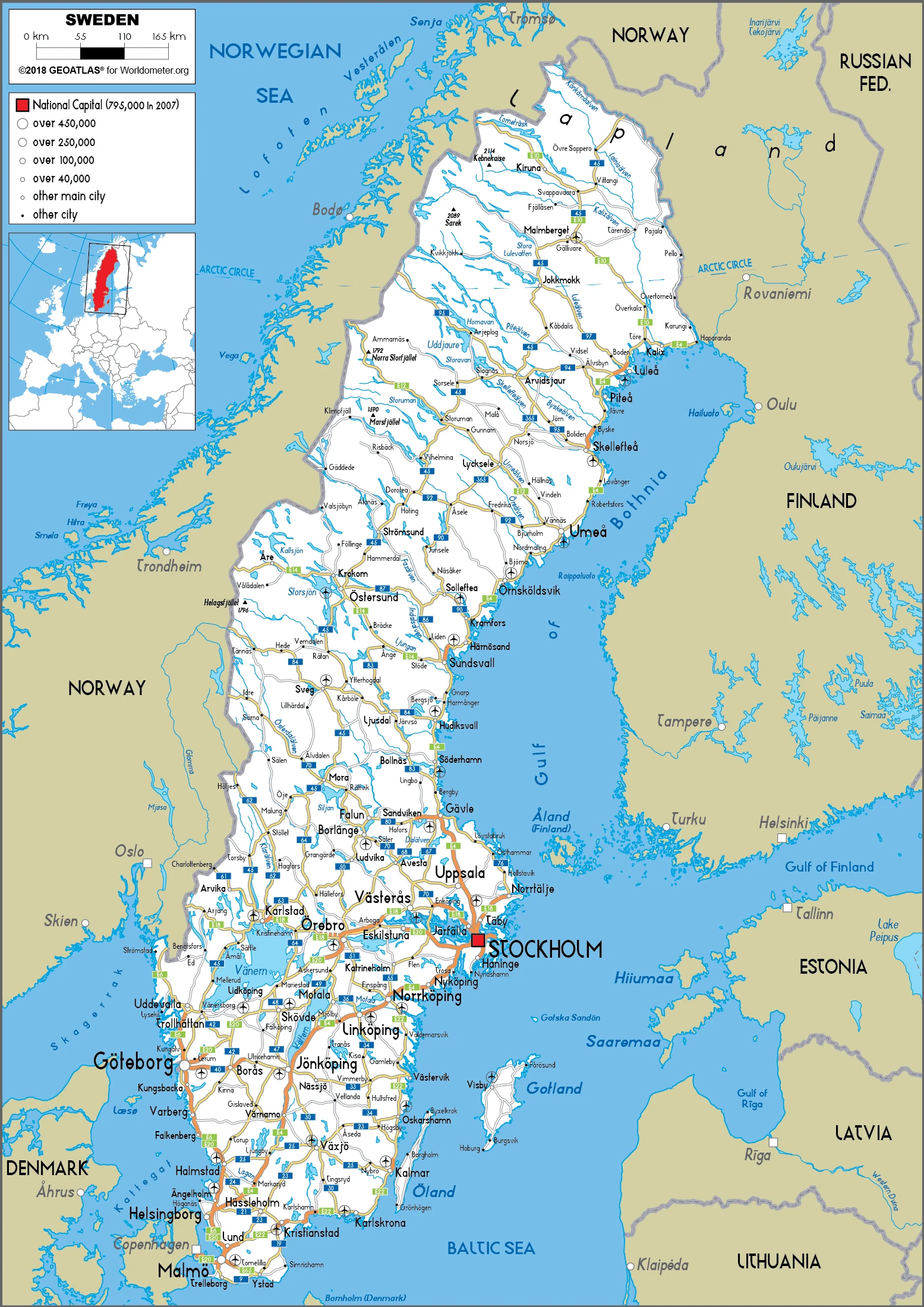
Sweden Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Sweden, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Sweden, Europe (47 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Stockholm, bordering countries like Finland, Norway, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this European state.
