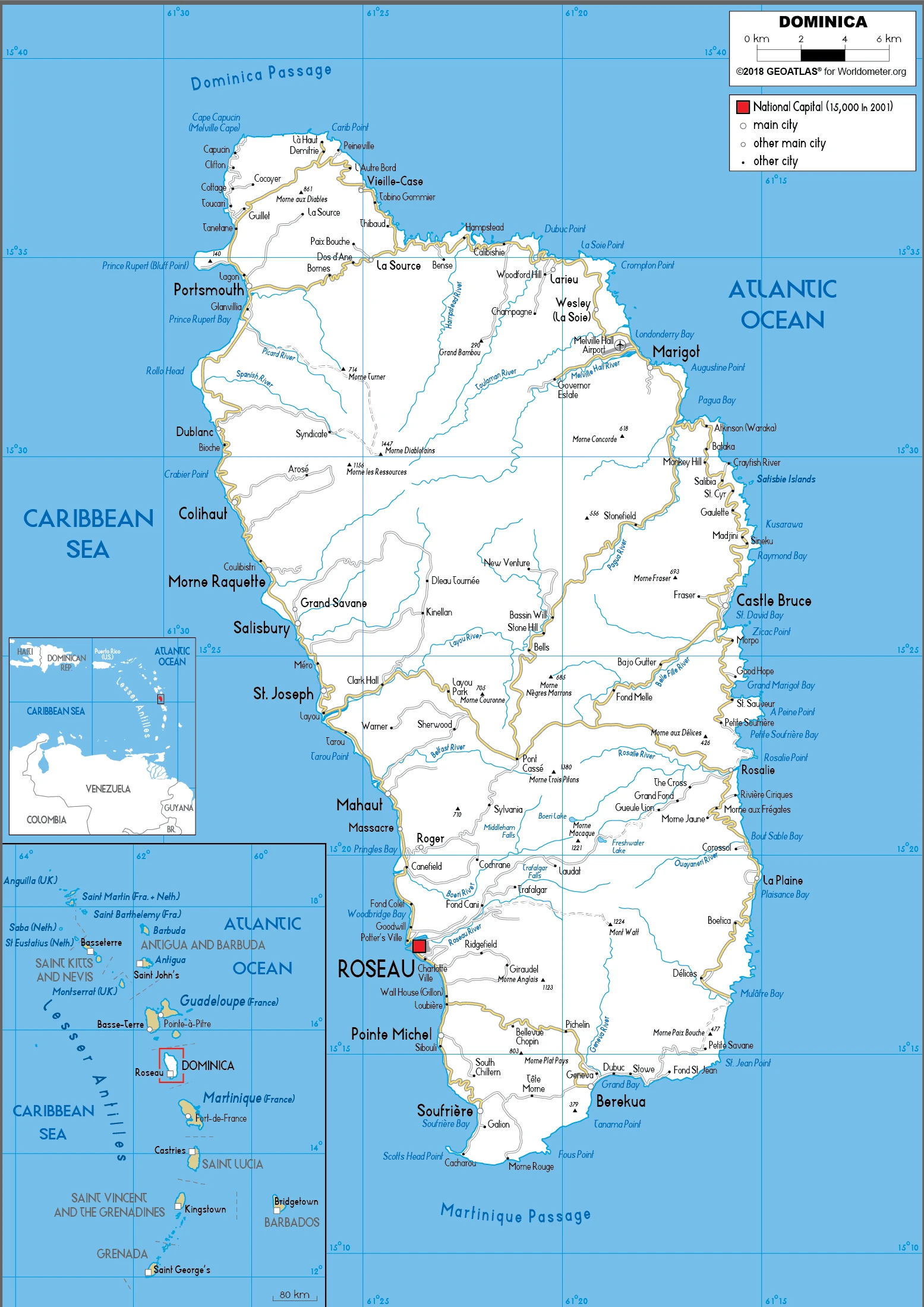
Dominica Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Dominica, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Dominica, Central America, and the Caribbean (35 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Roseau, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Central American and the Caribbean state.
Quick links: Google Maps Dominica, Roseau Google maps, Driving Directions Dominica, Printable Road Map.

About Dominica in a nutshell
- Dominica is known as “Nature Island,” due to its spectacular flora and fauna.
