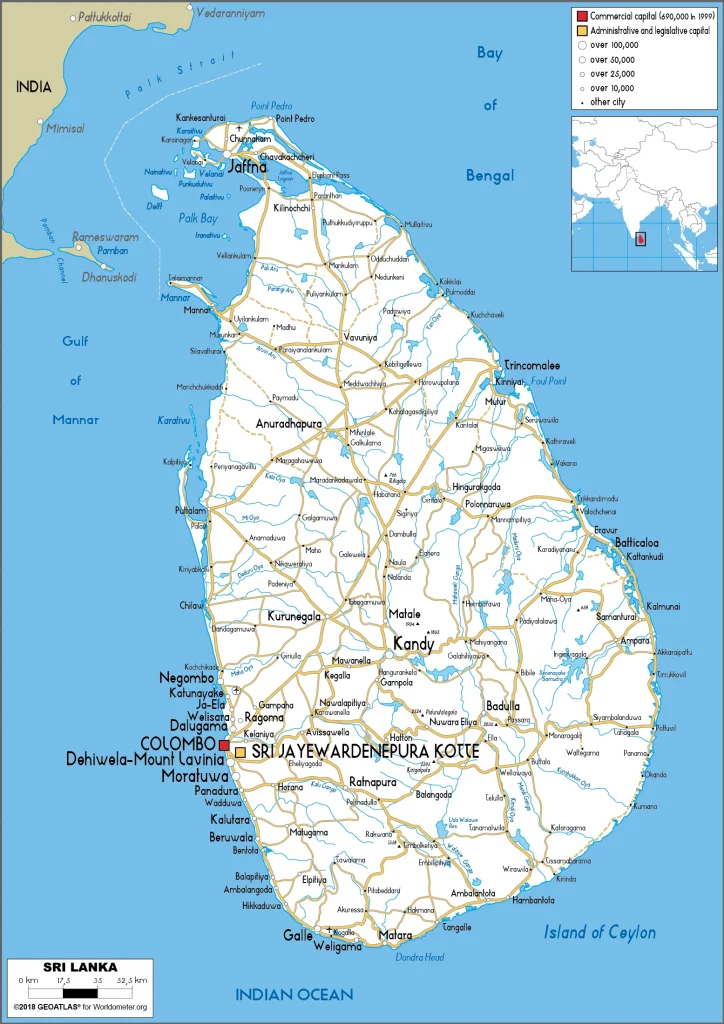
Sri Lanka Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Sri Lanka, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Sri Lanka, Asia (22 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Colombo (commercial capital); Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte (legislative capital), and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Asian state.
Quick links: Google Maps Sri Lanka, Colombo Google maps, Driving Directions Sri Lanka, Printable Road Map.

About Sri Lanka in a nutshell
- Sri Lanka elected the worlds first woman prime minister, Sirimavo Bandaranaike, in 1960.
- Conventional short form of the name: Sri Lanka
- The conventional long form of the name: Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka
- Local long form: Shri Lanka Prajatantrika Samajavadi Janarajaya / Ilankai Jananayaka Choshalichak Kutiyarachu
- Local short form: Shri Lanka / Ilankai
- Former name(s): Serendib, Ceylon
- Etymology: the name means resplendent island in Sanskrit.
- The legal system in Sri Lanka: mixed legal system of Roman-Dutch civil law, English common law, Jaffna Tamil customary law, and Muslim personal law.
- Climate: Tropical, with breezes on the coast and cooler air in the highlands. Northeast is driest and hottest.
- The national symbols are lion and water lily; the national colors: are maroon and yellow.
- Internet TLD: .lk
Sri Lanka, just 50 km from India, is connected to the subcontinent by a series of coral reefs known as the Adam’s Bridge. The southern part of the island is a mountainous region of Buddhist Sinhalese, rising to over 2,000 meters, while in the north, a wide plain of Hindu Tamils stretches as far as the Jaffna peninsula. Sri Lanka’s World Heritage Sites are a faithful reflection of the major milestones of two and a half thousand years of history. Tucked away in the depths of the rainforest, Anuradhapura, the first capital of the Sinhalese kingdom, dates back to the 3rd century BC. The fortress of Sigiriya, built on the ‘Lion’s Rock’, which rises 370 meters from the surrounding rainforest, was also the summer residence of the Sinhalese kings in the 5th century AD. Polonnaruwa was the second capital of the Sinhalese from the end of the 1st millennium AD for 300 years. Kandy, the last capital of the Sinhalese kings, flourished until the arrival of the British in 1815. The golden temple of Dambulla, with its five cave shrines, over 2,000 square meters of wall paintings, and 157 statues, was the most sacred pilgrimage site for Buddhism on the island for 2,200 years. The port town of Gallé and its 16th-century fortifications, built by Europeans, are reminiscent of the colonial period. Sinharaja’s tropical rainforest reserve with its indigenous wildlife is Sri Lanka’s only natural world heritage site.