Quick links: Google Maps Sweden, Stockholm Google maps, Driving Directions Sweden, Printable Road Map.

About Sweden in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Sweden
- The conventional long form of the name: Kingdom of Sweden
- Local long form: Konungariket Sverige
- Local short form: Sverige
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: name ultimately derives from the North Germanic Svear tribe, which inhabited central Sweden and was first mentioned in the first centuries A.D.
- The legal system in Sweden: civil law system influenced by Roman-Germanic law and customary law.
- Climate: Southern coasts warmed by Gulf Stream. Northern areas have a more extreme continental climate.
- The national symbols are three crowns, a lion, and national colors: blue and yellow.
- Internet TLD: .se
Stockholm was founded 7 centuries ago, but it wasn’t until the mid-1700s that it became Sweden’s capital. Stockholm is now the capital of a modern society that focuses on leisure activities and having access to nearby nature. Stockholm is the largest city in Scandinavia and presides over a country similar to California. Stockholm has a population of about 860,000 people, whereas California has a population much larger at 39,536,653.
Although it was unaffected by World War II, Stockholm has been at the forefront of modern architecture due to its proximity to Europe. The old town districts of Stockholm have many admiring features from the imperial times and have many wooden buildings affected by fire during World War II.
Sweden is perched on the eastern slopes of the Scandinavian Mountains and the western edge of the glacier-covered Baltic shield. The largest country in the region also boasts the most significant number of World Heritage sites. They include the barren and stark tundra of the Sámi Lapland and the Swedish Highlands on the western shore of the Gulf of Bothnia. The rock paintings of Tanum bear witness to the life, culture, and beliefs of the inhabitants of Bronze Age Europe. At the same time, the archaeological sites of Birka and Hovgarden provide evidence of the advanced trading networks of Viking Europe. On the island of Gotland, the port of Visby is one of the oldest surviving trading towns of the Hanseatic League, while the naval base at Karlskrona is a typical naval port of late 17th century Europe.
Two World Heritage Sites are located near Stockholm: the 18th century Drottningholm Royal Palace on an island in Lake Málaren and Skogskyrkogárden cemetery. The church village of Gammels-tad, near Luleå, with its 424 wooden houses, and the agricultural district of the island of South Öland are rural heritage sites. In contrast, the industrial World Heritage sites include the 17th-century Engelsberg ironworks, the copper mine in the village, the Varberg radio station, a wireless radio transmitter built in 1922 and still in operation today, and the Swedish section of the Struve surveying network.
Sweden has maintained a position of armed neutrality since 1815.
Background
A military power during the 17th century, Sweden has not participated in any war for two centuries. An armed neutrality was preserved in both World Wars. Since then, Sweden has pursued a successful economic formula consisting of a capitalist system intermixed with substantial welfare elements. Sweden joined the EU in 1995, but the public rejected the introduction of the euro in a 2003 referendum. Swedens population born abroad increased from 11.3% in 2000 to 19.1% in 2018.
Geography
Heavily forested, with many lakes. The northern plateau extends beyond the Arctic Circle. Southern lowlands are widely cultivated.
The largest Scandinavian country by both population and area, Sweden has one of the worlds most extensive welfare systems. It is among the leading proponents of equal rights for women.
This state is located in Northern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, Gulf of Bothnia, Kattegat, and Skagerrak, between Finland and Norway, under the coordinates of 62 00 N, 15 00 E, covering an area of 450,295 sq km with a coastline of 3,218 km. Sweden is almost three times the size of Georgia, slightly larger than California.
Sweden has 2,211 km of land boundaries and borders (2 nations): Finland 545 km, and Norway 1666 km.
Mostly flat or gently rolling lowlands, mountains in the west, with Kebnekaise south 2,100 m as the highest point of Sweden, while the reclaimed bay of Lake Hammarsjon, near Kristianstad -2.4 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 320 m throughout the country. With 450,295 sq km, Sweden has 410,335 sq km of land and 39,960 sq km of water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Vanern – 5,580 sq km; Vattern – 1,910 sq km; Malaren – 1,140 sq km (freshwater lake).