- Conventional short form of the name: Dominica
- The conventional long form of the name: Commonwealth of Dominica
- Etymology: the island was named by explorer Christopher COLUMBUS for the day of the week on which he spotted it, Sunday (Domingo in Latin), 3 November 1493.
- The legal system in Dominica: common law based on the English model.
- Climate: Tropical, cooled by constant trade winds. Heavy annual rainfall. Tropical depressions and hurricanes are likely JuneNovember.
- The national symbols are Sisserou parrot, Carib Wood flower; national colors: green, yellow, black, white, red.
- Internet TLD: .dm
Background
Dominica was the last of the Caribbean islands to be colonized by Europeans due chiefly to the fierce resistance of the native Caribs. France ceded possession to Great Britain in 1763, which colonized the island in 1805. Slavery ended in 1833, and in 1835 the first three men of African descent were elected to the legislative assembly of Dominica. In 1871, Dominica became part first of the British Leeward Islands and then the British Windward Islands until 1958.
In 1967 Dominica became an associated state of the UK and formally took responsibility for its internal affairs. In 1980, two years after independence, Dominica’s fortunes improved when a corrupt and tyrannical administration was replaced by Mary Eugenia CHARLES, the first female prime minister in the Caribbean, who remained in office for 15 years. On 18 September 2017, Hurricane Maria passed over the island, causing extensive damage to structures, roads, communications, and power supply and destroying critical agricultural areas.
Geography
Mountainous and densely forested. Volcanic activity has given the land fertile soils, hot springs, geysers, and black sand beaches.
Dominica is renowned as the Caribbean island that resisted European colonization until the 18th century. It achieved independence from the UK in 1978.
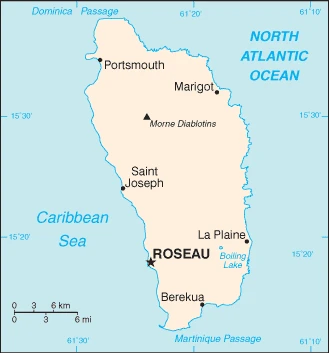
This state is located in the Caribbean, an island between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, about halfway between Puerto Rico and Trinidad and Tobago, under the coordinates of 15 25 N, 61 20 W, covering an area of 751 sq km with a coastline of 148 km. Dominica is Slightly more than four times the size of Washington, DC.
Rugged mountains of volcanic origin, with Morne Diablotins 1,447 m as the highest point of Dominica, while the Caribbean Sea 0 m as the lowest point. With 751 sq km, Dominica has 751 sq km of land and no water surface area.
Known as The Nature Island of the Caribbean due to its spectacular, lush, and varied flora and fauna, which are protected by an extensive natural park system; the most mountainous of the Lesser Antilles, its volcanic peaks are cones of lava craters and include Boiling Lake, the second-largest, thermally active lake in the world.
The climate in Dominica is as follows: Tropical, moderated by northeast trade winds, heavy rainfall.
When you visit Dominica, the natural hazards shall be considered: Flash floods are a constant threat; destructive hurricanes can be expected during the late summer months volcanism: Dominica was the last island to be formed in the Caribbean some 26 million years ago, it lies in the middle of the volcanic island arc of the lesser Antilles that extends from the island of Saba in the north to Grenada in the south; of the 16 volcanoes that make up this arc, five are located on Dominica, more than any other island in the Caribbean: Morne aux Diables (861 m), Morne Diablotins (1,430 m), Morne Trois pitons (1,387 m), watt mountain (1,224 m), which last erupted in 1997, and Morne Plat Pays (940 m); the two best known volcanic features on Dominica, the valley of desolation and the boiling lake thermal areas, lie on the flanks of watt mountain and both are popular tourist destinations.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Dominica: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Dominican people: water shortages a continuing concern; pollution from agrochemicals and untreated sewage; forests endangered by the expansion of farming; soil erosion; pollution of the coastal zone by agricultural and industrial chemicals; and untreated sewage.
Google Maps Dominica
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Roseau found under the coordinates 15 18 N, 61 24 W, applying the time zone UTC-4 (1 hour ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Roseau is a town in the southwest of Dominica that has been in existence for over 500 years. It is the capital and most populous city of the country and was founded by French planters, who named it Roseau from the frangipani trees that grew along its banks.
Dominica became independent on 3 November 1978 (from the UK), and its national holiday is Independence Day, 3 November (1978).
