productivity and wages up to western standards. In January 1999, Germany and 10 other EU countries introduced a common European exchange currency, the euro.
Geography
Central European coastal plains in the north rise to roll hills of the central region and Alps in the far south.
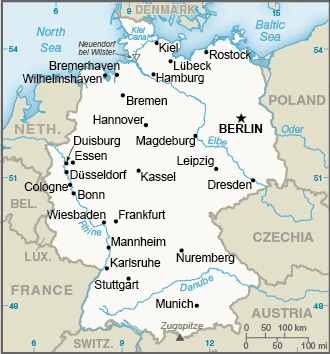
Europes most potent industrial power and its most populous nation, Germany, was divided after a military defeat in 1945 into a free-market west and a communist east but reunified in 1990.
This state is located in Central Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea and the North Sea, between the Netherlands and Poland, south of Denmark, under the coordinates of 51 00 N, 9 00 E, covering an area of 357,022 sq km with a coastline of 2,389 km. Germany is Three times the size of Pennsylvania, slightly smaller than Montana.
Germany has 3,694 km of land boundaries and borders with (9 nations): Austria 801 km, Belgium 133 km, Czechia 704 km, Denmark 140 km, France 418 km, Luxembourg 128 km, Netherlands 575 km, Poland 447 km, Switzerland 348 km.
Lowlands in the north, uplands in the center, bavarian alps in the south, Zugspitze 2,963 m as the highest point of Germany, while Neuendorf bei Wilster -3.5 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 263 m throughout the country. With 357,022 sq km, Germany has 348,672 sq km of land and 8,350 sq km of water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Lake Constance (shared with Switzerland and Austria) – 540 sq km (a freshwater lake), Stettiner Haff/Zalew Szczecinski (shared with Poland) – 900 sq km (saltwater lake) while the major rivers are: Danube river source (shared with Austria, Slovakia, Czechia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Bulgaria, Ukraine, Moldova, and Romania m) – 2,888 km, Elbe river mouth (shared with Czechia) – 1,252 km, Rhine (shared with Switzerland, France, and the Netherlands) – 1,233 km. The significant watersheds for Germany are Atlantic Ocean drainage: Rhine-Maas (198,735 sq km), (Black Sea) Danube (795,656 sq km).
Strategic location on North European Plain and along the entrance to the Baltic Sea; the most significant rivers in Germany – the Rhine, Weser, Oder, Elbe – flow northward; the Danube, which originates in the Black Forest, flows eastward.
The climate in Germany is as follows: Temperate and marine, cool, cloudy, wet winters and summers, occasional warm mountain (foehn) wind.
When you visit Germany, the natural hazards shall be considered: Flooding.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Germany: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the German people: emissions from coal-burning utilities and industries contribute to air pollution; acid rain, resulting from sulfur dioxide emissions, is damaging forests; pollution in the Baltic Sea from raw sewage and industrial effluents from rivers in eastern Germany; hazardous waste disposal; Government established a mechanism for ending the use of nuclear power by 2022; Government working to meet EU commitment to identify nature preservation areas in line with the EU’s Flora, Fauna, and Habitat directive.
Google Maps Germany
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Berlin found under the coordinates 52 31 N, 13 24 E, applying the time zone UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October.
Berlin is a city with more than 3.5 million people. It has a population of over 3.7 million when considering the metropolitan area. The city is situated in eastern Germany, on both banks of the River Spree, which flows into the River Oder. Berlin has three central districts: the Mitte district, located in the center of Berlin, which includes Potsdamer Platz and Alexanderplatz; the Charlottenburg-Wilmersdorf district, which is to the west of Mitte; and the Friedrichshain-Kreuzberg district, which lies to the east of Mitte. All three of these districts are part of Berlin’s central administrative area.
Germany became independent on 18 January 1871 (establishment of the German Empire); divided into four zones of occupation (UK, US, USSR, and France) in 1945 following World War II; the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG or West Germany) proclaimed on 23 May 1949 and included the former UK, US, and French zones; German Democratic Republic (GDR or East Germany) proclaimed on 7 October 1949 and included the former USSR zone; West Germany and East Germany unified on 3 October 1990; all four powers formally relinquished rights on 15 March 1991; notable earlier dates: 10 August 843 (Eastern Francia established from the division of the Carolingian Empire); 2 February 962 (crowning of OTTO I, recognized as the first Holy Roman Emperor), and its national holiday is German Unity Day, 3 October (1990).
Administrative divisions: 16 states (Laender, singular – Land); Baden-Wuerttemberg, Bayern (Bavaria), Berlin, Brandenburg, Bremen, Hamburg, Hessen (Hesse), Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania), Niedersachsen (Lower Saxony), Nordrhein-Westfalen (North Rhine-Westphalia), Rheinland-Pfalz (Rhineland-Palatinate), Saarland, Sachsen (Saxony), Sachsen-Anhalt (Saxony-Anhalt), Schleswig-Holstein, Thueringen (Thuringia).
People and society
Regionalism is strong. The north is mainly Protestant, while the south is staunchly Roman Catholic. Social and economic differences still exist between east and west. Turks are the most significant ethnic minority; many came as guest workers in the 1950s-1970s. Immigration rules now favor skilled workers. Feminism is strong.