Strategic location along Danish Straits linking Baltic and North Seas; Sweden has almost 100,000 lakes, the largest of which, Vanern, is the third-largest in Europe.
The climate in Sweden is as follows: Temperate in the south with cold, cloudy winters and cool, partly cloudy summers, and subarctic in the north.
When you visit Sweden, the natural hazards shall be considered: Ice floes in the surrounding waters, especially in the Gulf of Bothnia, can interfere with maritime traffic.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Sweden: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Swedish people: marine pollution (Baltic Sea and the North Sea); acid rain damage to soils and lakes; air pollution; inappropriate timber harvesting practices.
Google Maps Sweden
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Stockholm found under the coordinates 59 20 N, 18 03 E, applying the time zone UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October.
Stockholm is the capital of Sweden and the most populous city in the Nordic countries. At the same time, it is one of the most exciting cities in Europe. It has a lot of old buildings and landmarks and modern skyscrapers. Many people visit Stockholm for its unique culture and history, but it is also known for its vibrant nightlife. The city is home to many attractions such as the Nobel Museum, Vasa Museum, Gamla Stan (Old Town), Skansen, etc.
Sweden became independent on 6 June 1523 (Gustav VASA was elected king of Sweden, marking the abolishment of the Kalmar Union between Denmark, Norway, and Sweden), and its national holiday is National Day, 6 June (1983).
Administrative divisions: 21 counties (lan, singular and plural); Blekinge, Dalarna, Gavleborg, Gotland, Halland, Jamtland, Jonkoping, Kalmar, Kronoberg, Norrbotten, Orebro, Ostergotland, Skane, Sodermanland, Stockholm, Uppsala, Varmland, Vasterbotten, Vasternorrland, Vastmanland, Vastra Gotaland.
People and society
The nuclear family forms the basis of society, but the marriage rate is one of the lowest globally, and cohabitation is now standard. A high tax burden pays for the model welfare system. Women are well represented at all levels. A minority of 30,000 Sámi lives in the far north. Most industries and the bulk of the population are based in and around the southern cities. An EU member since 1995, Sweden has voted not to join the euro.
The population in Sweden is 10,261,767 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 0.74% (2021 estimate) change. That means Sweden is the No. 91 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 41.1 years median age (40.1 years for males and 40.1 years for women), Sweden ranks No. 47 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Swede(s) (noun) or Swedish (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Swedish 80.3%, Syrian 1.9%, Iraqi 1.4%, Finnish 1.4%, other 15% (2020 estimate). Note: data represent the population by country of birth; the indigenous Sami people are estimated to number between 20,000 and 40,000.
They speak Swedish (official language) languages and practice the following religions: Church of Sweden (Lutheran) 57.6%, other (includes Roman Catholic, Orthodox, Baptist, Muslim, Jewish, and Buddhist) 8.9%, none or unspecified 33.5% (2019 estimate) note: estimates reflect registered members of faith communities eligible for state funding (not all religions are state-funded and not all people who identify with a particular religion are registered members) and the Church of Sweden.
We can conclude the following about the population in Sweden: Most Swedes live in the south, where the climate is milder, and there is better connectivity to mainland Europe. Population clusters are found all along the Baltic coast in the east. The interior areas of the north remain sparsely populated. In Sweden, we are talking about 88.2% (2021) of the total population living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 1.657 million, Stockholm (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Companies of global importance, including Volvo, Saab, SFK, and Ericsson. Highly developed infrastructure. Up-to-date technology. Skilled workforce.
