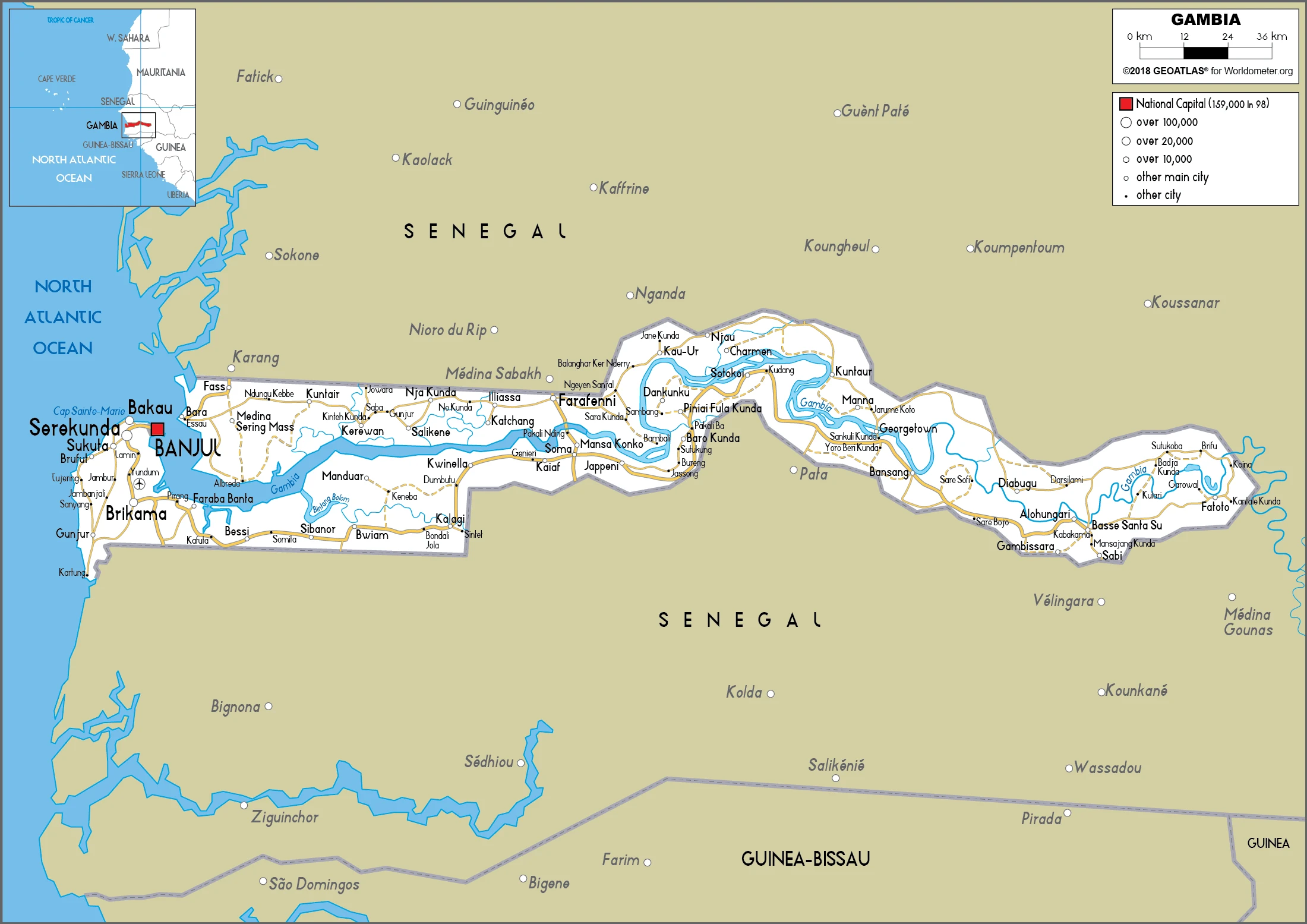
Gambia Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like the Gambia, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to the Gambia, Africa (54 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Banjul, bordering countries like Senegal, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this African state.
Quick links: Google maps Gambia, Banjul Google maps, Driving Directions Gambia, Printable Road Map.

About Gambia in a nutshell
- Overfishing in the waters off Gambia and Senegal, mainly by foreign vessels, is a growing problem.
- Conventional short form of the name: The Gambia
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of The Gambia
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: named for the Gambia River that flows through the heart of the country.
- The legal system in Gambia: mixed legal system of English common law, Islamic law, and customary law.
- Climate: Subtropical, with wet, humid months JulyOctober, and warm, dry season NovemberMay.
- The national symbols are lion; national colors: red, blue, green, white.
