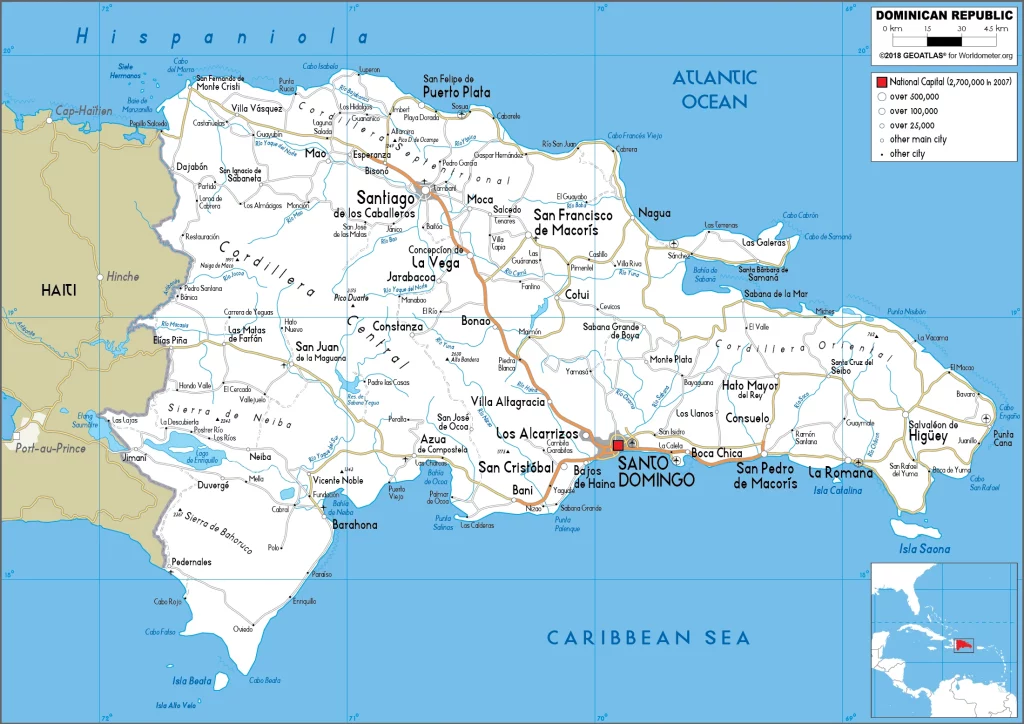
Dominican Republic Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like the Dominican Republic, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to the Dominican Republic, Central America, and the Caribbean (35 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Santo Domingo, bordering countries like Haiti, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Central American and the Caribbean state.
Quick links: Google Maps Dominican Republic, Santo Domingo Google maps, Driving Directions Dominican Republic, Printable Road Map.

About Dominican Republic in a nutshell
- Santo Domingo is the oldest city in the Americas. It was founded in 1496 by the brother of Christopher Columbus.
- Conventional short form of the name: The Dominican
- The conventional long form of the name: Dominican Republic
- Local long form: Republica Dominicana
- Local short form: La Dominicana
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: the country name derives from the capital city of Santo Domingo (Saint Dominic).
- The legal system in Dominican Republic: civil law system based on the French civil code; Criminal Procedures Code modified in 2004 to include important elements of an accusatory system.
- Climate: Hot and humid close to sea level, cooler at altitude. Heavy rainfall, especially in the northeast.
- The national symbols are palmchat (bird); national colors: red, white, blue.
- Internet TLD: .do
The island of Hispaniola was named “Little Spain” by the first European explorers. Its indigenous inhabitants, the Arawak Indians, who called themselves “taíno”, “friendly people”, were wiped out by the colonizers in a quarter of a century. The lost labor was replaced by enslaved people imported from Africa. The western third of the divided island fell to the French and the eastern third to the Spanish. Haiti means ‘land of mountains’ in the indigenous language, and indeed 60% of its territory is made up of steeply sloping mountain ranges rising well over 2,000 m.
The burning of coal, valuable timber, and the acquisition of new arable land have sealed the fate of the lush tropical forests that once covered the entire island: today, barely 3% of the forests remain. Haiti’s two centuries of independence have been “colored” by invasions, rebellions, coups, and bloodthirsty dictators, the latter of which have benefited Dominica, which has been independent since 1865. Haiti’s black Catholic population of African descent also practices the voodoo religion. European mass tourism has targeted Dominica’s tropical beaches, with charter flights taking holidaymakers to its luxury hotels. Santo Domingo is the oldest European-inhabited city in the New World, home to America’s first church, hospital, customs house, and university. In Haiti, in the National Historical Park, the Sanssouci Castle, home of the former government, the Ramiers’ houses, and the Citadel commemorate the independence won by enslaved Black people in 1804.