The population in Germany is 79,903,481 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of -0.21% (2021 estimate) change. That means Germany is the No. 19 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 47.8 years median age (46.5 years for males and 46.5 years for women), Germany ranks No. 4 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the German(s) (noun) or German (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: German 86.3%, Turkish 1.8%, Polish 1%, Syrian 1%, Romanian 1%, other/stateless/unspecified 8.9% (2020 estimate). Note: data represent population by nationality.
They speak German (official language); languages and practice the following religions: Roman Catholic 27.1%, Protestant 24.9%, Muslim 5.2%, Orthodox 2%, other Christian 1%, other 1%, none 38.8% (2019 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Germany: The most populous country in Europe. A fairly even distribution throughout most of the country, with urban areas attracting larger and denser populations, particularly in the far western part of the industrial state of North Rhine-Westphalia. In Germany, we are talking about 77.5% (2021) of the total population lives in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 3.567 million, Berlin (capital city), 1.789 million, Hamburg, 1.553 million, Munich, 1.129 million, Cologne, 785,000 Frankfurt (2021).
Industry
Major exporter of electronics, heavy engineering, chemicals, and cars. The worst recession in 60 years in 2008-2009.
The German economy – the fifth largest economy in the world in PPP terms and Europe’s largest – is a leading exporter of machinery, vehicles, chemicals, and household equipment. Germany benefits from a highly skilled labor force but faces significant demographic challenges to sustained long-term growth like its Western European neighbors. Low fertility rates and a significant increase in net immigration are increasing pressure on the country’s social welfare system and necessitate structural reforms., Reforms launched by the Government of Chancellor Gerhard SCHROEDER (1998-2005), deemed necessary to address chronically high unemployment and low average growth, contributed to strong economic growth and falling unemployment. These advances and a government subsidized, reduced working hour scheme help explain the relatively modest increase in unemployment during the 2008-09 recession – the deepest since World War II.
The German Government introduced a minimum wage in 2015 that increased to $9.79 (8.84 euros) in January 2017. Stimulus and stabilization efforts initiated in 2008 and 2009 and tax cuts introduced in Chancellor Angela Merkel’s second term increased Germany’s total budget deficit – including federal, state, and municipal – to 4.1% in 2010. Still, slower spending and higher tax revenues reduced the deficit to 0.8% in 2011, and in 2017 Germany reached a budget surplus of 0.7%. A constitutional amendment approved in 2009 limits the federal government to structural deficits of no more than 0.35% of GDP per annum as of 2016, though the target was already reached in 2012., Following the March 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster, Chancellor Angela MERKEL announced in May 2011 that eight of the country’s 17 nuclear reactors would be shut down immediately, and the remaining plants would close by 2022.
Germany plans to replace nuclear power primarily with renewable energy, which accounted for 29.5% of gross electricity consumption in 2016, up from 9% in 2000. Before the shutdown of the eight reactors, Germany relied on nuclear power for 23% of its electricity generating capacity and 46% of its base-load electricity production., The German economy suffers from low levels of investment, and a government plan to invest 15 billion euros during 2016-18, mainly in infrastructure, is intended to spur needed private investment. Domestic consumption, investment, and exports are likely to drive German GDP growth in 2018, and the country’s budget and trade surpluses are likely to remain high.
Germany is rich in the following natural resources: Coal, lignite, natural gas, iron ore, copper, nickel, uranium, potash, salt, construction materials, timber, and arable land.
The main industrial sectors are typically among the world’s largest and most technologically advanced iron, steel, coal, cement, chemicals, machinery, vehicles, machine tools, electronics, automobiles, food and beverages, shipbuilding, and textiles.
The country’s export sectors are robust in cars and vehicle parts, packaged medicines, aircraft, medical cultures/vaccines, and industrial machinery (2019), partnering with these nations: the United States 9%, France 8%, China 7%, Netherlands 6%, United Kingdom 6%, Italy 5%, Poland 5%, Austria 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $1,671,650,000,000. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Germany’s position of 3.
Land use in Germany: 31.8% (2018 estimate) forest, 20.2% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 34.1% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 48% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.6% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 13.3% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 6,500 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Germany are milk, sugar beet, wheat, barley, potatoes, pork, maize, rye, rapeseed, and triticale.
The country typically needs to import: cars and vehicle parts, packaged medicines, crude petroleum, refined petroleum, medical cultures/vaccines (2019), partnering with the following nations: Netherlands 9%, China 8%, France 7%, Belgium 6%, Poland 6%, Italy 6%, Czechia 5%, United States 5% (2019) in a sum value of $1,452,560,000,000. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $1,593,720,000,000. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $1,635,580,000,000. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Germany 3.
Germany Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Germany, and Central Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea and the North Sea, between the Netherlands and Poland, south of Denmark. We published some basic information about its capital Berlin, and the German nation.
Are you interested in visiting Germany and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Germany below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Germany
Did you know about Germany?
Germany is one of the top 20 economies globally, and it is a big consumer of oil. In 2016, Germany’s domestic crude oil production was 1.6 billion barrels. This was 6% less than 2015’s production. But, if you travel to Europe, you’ll find that most countries are using more renewable energy sources. Germany plans to use nuclear power for less than 25% of its total power consumption by 2021.
After virtually visiting Germany, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Austria, Belgium, Czechia, Denmark, France, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Poland, and Switzerland.
If you liked our Google map and Germany information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.