- Internet TLD: .gm
The ‘Mesopotamia’ of West Africa, sandwiched between three rivers, Senegal boasts two natural and three cultural World Heritage sites. The wetland of the Djoudj Bird Reserve in the Senegal River delta is one of the largest bird reserves in Africa: a resting place for three million migratory birds each year and a breeding ground for a variety of waterfowl. The Niokolo-Koba National Park, along the Senegal stretch of the Gambia River, is the last refuge for the distinctive wildlife of the West African savannah. Gorée Island, opposite Dakar, was the major center of the slave trade between the 15th and 19th centuries. The French colony founded in the 17th century, Saint-Louis, which grew into a city in two centuries, was the country’s capital from 1872 to 1857. The stone circles and monoliths found in about 100 km2 in the center of the tiny Gambia, which is nestled in the body of Senegal along the Gambia River, are relics of a 1500-year-old culture and a World Heritage site shared with Senegal. James Island and five other sites on the river are sad reminders of the slave trade.
Background
In the 10th century, Muslim merchants established The Gambia’s earliest large settlements as trans-Saharan trade hubs. These settlements eventually grew into significant export centers sending enslaved people, gold, and ivory across the Sahara. Between the 16th and 17th centuries, European colonial powers began establishing trade with The Gambia. In 1664, the United Kingdom established a colony in The Gambia focused on exporting enslaved people across the Atlantic. During the roughly 300 years of the trans-Atlantic slave trade, the UK and other European powers may have exported as many as 3 million people from The Gambia.
In 1965, The Gambia gained its independence from the UK. Geographically surrounded by Senegal, it formed the short-lived confederation of Senegambia between 1982 and 1989. In 1994, Yahya JAMMEH led a military coup overthrowing the president and banning political activity. JAMMEH won every presidential election until 2016. In December 2016, after 22 years of authoritarian rule, President JAMMEH lost to Adama BARROW during free and fair elections. Due to The Gambia’s poor human rights record under JAMMEH, international development partners had substantially reduced aid to the country. These channels have now reopened under the administration of President BARROW. Since the 2016 election, The Gambia and the US have enjoyed improved relations. US assistance has supported military education and training programs, capacity building, and democracy-strengthening activities.
Geography
Located on the narrow strip of land bordering the Gambia River. Long, sandy beaches are backed by mangrove swamps along the river. Savanna and tropical forests are higher up.
The Gambia is a riverbank state on the west coast of Africa, almost surrounded by Senegal. It was renowned for its stability until its government was overthrown in a coup in 1994.
This state is located in Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean and Senegal, under the coordinates of 13 28 N, 16 34 W, covering an area of 11,300 sq km with a coastline of 80 km. The Gambia is slightly less than twice the size of Delaware.
The Gambia has 749 km of land boundaries in total and borders with (1 nation): Senegal 749 km.
The flood plain of the Gambia River is flanked by some low hills, with an Unnamed elevation of 53 m as the highest point of Gambia, while lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at a mean elevation: 34 m throughout the country. With a total of 11,300 sq km, Gambia has 10,120 sq km of land and 1,180 sq km water surface area.
The principal river is the Gambia river mouth (shared with Senegal and Guinea) – 1,094 km.
Almost an enclave of Senegal, the smallest country on the African mainland.
The climate in the Gambia is as follows: Tropical, hot, rainy season (June to November), more relaxed, dry season (November to May).
When you visit the Gambia, the natural hazards are droughts.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting the Gambia: degree of risk: very high (2020), bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, typhoid fever, malaria, and dengue fever, schistosomiasis, rabies, meningococcal meningitis.
Current environmental issues affecting the Gambian people: deforestation due to slash-and-burn agriculture; desertification; water pollution; water-borne diseases.
Google maps Gambia
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Banjul found under the coordinates 13 27 N, 16 34 W, applying the time zone UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
The capital of Gambia, Banjul, is a bustling city where the streets are clogged with motorbikes and pedestrians. But despite its busyness, people come from all over the world to visit its magnificent beaches, castles, and museums.
Gambia became independent on 18 February 1965 (from the UK), and its national holiday is Independence Day, 18 February (1965).
Administrative divisions: 5 regions, 1 city, and 1 municipality; Banjul, Central River, Kanifing, Lower River, North Bank, Upper River, West Coast.
People and society
Little tension between various ethnic groups. The largest group, the Mandinka, has traditionally held power. Islam is a strong social influence, though there is no official state religion. A small expatriate community from the UK lives on the coast. Seasonal migrants come from neighboring states to harvest groundnuts each year. Women are active as traders. Yahya Jammeh, who led the 1994 coup, is still the elected president.
The population in the Gambia is 2,221,301 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 1.82% (2021 estimate) change. That means the Gambia is the No. 146 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 21.8 years median age (21.5 years for males and 21.5 years for women), Gambia ranks No. 182 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Gambian(s) (noun) or Gambian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Mandinka/Jahanka 34%, Fulani/Tukulur/Lorobo 22.4%, Wolof 12.6%, Jola/Karoninka 10.7%, Serahuleh 6.6%, Serer 3.2%, Manjago 2.1%, Bambara 1%, Creole/Aku Marabout 0.7%, other 0.9%, non-Gambian 5.2%, no answer 0.6% (2013 estimate).