Background
The Taino – indigenous inhabitants of Hispaniola before the arrival of the Europeans – divided the island into five chiefdoms and territories. Christopher COLUMBUS explored and claimed the island on his first voyage in 1492. It became a springboard for the Spanish conquest of the Caribbean and the American mainland. In 1697, Spain recognized French dominion over the western third of the island, which in 1804 became Haiti.
By then known as Santo Domingo, the remainder of the island sought to gain its independence in 1821 but was conquered and ruled by the Haitians for 22 years. It finally attained independence from the Dominican Republic in 1844. In 1861, the Dominicans voluntarily returned to the Spanish Empire, but two years later, they launched a war that restored independence in 1865. A legacy of the unsettled, mostly non-representative rule followed, capped by the dictatorship of Rafael Leonidas TRUJILLO from 1930 to 1961. Juan BOSCH was elected president in 1962 but was deposed in a military coup in 1963. In 1965, the US led an intervention during a civil war sparked by an uprising to restore BOSCH.
In 1966, Joaquin BALAGUER defeated BOSCH in the presidential election. BALAGUER maintained a tight grip on power for most of the next 30 years when international reaction to flawed elections forced him to curtail his term in 1996. Since then, regular competitive elections have been held in which opposition candidates have won the presidency. Former President Leonel FERNANDEZ Reyna (first term 1996-2000) won election to a new term in 2004 following a constitutional amendment allowing presidents to serve more than one term and was later reelected to a second consecutive term. Following the two-term presidency of Danilo MEDINA Sanchez (2012-2020), Luis Rodolfo ABINADER Corona was elected president in July 2020.
Geography
Highlands and rainforested mountains , including the highest peak in the Caribbean, Pico Duarte, interspersed with fertile valleys. An extensive coastal plain takes place in the east.
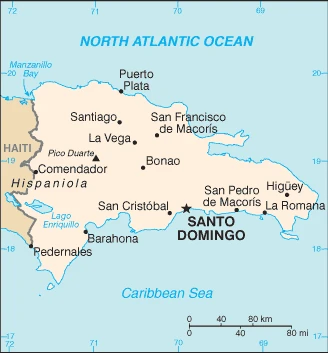
The Dominican Republic occupies the eastern two-thirds of the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean. Spanish- speaking, it seeks closer ties to the anglophone West Indies.
This state is located in the Caribbean, eastern two-thirds of the island of Hispaniola, between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, east of Haiti, under the coordinates of 19 00 N, 70 40 W, covering an area of 48,670 sq km with a coastline of 1,288 km. The Dominican Republic is slightly more than twice the size of New Jersey.
The Dominican Republic has 376 km of land boundaries in total and borders with (1 nation): Haiti 376 km.
Rugged highlands and mountains interspersed with fertile valleys, with Pico Duarte 3,098 m as the highest point of Dominican Republic, while Lago Enriquillo -46 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 424 m throughout the country. With a total of 48,670 sq km, Dominican Republic has 48,320 sq km of land and 350 sq km water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Lago de Enriquillo – 500 sq km (saltwater lake) while there are no significant rivers.
Shares island of Hispaniola with Haiti (eastern two-thirds makes up the Dominican Republic, western one-third is Haiti); the second-largest country in the Antilles (after Cuba); geographically diverse with the Caribbeans tallest mountain, Pico Duarte, and lowest elevation and largest lake, Lago Enriquillo.
The climate in the Dominican Republic is as follows: Tropical maritime, slight seasonal temperature variation, seasonal variation in rainfall.
When you visit the Dominican Republic, the natural hazards shall be considered: Lies in the middle of the hurricane belt and subject to severe storms from June to October; occasional flooding; periodic droughts.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting the Dominican Republic: degree of risk: high (2020), bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, typhoid fever, dengue fever.
Current environmental issues affecting the Dominican people: water shortages; soil eroding into the sea damages coral reefs; deforestation.
Google Maps Dominican Republic
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Santo Domingo found under the coordinates 18 28 N, 69 54 W, applying the time zone UTC-4 (1 hour ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
While visiting Santo Domingo for the first time, one feels that history is everywhere. The city has a rich and varied past, with many historic landmarks, including the Palace of the Inquisition and the Cathedral of Santo Domingo, visible from far off in the distance.
The Dominican Republic became independent on 27 February 1844 (from Haiti), and its national holiday is Independence Day, 27 February (1844).
Administrative divisions: 10 regions (regiones, singular – region); Cibao Nordeste, Cibao Noroeste, Cibao Norte, Cibao Sur, El Valle, Enriquillo, Higuamo, Ozama, Valdesia, Yuma.
