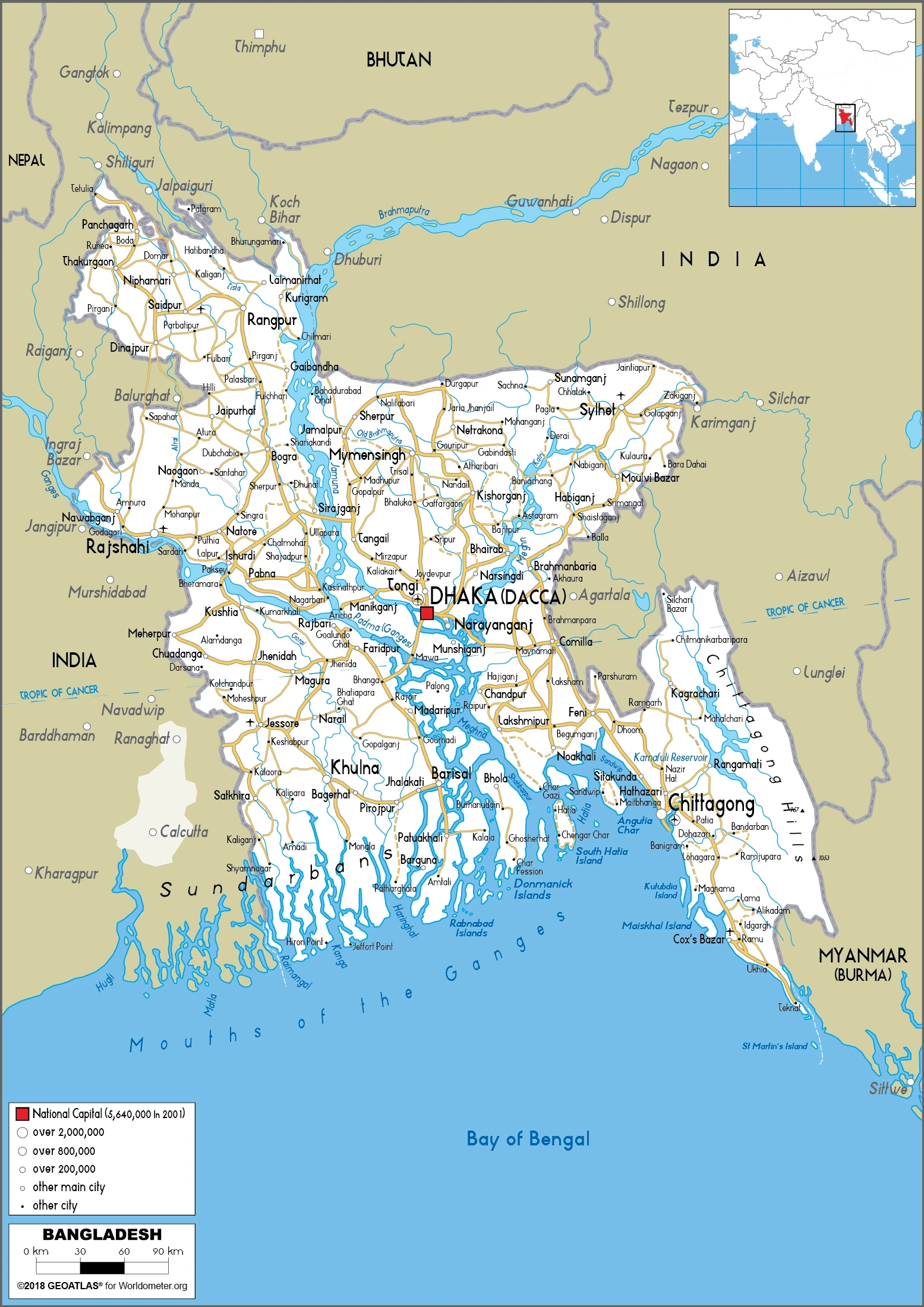
Bangladesh Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Bangladesh, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Bangladesh, Asia (22 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Dhaka, bordering countries like Burma, India, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Asian state.
Quick links: Google maps Bangladesh, Dhaka Google maps, Driving Directions Bangladesh, Printable Road Map.

About Bangladesh in a nutshell
- Torrential monsoon rains flood two-thirds of the country every year.
- Conventional short form of the name: Bangladesh
- The conventional long form of the name: Peoples Republic of Bangladesh
- Local long form: Gana Prajatantri Bangladesh
- Local short form: Bangladesh
- Former name(s): East Bengal, East Pakistan
- Etymology: the name – a compound of the Bengali words Bangla (Bengal) and desh (country) – means Country of Bengal.
