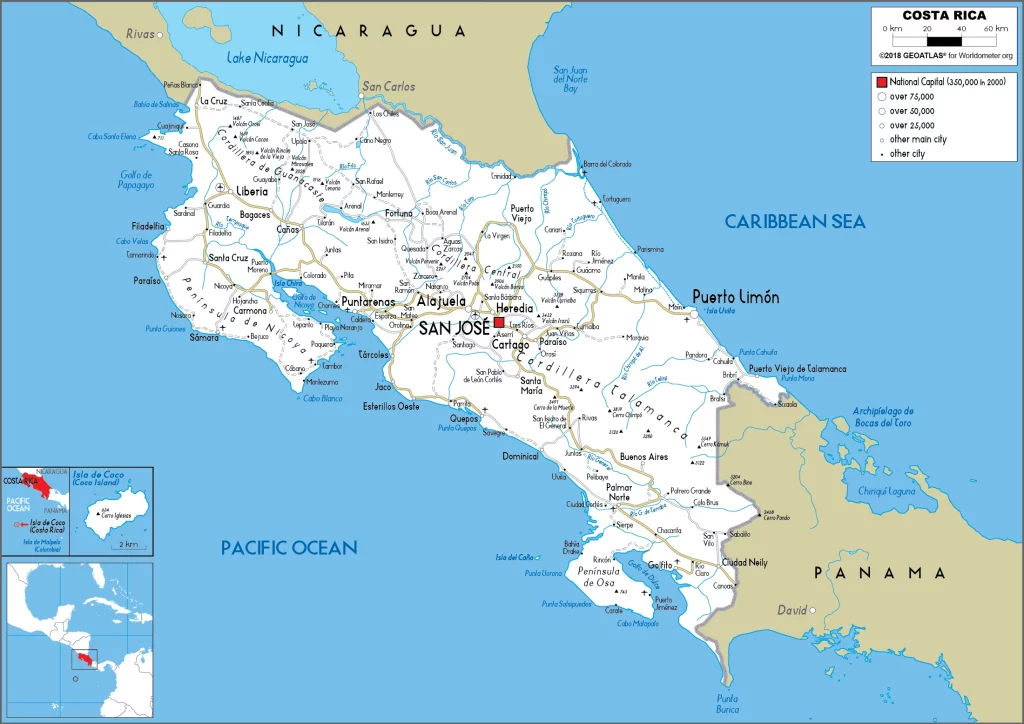
Costa Rica Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Costa Rica, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Costa Rica, Central America, and the Caribbean (35 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city San Jose, bordering countries like Nicaragua Panama, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Central American and the Caribbean state.
Quick links: Google Maps Costa Rica, San Jose Google maps, Driving Directions Costa Rica, Printable Road Map.

About Costa Rica in a nutshell
- Costa Ricas 1949 constitution bans a national army.
- Conventional short form of the name: Costa Rica
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of Costa Rica
- Local long form: Republica de Costa Rica
- Local short form: Costa Rica
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: the name means rich coast in Spanish and was first applied in the early colonial period of the 16th century.
- The legal system in Costa Rica: civil law system based on Spanish civil code; judicial review of legislative acts in the Supreme Court.
- Climate: Hot and humid in coastal regions. Temperate central uplands. High annual rainfall.
- The national symbols are yiguirro (clay-colored robin); national colors: blue, white, red.
- Internet TLD: .cr
Background
Although explored by the Spanish early in the 16th century, initial attempts at colonizing Costa Rica proved unsuccessful due to a combination of factors, including disease from mosquito-infested swamps, brutal heat, resistance by natives, and pirate raids. It was not until 1563 that a permanent settlement of Cartago was established in the cooler, fertile central highlands. The area remained a colony for some two and a half centuries. In 1821, Costa Rica became one of several Central American provinces that jointly declared their independence from Spain. Two years later, it joined the United Provinces of Central America, but this federation disintegrated in 1838, at which time Costa Rica proclaimed its sovereignty and independence.
Since the late 19th century, only two brief periods of violence have marred the country’s democratic development. On 1 December 1948, Costa Rica dissolved its armed forces. Although it still maintains a large agricultural sector, Costa Rica has expanded its economy to include robust technology and tourism industries. The standard of living is relatively high. Land ownership is widespread.