The swedens small, open, and competitive economy has been thriving, and Sweden has achieved a desirable standard of living with its combination of free-market capitalism and extensive welfare benefits. Sweden remains outside the eurozone mainly out of concern that joining the European Economic and Monetary Union would diminish the country’s sovereignty over its welfare system. Timber, hydropower, and iron ore constitute the resource base of a manufacturing economy that relies heavily on foreign trade. Exports, including engines and other machines, motor vehicles, and telecommunications equipment, account for more than 44% of GDP. Sweden enjoys a current account surplus of about 5% of GDP, which is one of the highest margins in Europe. GDP grew an estimated 3.3% in 2016 and 2017, mainly driven by investment in the construction sector. Swedish economists expect economic growth to ease slightly in the coming years as this investment subsides. Global economic growth boosted exports of Swedish manufacturers further, helping drive domestic economic growth in 2017. The Central Bank is keeping an eye on deflationary pressures, and bank observers expected it to maintain an expansionary monetary policy in 2018. Swedish prices and wages have grown only slightly over the past few years, helping to support the country’s competitiveness. In the short and medium term, Sweden’s economic challenges include providing affordable housing and successfully integrating migrants into the labor market.
Sweden is rich in the following natural resources: Iron ore, copper, lead, zinc, gold, silver, tungsten, uranium, arsenic, feldspar, timber, and hydropower.
The main industrial sectors are iron and steel, precision equipment (bearings, radio and telephone parts, armaments), wood pulp and paper products, processed foods, and motor vehicles.
The country’s export sectors are robust in cars and vehicle parts, packaged medicines, refined petroleum, broadcasting equipment, and lumber (2019), partnering with these nations: Germany 10%, Norway 9%, United States 8%, Denmark 7%, Finland 6%, United Kingdom 5%, Netherlands 5%, China 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $240.08 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Sweden’s position of 26.
Land use in Sweden: 68.7% (2018 estimate) forest, 23.8% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 6.4% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 7.5% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 1.1% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 1,640 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Sweden are wheat, milk, sugar beet, barley, potatoes, oats, rapeseed, pork, rye, and triticale.
The country typically needs to import: cars and vehicle parts, crude petroleum, refined petroleum, broadcasting equipment, and computers (2019), partnering with the following nations: Germany 18%, Netherlands 9%, Denmark 7%, Norway 7%, China 6%, Finland 5%, Belgium 5%, Poland 5% (2019) in a sum value of $217.68 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $232.81 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $241.53 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Sweden 28.
Sweden Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Sweden, Northern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, Gulf of Bothnia, Kattegat, and Skagerrak, between Finland and Norway. We published some basic information about its capital Stockholm, and the Swedish nation.
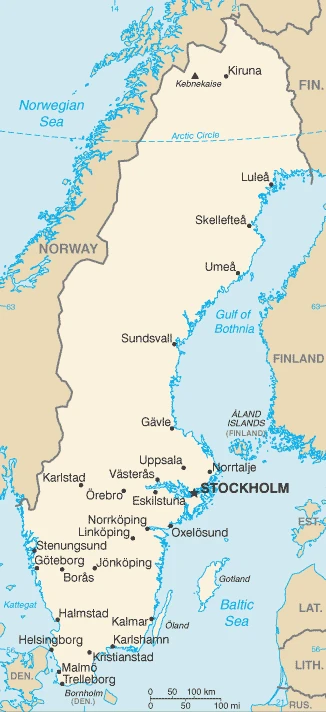
Are you interested in visiting Sweden and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Sweden below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Sweden
Did you know about Sweden?
Sweden is a country in Northern Europe. It has a long coastline and is bordered by Norway and Finland on the east. Sweden’s capital city is Stockholm, which sits on 14 islands. Stockholm is known for its famous landmarks like the Royal Palace, the Royal Opera House, and the Globe Theatre. Despite being cold much of the year (the average temperature in winter is 10 degrees Fahrenheit), Sweden has a rich cultural heritage.
Did you know that Sweden is the best country for human rights? The government has created a “gender-equal” society where women and men are given equal opportunities. Workers are paid fairly, and maternity leave is offered for up to 16 months in health care.
After virtually visiting Sweden, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Finland and Norway.
If you liked our Google map and Sweden information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.