Administrative divisions: 10 parishes; Saint Andrew, Saint David, Saint George, Saint John, Saint Joseph, Saint Luke, Saint Mark, Saint Patrick, Saint Paul, Saint Peter.
People and society
The majority of Dominicans are descendants of enslaved Africans brought over to work on banana plantations. The Carib Territory on the northeast of the island is home to the only surviving indigenous community in the Caribbean. Wealth disparities are not as marked as elsewhere in the region, but poverty alleviation has become a significant plank of government policy.
The population in Dominica is 74,584 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 0.07% (2021 estimate) change. That means Dominica is No. 201 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 34.9 years median age (34.4 years for males and 34.4 years for women), Dominica ranks No. 87 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Dominican(s) (noun) or Dominican (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: African descent 84.5%, mixed 9%, Indigenous 3.8%, other 2.1%, unspecified 0.6% (2011 estimate).
They speak English (official language), French patois languages and practice the following religions: Roman Catholic 52.7%, Protestant 29.7% (includes Seventh Day Adventist 6.7%, Pentecostal 6.1%, Baptist 5.2%, Christian Union Church 3.9%, Methodist 2.6%, Gospel Mission 2.1%, other Protestant 3.1%), Jehovahs Witness 1.3%, Rastafarian 1.1%, other 4.3%, none 9.4%, unspecified 1.4% (2011 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Dominica: Population is mainly clustered along the coast, with roughly a third living in the parish of st. George, in or around the capital of Roseau. The volcanic interior is sparsely populated. In Dominica, we are talking about 71.4% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 15,000 Roseau (capital city) (2018).
Industry
Based on bananas, but has lost preferential access to the EU market. Some diversification: flowers, coffee, fruit. Agriculture is vulnerable to hurricanes. Eco-tourism. Some offshore banking.
In years past, the Dominican economy was dependent on agriculture – primarily bananas – but increasingly has been driven by tourism, as the government seeks to promote Dominica as an eco-tourism destination. However, Hurricane Maria, which passed through the island in September 2017, destroyed much of the country’s agricultural sector and caused damage to all of the country’s transportation and physical infrastructure. Before Hurricane Maria, the government had attempted to foster an offshore financial industry and planned to sign agreements with the private sector to develop geothermal energy resources.
When government finances are fragile, the government’s focus has been to get the country back in shape to service cruise ships. The economy contracted in 2015 and recovered to positive growth in 2016 due to a recovery of agriculture and tourism. Dominica suffers from high debt levels, which increased from 67% of GDP in 2010 to 77% in 2016. Dominica is one of five countries in the East Caribbean that have citizenship by investment programs whereby foreigners can obtain passports for a fee, contributing to government budgets.
Dominica is rich in the following natural resources: Timber, hydropower, arable land.
The main industrial sectors are soap, coconut oil, tourism, copra, furniture, cement blocks, shoes.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in medical instruments, pharmaceuticals, low-voltage protection equipment, tropical fruits, and bandages (2019), partnering with Saudi Arabia 47%, Qatar 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $160 million. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Dominica’s position of 206.
Land use in Dominica: 59.2% (2018 estimate) forest, 6.1% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 8% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 34.7% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 24% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 2.7% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is N/A.
The main agro-industrial products of Dominica are bananas, yams, grapefruit, taro, milk, coconuts, oranges, yautia, plantains, sugar cane. Note: forest and fishery potential not exploited.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, natural gas, crude petroleum, recreational boats, cars (2019), partnering with the following nations: the United States 57%, Nigeria 11%, China 6%, Italy 5% (2019) in a sum value of $430 million. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate) $188.4 million (2016 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Dominica 206.
Dominica Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Dominica, the Caribbean island between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, about halfway between Puerto Rico and Trinidad and Tobago. We published some basic information about its capital Roseau, and the Dominican nation.
Are you interested in visiting Dominica and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Dominica below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Dominica
Did you know about Dominica?
Located in the Caribbean, Dominica is a beautiful island with many opportunities for adventure. At only 290 square miles, it’s not difficult to get from one end of the island to the other. However, if you’re more interested in relaxing and making the most of life on the beach, you’ll find plenty of blissful white sandy beaches to choose from.
It’s one of the few remaining Caribbean countries European forces have never conquered. It’s also home to many rare species of animals, including the Sisserou parrot.
After virtually visiting Dominica, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: none.
If you liked our Google map and Dominica information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.