Background
The first Sinhalese arrived in Sri Lanka in the 6th century B.C., probably from northern India. Buddhism was introduced circa 250 B.C., and the first kingdoms developed in the cities of Anuradhapura (from circa 200 B.C. to circa A.D. 1000) and Polonnaruwa (from about 1070 to 1200). In the 14th century, a south Indian dynasty established a Tamil kingdom in northern Sri Lanka. The Portuguese controlled the island’s coastal areas in the 16th century, followed by the Dutch in the 17th century. The island was ceded to the British in 1796, became a crown colony in 1802, and was formally united under British rule by 1815. As Ceylon, it became independent in 1948. Its name was changed to Sri Lanka in 1972. Prevailing tensions between the Sinhalese majority and Tamil separatists erupted into war in July 1983. Fighting between the government and Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) continued for over a quarter century. Although Norway brokered peace negotiations that led to a ceasefire in 2002, the fighting slowly resumed and was again in full force by 2006. The government defeated the LTTE in May 2009.
During the post-conflict years under President Mahinda RAJAPAKSA, the government initiated infrastructure development projects, many financed by loans from China. His regime faced significant allegations of human rights violations and a shrinking democratic space for civil society. In 2015, a new coalition government headed by President Maithripala Sirisena of the Sri Lanka Freedom Party and Prime Minister Ranil WICKREMESINGHE of the United National Party came to power with pledges to advance economic, governance, anti-corruption, reconciliation, justice, and accountability reforms. However, the implementation of these reforms has been uneven. In October 2018, President SIRISENA attempted to oust Prime Minister WICKREMESINGHE, swearing in former President RAJAPAKSA as the new prime minister and issuing an order to dissolve the Parliament and hold elections. This sparked a seven-week constitutional crisis that ended when the Supreme Court ruled SIRISENAs actions unconstitutional, RAJAPAKSA resigned, and WICKREMESINGHE was reinstated. In November 2019, Gotabaya RAJAPAKSA won the presidential election and appointed his brother, Mahinda, prime minister.
Geography
Rugged central highlands dominate the main island. Rivers dissect fertile northern plains. Much of the land is a tropical jungle.
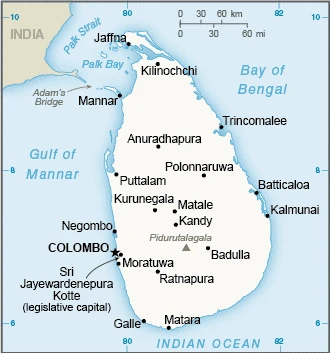
The teardrop-shaped island of Sri Lanka is separated from India by the Palk Strait. Ethnic Tamil rebels, the Tamil Tigers, were defeated in 2009 after a brutal 26-year civil war.
This state is located in Southern Asia, an island in the Indian Ocean, south of India, under the coordinates of 7 00 N, 81 00 E, covering an area of 65,610 sq km with a coastline of 1,340 km. Sri Lanka is Slightly larger than West Virginia.
Mostly low, flat to rolling plain, mountains in south-central interior, with Pidurutalagala 2,524 m as the highest point of Sri Lanka, while Indian Ocean 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 228 m throughout the country. With a total of 65,610 sq km, Sri Lanka has 64,630 sq km of land and 980 sq km of water surface area.
Strategic location near major Indian Ocean sea lanes; Adams Bridge is a chain of limestone shoals between the southeastern coast of India and the northwestern coast of Sri Lanka; geological evidence suggests that this 50-km long Bridge once connected India and Sri Lanka; ancient records seem to indicate that a foot passage was possible between the two land masses until the 15th century when the land bridge broke up in a cyclone.
The climate in Sri Lanka is as follows: Tropical monsoon, northeast monsoon (December to March), and the southwest monsoon (June to October).
When you visit Sri Lanka, the natural hazards shall be considered: Occasional cyclones and tornadoes.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Sri Lanka: degree of risk: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Sri Lankan people: deforestation; soil erosion; wildlife populations threatened by poaching and urbanization; coastal degradation from mining activities and increased pollution; coral reef destruction; freshwater resources being polluted by industrial wastes and sewage runoff; waste disposal; air pollution in Colombo.
Google Maps Sri Lanka
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Colombo (commercial capital); Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte (legislative capital) found under the coordinates 6 55 N, 79 50 E, applying the time zone UTC+5.5 (10.5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Colombo is the capital of Sri Lanka. The city can be found on the southwestern coast of the island. Colombo is surrounded by a wall known as Galle Face Green. Colombo is an essential commercial hub in South Asia, with links to India, Africa, and Europe.
Sri Lanka became independent on 4 February 1948 (from the U.K.), and its national holiday is Independence Day (National Day), 4 February (1948).
Administrative divisions: 9 provinces; Central, Eastern, North Central, Northern, North Western, Sabaragamuwa, Southern, Uva, and Western.