Geography
Coastal plains of swamp and savanna rise to a fertile central plateau, which leads to a mountain range with active volcanic peaks.
Costa Rica, Central Americas most stable country, is rich in pristine scenery and exotic wildlife. Its neutrality in foreign affairs is long-standing, but it has strong ties with the US.
This state is located in Central America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean, between Nicaragua and Panama, under the coordinates of 10 00 N, 84 00 W, covering an area of 51,100 sq km with a coastline of 1,290 km. Costa Rica is slightly smaller than West Virginia.
Costa Rica has 661 km of land boundaries and borders with (2 nations): Nicaragua 313 km, Panama 348 km.
Coastal plains are separated by rugged mountains, including over 100 volcanic cones. Several are major active volcanoes, with Cerro Chirripo 3,819 m as the highest point of Costa Rica, while the Pacific Ocean 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 746 m throughout the country. With a total of 51,100 sq km, Costa Rica has 51,060 sq km of land and 40 sq km water surface area.
Four volcanoes, two of them active, rise near the capital of San Jose in the center of the country; one of the volcanoes, Irazu, erupted destructively in 1963-65.
The climate in Costa Rica is as follows: Tropical and subtropical, dry season (December to April), rainy season (May to November), more relaxed in highlands.
When you visit Costa Rica, the natural hazards shall be considered: Occasional earthquakes, hurricanes along the Atlantic coast; frequent flooding of lowlands at the onset of the rainy season and landslides; active volcanoes volcanism: Arenal (1,670 m), which erupted in 2010, is the most active volcano in Costa Rica; a 1968 eruption destroyed the town of Tabacon; Irazu (3,432 m), situated just east of San Jose, has the potential to spew ash over the capital city as it did between 1963 and 1965; other historically active volcanoes include Miravalles, Poas, Rincon de la Vieja, and Turrialba.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Costa Rica: degree of risk: intermediate (2020), bacterial diarrhea, dengue fever.
Current environmental issues affecting the Costa Rican people: deforestation and land-use change, primarily due to the clearing of land for cattle ranching and agriculture; soil erosion; coastal marine pollution; fisheries protection; solid waste management; air pollution.
Google Maps Costa Rica
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: San Jose found under the coordinates 9 56 N, 84 05 W, applying the time zone UTC-6 (1 hour behind Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
The capital city of Costa Rica, San Jose, is one of the best destinations for visitors in the country. With lively nightlife, shopping opportunities, and plenty of local cuisine and art, San Jose is a fantastic place to explore for anyone looking for an exciting adventure!
Costa Rica became independent on 15 September 1821 (from Spain), and its national holiday is Independence Day, 15 September (1821).
Administrative divisions: 7 provinces (provincias, singular – provincia); Alajuela, Cartago, Guanacaste, Heredia, Limon, Puntarenas, San Jose.
People and society
Most people are mestizo, of partly Spanish, partly Amerindian origin. There is a black, English-speaking minority and around 35,000 indigenous Amerindians. Plantation owners are the wealthiest group, while one in five people live in poverty. Nonetheless, living standards are high for the region, and education and healthcare provision is good.
The population in Costa Rica is 5,151,140 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 1.04% (2021 estimate) change. That means Costa Rica is the No. 124 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 32.6 years median age (32.1 years for males and 32.1 years for women), Costa Rica ranks No. 109 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Costa Rican(s) (noun) or Costa Rican (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: White or Mestizo 83.6%, Mulatto 6.7%, Indigenous 2.4%, Black or African descent 1.1%, other 1.1%, none 2.9%, unspecified 2.2% (2011 estimate).
They speak Spanish (official language), English languages, and practice the following religions: Roman Catholic 71.8%, Evangelical and Pentecostal 12.3%, other Protestant 2.6%, Jehovahs Witness 0.5%, other 2.4%, none 10.4% (2016 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Costa Rica: Roughly half of the nation’s population resides in urban areas. The capital of San Jose is the largest city and home to approximately one-fifth of the population. In Costa Rica, we are talking about 81.4% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 1.421 million, San Jose (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Main exports are bananas, coffee, pineapples, and beef, but all are vulnerable to fluctuating world prices. Stability has attracted multinationals. History of high inflation. Pioneer of ecotourism. Plans to be the world’s first carbon-neutral country (by 2025).