- The legal system in Bangladesh: mixed legal system of mostly English common law and Islamic law.
- Climate: Hot and humid. During the monsoon, water levels can rise 20 ft (6 m) above sea level.
- The national symbols are Bengal tiger, water lily; national colors: green, red.
- Internet TLD: .bd
Background
The huge delta region formed at the confluence of the Ganges and Brahmaputra River systems – now referred to as Bangladesh – was a loosely incorporated outpost of various empires centered on the Gangetic plain for much of the first millennium A.D. Muslim conversions and settlement in the region began in the 10th century, primarily from Arab and Persian traders and preachers. Europeans established trading posts in the area in the 16th century.
Eventually, the area known as Bengal, primarily Hindu in the western section and predominantly Muslim in the eastern half, became part of British India. Partition in 1947 resulted in an eastern wing of Pakistan in the Muslim-majority area, which became East Pakistan. Calls for greater autonomy and animosity between Pakistan’s eastern and western wings led to a Bengali independence movement. That movement, led by the Awami League (A.L.) and supported by India, won the independence war for Bangladesh in 1971. The post-independence A.L. government faced daunting challenges, and in 1975 it was overthrown by the military, triggering a series of military coups that resulted in a military-backed government and subsequent creation of the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) 1978. That government also ended in a coup in 1981, followed by military-backed rule until democratic elections occurred in 1991. The BNP and A.L. have alternated in power since 1991, except for a military-backed, emergency caretaker regime that suspended parliamentary elections planned for January 2007 to reform the political system and root out corruption. That government returned the country to fully democratic rule in December 2008 with the election of the A.L. and Prime Minister Sheikh HASINA.
In January 2014, the incumbent A.L. won the national election by an overwhelming majority after the BNP boycotted the election, which extended Hasina’s term as prime minister. In December 2018, HASINA secured a third consecutive term (fourth overall), with the A.L. coalition securing 96% of available seats amid widespread claims of election irregularities. With the help of international development assistance, Bangladesh has reduced the poverty rate from over half of the population to less than a third, achieved Millennium Development Goals for maternal and child health, and made significant progress in food security since independence. The economy has grown at an annual average of about 6% for the last two decades, and the country reached World Bank’s lower-middle-income status in 2014.
Geography
Mostly flat alluvial plains and deltas of the Brahmaputra and Ganges rivers. Southeast coasts are fringed with mangrove forests.
Bangladesh lies at the north end of the Bay of Bengal and frequently suffers devastating floods, cyclones, and famine. It seceded from Pakistan in 1971.
This state is located in Southern Asia, bordering the Bay of Bengal, between Burma and India, under the coordinates of 24 00 N, 90 00 E, covering an area of 148 460 sq km with a coastline of 580 km. Bangladesh is slightly larger than Pennsylvania, and New Jersey combined; slightly smaller than Iowa.
Bangladesh has 4,413 km of land boundaries in total, and bordering with (2 nations): Burma 271 km, India 4142 km.
Mostly flat alluvial plain, hilly in the southeast, with 986 m as the highest point of Bangladesh, while lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m as the lowest point. With a total of 148 460 sq km, Bangladesh has 130 170 sq km of land and 18,290 sq km water surface area.
The principal rivers are Brahmaputra river mouth (shared with China s and India) – 3,969 km, Gange’s river mouth (shared with India s) – 2,704 km. The significant watersheds for Bangladesh are Indian Ocean drainage: Brahmaputra (651,335 sq km) Ganges (1,016,124 sq km).
Most of the country is situated on deltas of large rivers flowing from the Himalayas: the Ganges unites with the Jamuna (main channel of the Brahmaputra) and later joins the Meghna to empty into the Bay of Bengal eventually.
The climate in Bangladesh is as follows: Tropical, mild winter (October to March), hot, humid summer (March to June), humid, warm rainy monsoon (June to October).
When you visit Bangladesh, the natural hazards shall be considered: Droughts cyclones; much of the country is routinely inundated during the summer monsoon season.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Bangladesh: degree of risk: high (2020), bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever, dengue fever, and malaria are high risks in some locations, leptospirosis, rabies.
Current environmental issues affecting the Bangladeshi people: many people are landless and forced to live on and cultivate flood-prone land; waterborne diseases prevalent in surface water; water pollution, especially of fishing areas, results from the use of commercial pesticides; groundwater contaminated by naturally occurring arsenic; intermittent water shortages because of falling water tables in the northern and central parts of the country; soil degradation and erosion; deforestation; destruction of wetlands; severe overpopulation with noise pollution.