People and society
The Sinhalese are predominantly Buddhist, while the Tamils are primarily Hindu. Moors are the Muslim descendants of Arab traders. Tamils were the minority group favored by the British colonists. Majority-Sinhalese power since independence in 1948 fueled tensions, erupting into civil war in 1983. The eventual government victory in 2009 made this the only rebel insurgency ever defeated in modern times.
The population in Sri Lanka is 23,044,123 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 0.63% (2021 estimate) change. That means Sri Lanka is the No. 58 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 33.7 years median age (32.3 years for males and 32.3 years for women), Sri Lanka ranks No. 97 on the globe’s median age list.
The people living in this country are the Sri Lankan(s) (noun) or Sri Lankan (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Sinhalese 74.9%, Sri Lankan Tamil 11.2%, Sri Lankan Moors 9.2%, Indian Tamil 4.2%, other 0.5% (2012 estimate).
They speak Sinhala (official language and national language) 87%, Tamil (official language and national language) 28.5%, and English 23.8% (2012 estimate). Note: data represent the main languages spoken by the population aged 10 years and older; shares sum to more than 100% because some respondents gave more than one answer on the census; English is commonly used in government and is referred to as the link language in the constitution languages and practice the following religions: Buddhist (official) 70.2%, Hindu 12.6%, Muslim 9.7%, Roman Catholic 6.1%, other Christian 1.3%, other 0.05% (2012 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Sri Lanka: The population is primarily concentrated within a broad wet zone in the southwest, urban centers along the eastern coast, and on the Jaffna peninsula in the north. In Sri Lanka, we are talking about 18.9% (2021) of the total population lives in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 103,000 Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte (Legislative Capital) (2018), 619,000 Colombo (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Sri Lanka is attempting to sustain economic growth while maintaining macroeconomic stability under the IMF program it began in 2016. The government’s high debt payments and bloated civil service, which have contributed to historically high budget deficits, remain a concern. Government debt is about 79% of GDP and remains among the highest emerging markets. In the coming years, Sri Lanka will need to balance its elevated debt repayment schedule with its need to maintain adequate foreign exchange reserves., In May 2016, Sri Lanka regained its preferential trade status under the European Unions Generalized System of Preferences Plus, enabling many of its firms to export products, including its top export garments, tax-free to the E.U. In 2017, Parliament passed a new Inland Revenue Act to increase tax collection and broaden the tax base in response to recommendations made under its IMF program. In November 2017, the Financial Action Task Force on money laundering and terrorist financing listed Sri Lanka as non-compliant but reported that Sri Lanka had made good progress in implementing an action plan to address deficiencies. Tourism has experienced substantial growth since the resolution of the government’s 26-year conflict with the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam. In 2017, the government promulgated plans to transform the country into a knowledge-based, export-oriented Indian Ocean hub by 2025.
Sri Lanka is rich in the following natural resources: Limestone, graphite, mineral sands, gems, phosphates, clay, hydropower, and arable land.
The main industrial sectors are typically the processing of rubber, tea, coconuts, tobacco, and other agricultural commodities; telecommunications, insurance, banking; tourism, shipping; clothing, textiles; cement, petroleum refining, information technology services, and construction.
The country’s export sectors are robust in clothing and apparel, tea, used tires, rubber products, precious stones, and cinnamon (2019), partnering with these nations: the United States 24%, India 8%, United Kingdom 7%, Germany 7% (2019). The export trade resulted in $19.41 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate). Values in a global export rank resulted in Sri Lanka’s position of 83.
Land use in Sri Lanka: 29.4% (2018 estimate) forest, 27.1% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 20.7% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 43.5% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 15.8% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 7% (2018 estimate). The area of the irrigated land is 5,700 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Sri Lanka are rice, coconuts, sugar cane, plantains, milk, tea, cassava, maize, poultry, and coir.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, textiles, gold, cars, and broadcasting equipment (2019), partnering with the following nations: India 24%, China 23%, Singapore 7%, United Arab Emirates 6%, Malaysia 5% (2019) in a sum value of $24.56 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $26.84 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate) $26.063 billion (2017 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Sri Lanka 75.
Sri Lanka Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Sri Lanka, Southern Asia, an island in the Indian Ocean, south of India. We published basic information about its capital Colombo (commercial capital), Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte (legislative capital), and the Sri Lankan nation.
Are you interested in visiting Sri Lanka and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Sri Lanka below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Sri Lanka
Did you know about Sri Lanka?
Sri Lanka is a beautiful country located in the Indian Ocean. It is an island nation home to many different cultures and religions. The official languages of Sri Lanka are Sinhala and Tamil. Sri Lanka has a rich history and was once a colony of the British Empire. The country is also home to some of the world’s most endangered animals, including the elephant, leopard, and rhinoceros. Sri Lanka is also the world’s largest producer of cinnamon. Today, Sri Lanka is a popular tourist destination, known for its beautiful beaches and friendly people.
After virtually visiting Sri Lanka, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: none.
If you liked our Google map and Sri Lanka information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.