They speak English (official language), Mandinka, Wolof, Fula, other indigenous vernaculars languages and practice the following religions: Muslim 95.7%, Christian 4.2%, none 0.1%, no response 0.1% (2013 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in the Gambia: Settlements are found scattered along the Gambia River. The largest communities, including the capital of Banjul, and the country’s largest city, Serekunda, are found at the mouth of the Gambia river along the Atlantic coast, as shown in this population distribution map. In the Gambia, we are talking about 63.2% (2021) of the total population is living in cities.
Industry
Around 75% of the labor force is involved in agriculture. Groundnuts are the principal crop. Fish stocks are declining. Eco-tourism is promoted, though most visitors come for the beaches. Banjul is one of west Africas finest deepwater ports: significant re-export trade. Smuggling problems.
The government has invested in the agriculture sector because three-quarters of the population depends on the sector for its livelihood. Agriculture provides about one-third of GDP, making The Gambia largely reliant on sufficient rainfall. The agricultural sector has untapped potential – less than half of arable land is cultivated, and agricultural productivity is low. Small-scale manufacturing activity features the processing of cashews, groundnuts, fish, and hides. The Gambia’s re-export trade accounts for almost 80% of goods exports, and China has been its largest trade partner for exports and imports for several years. The Gambia has sparse natural resource deposits. It relies heavily on remittances from workers overseas and tourist receipts. Remittance inflows to The Gambia amount to about one-fifth of the country’s GDP.
The Gambia’s location on the ocean and proximity to Europe has made it one of the most frequented tourist destinations in West Africa, boosted by private sector investments in eco-tourism and facilities. Tourism typically brings in about 20% of GDP, but it suffered in 2014 from tourists’ fears of the Ebola virus in neighboring West African countries. Unemployment and underemployment remain high. Economic progress depends on sustained bilateral and multilateral aid, responsible government economic management, and continued technical assistance from multilateral and bilateral donors. International donors and lenders were concerned about the quality of fiscal management under the administration of former President Yahya JAMMEH, who reportedly stole hundreds of millions of dollars of the country’s funds during his 22 years in power, but anticipate significant improvements under the new administration of President Adama BARROW, who assumed power in early 2017.
As of April 2017, the IMF, the World Bank, the European Union, and the African Development Bank were all negotiating with the new government of The Gambia to provide financial support in the coming months to ease the country’s financial crisis. The country faces a limited availability of foreign exchange, weak agricultural output, a border closure with Senegal, a slowdown in tourism, high inflation, a large fiscal deficit, and a high domestic debt burden that has crowded out the private sector investment-driven interest rates to new highs. The government has committed to reducing the deficit, including through expenditure caps, debt consolidation, and reform of state-owned enterprises.
The Gambia is rich in the following natural resources: Fish, clay, silica sand, titanium (rutile and ilmenite), tin, zircon.
The main industrial sectors are typically peanuts, fish, hides, tourism, beverages, agricultural machinery assembly, woodworking, metalworking, clothing.
The country’s export sectors are influential in lumber, cashews, refined petroleum, fish oil, groundnut oil (2019), partnering with these nations: China 38%, India 22%, Mali 7%, Chile 5% (2017). The export trade resulted in $350 million. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Gambia’s position of 198.
Land use in Gambia: 43.9% (2018 estimate) forest, 0% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 41% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 56.1% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.5% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture permanent pasture: 14.6% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 50 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Gambia are groundnuts, milk, oil palm fruit, millet, sorghum, rice, maize, vegetables, cassava, fruit.
The country typically needs to import: clothing and apparel, refined petroleum, rice, raw sugar, palm oil (2019), partnering with the following nations: China 33%, India 10%, Senegal 5%, Brazil 5% (2019) in a sum value of $620 million. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate) $851 million (2018 estimate) $754 million (2017 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Gambia 198.
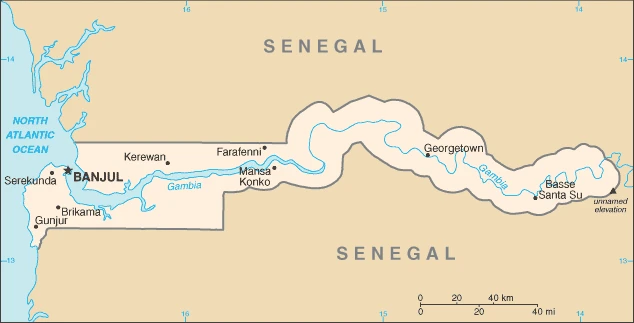
Gambia Driving Directions
You learned about Gambia, Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, and Senegal in this post. We published some basic information about its capital Banjul, and the Gambian nation.
Are you interested in visiting the Gambia and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of the Gambia below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Gambia
Did you know about Gambia?
Indigenous peoples initially inhabited it, later joined by African and Arab traders. Today, it is a nation of 18 million people living on the edge of the Sahara Desert with a medieval style of government that includes an emir and a sultan. In addition to being rich in natural resources, Gambia’s trade in minerals has made it one of the wealthiest nations per capita.
After virtually visiting the Gambia, you may also be interested in the neighboring country: Senegal.
If you liked our Google map and the Gambia information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.