Since 2010, Costa Rica has enjoyed strong and stable economic growth – 3.8% in 2017. Exports of bananas, coffee, sugar, and beef are the backbone of its commodity exports. Various industrial and processed agricultural products have broadened exports in recent years, as have high value-added goods, including medical devices. Costa Rica’s impressive biodiversity also makes it a key destination for ecotourism., Foreign investors remain attracted by the country’s political stability and relatively high education levels, as well as the incentives offered in the free-trade zones; Costa Rica has attracted one of the highest levels of foreign direct investment per capita in Latin America.
The US-Central American-Dominican Republic Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA-DR), which became effective for Costa Rica in 2009, helped increase foreign direct investment in critical sectors of the economy, including insurance and telecommunication. However, poor infrastructure, high energy costs, a complex bureaucracy, weak investor protection, and uncertainty of contract enforcement impede more significant investment., Costa Rica’s economy also faces challenges due to a rising fiscal deficit, rising public debt, and relatively low levels of domestic revenue. Poverty has remained around 20-25% for nearly 20 years, and the government’s strong social safety net has eroded due to increased constraints on its expenditures. Costa Rica’s credit rating was downgraded from stable to negative in 2015 and again in 2017, upping pressure on lending rates – which could hurt small businesses, on the budget deficit – which could hurt infrastructure development, and on the rate of return on investment – which could soften foreign direct investment (FDI). Unlike the rest of Central America, Costa Rica is not highly dependent on remittances – which represented just 1 % of GDP in 2016 but instead relied on FDI – which accounted for 5.1% of GDP.
Costa Rica is rich in the following natural resources: Hydropower.
The main industrial sectors are medical equipment, food processing, textiles and clothing, construction materials, fertilizer, plastic products.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in medical instruments, bananas, tropical fruits, orthopedic appliances, food preparations (2019), partnering with these nations: the United States 38%, Netherlands 6%, Belgium 5%, Guatemala 5%, Panama 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $21.2 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Costa Rica’s position of 79.
Land use in Costa Rica: 51.5% (2018 estimate) forest, 11.4% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 4.9% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 37.1% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 6.7% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 25.5% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 1,015 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Costa Rica are sugar cane, pineapples, bananas, milk, oil palm fruit, fruit, oranges, watermelons, cassava, rice.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, broadcasting equipment, cars, medical instruments, packaged medicines (2019), partnering with the following nations: the United States 41%, China 13%, Mexico 7% (2019) in a sum value of $19.39 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $19.64 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Costa Rica 86.
Costa Rica Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Costa Rica, Central America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean, between Nicaragua and Panama. We published some basic information about its capital San Jose, and the Costa Rican nation.
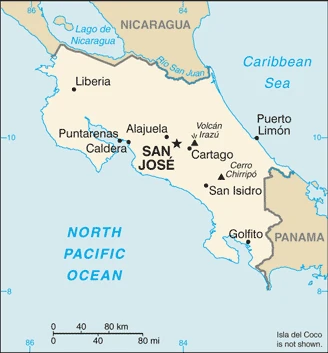
Are you interested in visiting Costa Rica and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Costa Rica below to overview the route network.
Printable map of Costa Rica
Did you know about Costa Rica?
Costa Rica is a great place to visit. It has a tropical climate, beautiful beaches, and diverse ecosystems. Costa Rica is a bilingual country where Spanish and English are both spoken. The “Ticos,” as the natives call themselves, are very friendly and welcoming.
Costa Rica is the only country globally with a rainforest running its entire length of the coast. The country also provides all its energy needs through renewable sources like wind, water, and geothermal power. This small Central American nation has plenty of natural beauty that you can enjoy by visiting places like Arenal Volcano National Park or Monteverde cloud forest preserves.
After virtually visiting Costa Rica, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Nicaragua and Panama.
If you liked our Google map and Costa Rica information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.