Google maps Bangladesh
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Dhaka found under the coordinates 23 43 N, 90 24 E, applying the time zone UTC+6 (11 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Dhaka is a large city in Bangladesh and is one of the most populated cities in the world. It’s surrounded by the major rivers of Padma and Buriganga; about 70% of Dhaka’s population lives near these two rivers. Dhaka is considered among the best places for living in the country.
Bangladesh became independent on 16 December 1971 (from Pakistan), and its national holiday is Independence Day, 26 March (1971); Victory Day, 16 December (1971);.
Administrative divisions: 8 divisions; Barishal, Chattogram, Dhaka, Khulna, Mymensingh, Rajshahi, Rangpur, Sylhet.
People and society
After a period of military rule, Bangladesh returned to democracy in 1991; however, political instability has continued, corruption is a significant problem. A third of the population lives in poverty, but living standards improve. Women are prominent in politics, but their rights are neglected.
The population in Bangladesh is 164,098,818 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 0.95% (2021 estimate) change. That means Bangladesh is the No. 8 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 27.9 years median age (27.1 years for males and 27.1 years for women), Bangladesh ranks No. 143 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Bangladeshi(s) (noun) or Bangladeshi (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Bengali at least 98%, other indigenous ethnic groups 1.1% (2011 estimate). Note: Bangladesh’s government recognizes 27 indigenous ethnic groups under the 2010 Cultural Institution for Small Anthropological Groups Act; other sources estimate there are about 75 ethnic groups; critics of the 2011 census claim that it underestimates the size of Bangladesh’s ethnic population.
They speak Bangla 98.8% (official language, also known as Bengali), other 1.2% (2011 estimate) languages and practice the following religions: Muslim 89.1%, Hindu 10%, other 0.9% (includes Buddhist, Christian) (2013 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Bangladesh: N/A In Bangladesh, we are talking about 38.9% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 21.741 million, Dhaka (capital city), 5.133 million, Chittagong, 949,000 Khulna, 924,000 Rajshahi, 890,000 Sylhet, Bogra 820,000 (2021).
Industry
Agriculture is vulnerable to unpredictable climate. Bangladesh accounts for 80% of world jute fiber exports. Poor infrastructure deters investment. Growing textile industry.
Bangladesh’s economy has grown roughly 6% per year since 2005 despite prolonged periods of political instability, poor infrastructure, endemic corruption, insufficient power supplies, and slow implementation of economic reforms. Although more than half of GDP is generated through the services sector, almost half of Bangladeshis are employed in the agriculture sector, with rice as the single-most-important product., Garments, the backbone of Bangladesh’s industrial sector, accounted for more than 80% of total exports in F.Y. 2016-17. The industrial sector continues to grow, despite the need for improvements in factory safety conditions. Steady export growth in the garment sector, combined with $13 billion in remittances from overseas Bangladeshis, contributed to Bangladesh’s rising foreign exchange reserves in F.Y. 2016-17. Recent improvements to energy infrastructure, including the start of liquefied natural gas imports in 2018, represent a significant step forward in resolving a critical growth bottleneck.
Bangladesh is rich in natural gas, arable land, timber, coal.
The main industrial sectors are typically jute, cotton, garments, paper, leather, fertilizer, iron, and steel, cement, petroleum products, tobacco, pharmaceuticals, ceramics, tea, salt, sugar, edible oils, soap and detergent, fabricated metal products, electricity, natural gas.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in clothing, knitwear, leather footwear (2019), partnering with these nations: the United States 15%, Germany 14%, United Kingdom 8%, Spain 7%, France 7% (2019). The export trade resulted in $38.78 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Bangladesh’s position of 66.
Land use in Bangladesh: 11.1% (2018 estimate) forest, 18.8% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 59% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 70.1% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 6.5% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 4.6% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 53,000 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Bangladesh are rice, potatoes, maize, sugar cane, milk, vegetables, onions, jute, mangoes/guavas, wheat.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, cotton, natural gas, scrap iron, wheat (2019), partnering with the following nations: China 31%, India 15%, Singapore 5% (2019) in a sum value of $57.26 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $64.23 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $65.59 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Bangladesh 54.
Bangladesh Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Bangladesh, Southern Asia, bordering the Bay of Bengal, between Burma and India. We published some basic information about its capital Dhaka, and the Bangladeshi nation.
Are you interested in visiting Bangladesh and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Bangladesh below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Bangladesh
Did you know about Bangladesh?
You’ve probably heard about the Rohingya refugee crisis in Bangladesh. Hundreds of thousands of Rohingyas fled Myanmar for Bangladesh in what is now considered one of the largest mass migrations in recent years. Around 650,000 people are left homeless in this humanitarian disaster.
After virtually visiting Bangladesh, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Myanmar (Burma) and India.
If you liked our Google map and Bangladesh information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.