People and society
White landowners, especially those descended from the original Spanish settlers, form the wealthy elite. The mixed-race majority controls commerce and forms the bulk of the professional middle classes. White and mixed-race women are entering the professions. Great wealth disparities exist; the black and Haitian-immigrant populations occupy the bottom of the social ladder.
The population in the Dominican Republic is 10,597,348 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 0.92% (2021 estimate) change. That means the Dominican Republic is the No. 87 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 27.9 years median age (27.8 years for males and 27.8 years for women), Dominican Republic ranks No. 144 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Dominican(s) (noun) or Dominican (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: mixed 70.4% (Mestizo/Indio 58%, Mulatto 12.4%), Black 15.8%, White 13.5%, other 0.3% (2014 estimate). Note: respondents self-identified their race; the term Indio in the Dominican Republic is not associated with people of indigenous ancestry but people of mixed ancestry or skin color between light and dark.
They speak Spanish (official language) languages and practice the following religions: Roman Catholic 44.3%, Evangelical 13%, Protestant 7.9%, Adventist 1.4%, other 1.8%, atheist 0.2%, none 29.4%, unspecified 2% (2018 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in the Dominican Republic: Coastal development is significant, especially in the southern coastal plains and the Cibao valley, where population density is highest. Smaller population clusters exist in the interior mountains (cordillera central). In the Dominican Republic, we are talking about 83.2% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 3.389 million, Santo Domingo (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Mining (nickel and gold), sugar, and textiles. Tourism, remittances, and exports all rely heavily on the US market. A hidden economy based on the transshipment of narcotics to the US.
For most of its history, the Dominican Republic was primarily an exporter of sugar, coffee, and tobacco. Still, over the last three decades, the economy has become more diversified as the service sector has overtaken agriculture as the economy’s largest employer due to growth in construction, tourism, and free trade zones. The mining sector has also played a more significant role in the export market since late 2012 with the commencement of the extraction phase of the Pueblo Viejo Gold and Silvermine, one of the largest gold mines in the world., For the last 20 years, the Dominican Republic has been one of the fastest-growing economies in Latin America.
The economy rebounded from the global recession in 2010-16, improving the fiscal situation. A tax reform package passed in November 2012, a reduction in government spending, and lower energy costs helped narrow the central government budget deficit from 6.6% of GDP in 2012 to 2.6% in 2016, and public debt is declining. Marked income inequality, high unemployment, and underemployment remain critical long-term challenges; the poorest half of the population receives less than one-fifth of GDP, while the wealthiest 10% enjoys nearly 40% of GDP. The economy is highly dependent upon the US, the destination for approximately half of exports and the source of 40% of imports. Remittances from the US amount to about 7% of GDP, equivalent to about one-third of exports and two-thirds of tourism receipts. The Central America-Dominican Republic Free Trade Agreement came into force in March 2007, boosting investment and manufacturing exports.
The Dominican Republic is rich in the following natural resources: Nickel, bauxite, gold, silver, arable land.
The main industrial sectors are typically tourism, sugar processing, gold mining, textiles, cement, tobacco, electrical components, medical devices.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in gold, medical instruments, cigars, low-voltage protection equipment, bananas (2019), partnering with these nations: the United States 54%, Switzerland 8%, Canada 5%, India 5%, China 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $14.44 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in the Dominican Republic’s position of 93.
Land use in Dominican Republic: 40.8% (2018 estimate) forest, 7.7% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 16.6% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 51.5% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 10.1% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 24.8% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 3,070 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of the Dominican Republic are sugar cane, bananas, papayas, rice, plantains, milk, avocados, fruit, pineapples, coconuts.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, cars, jewelry, natural gas, broadcasting equipment (2019), partnering with the following nations: the United States 50%, China 13% (2019) in a sum value of $20.19 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $24.53 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $24.11 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in the Dominican Republic 82.
Dominican Republic Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about the Dominican Republic, the Caribbean, eastern two-thirds of the island of Hispaniola, between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, east of Haiti. We published some basic information about its capital Santo Domingo, and the Dominican nation.
Are you interested in visiting the Dominican Republic and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of the Dominican Republic below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Dominican Republic
Did you know about Dominican Republic?
The Dominican Republic is a beautiful and diverse country. It is the largest country in the Caribbean and occupies the eastern two-thirds of Hispaniola, an island split by Haiti. The Dominican Republic’s capital and largest city is Santo Domingo. With almost 8.5 million people (3rd Spanish speaking country in the world), it is the most populous nation in both the Caribbean and Central America.
Its capital city is Santo Domingo, and it’s known as la Perla de todos Los mares (the pearl of all seas).
After virtually visiting the Dominican Republic, you may also be interested in the neighboring country: Haiti.
If you liked our Google map and the Dominican Republic information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.