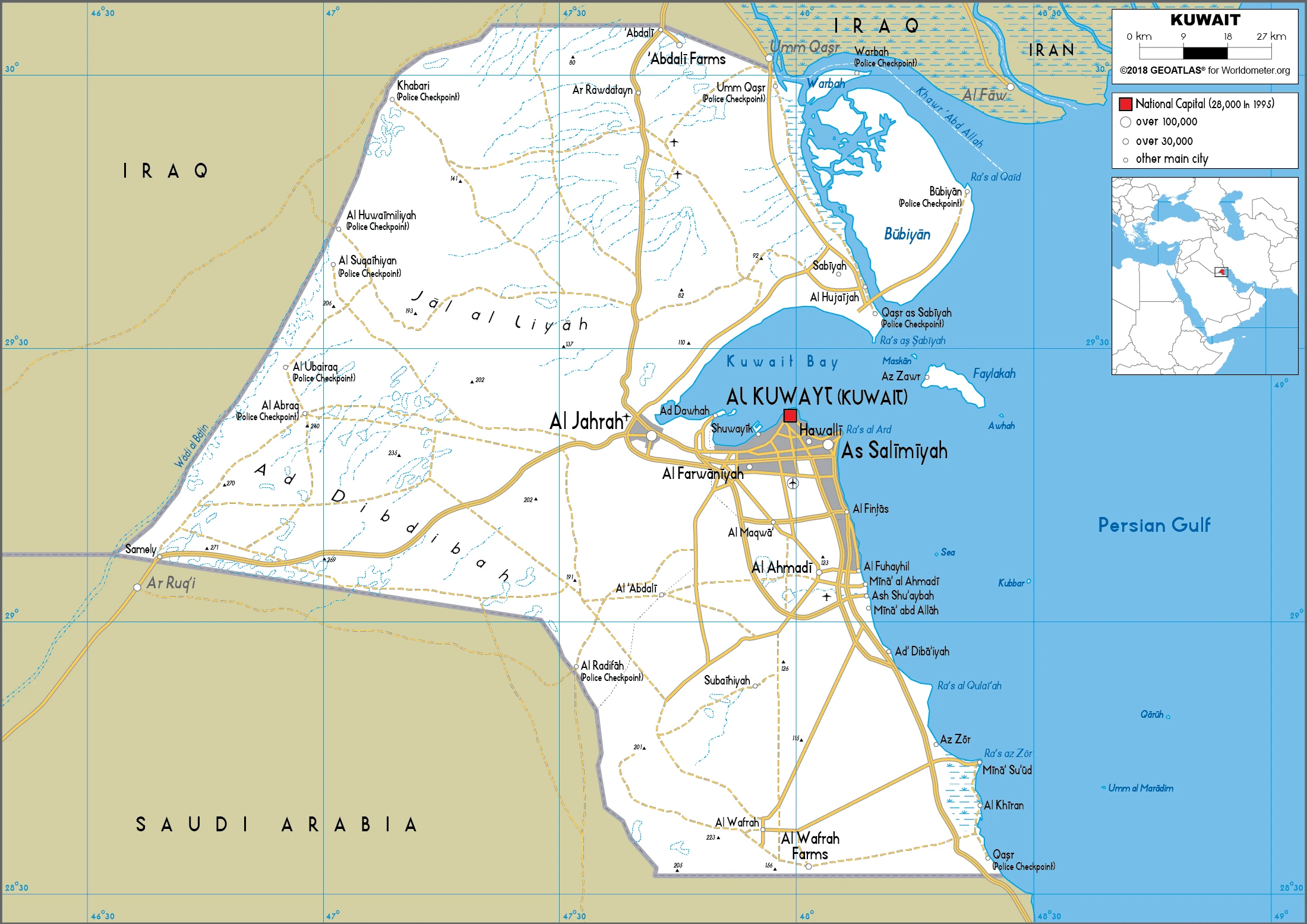
Kuwait Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Kuwait, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Kuwait, Middle East (19 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Kuwait City, bordering countries like Iraq Saudi Arabia, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Middle Eastern state.
Quick links: Google Maps Kuwait, Kuwait City Google maps, Driving Directions Kuwait, Printable Road Map.

About Kuwait in a nutshell
- During the 1991 Gulf War, Iraq deliberately set fire to 800 of Kuwaits 950 oil wells.
- Conventional short form of the name: Kuwait
- The conventional long form of the name: State of Kuwait
- Local long form: Dawlat al Kuwayt
- Local short form: Al Kuwayt
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: the name derives from the capital city, which is from Arabic al-Kuwayt a diminutive of kut meaning fortress, possibly a reference to a small castle built on the current location of Kuwait City by the Beni Khaled tribe in the 17th century.
- The legal system in Kuwait: mixed legal system consisting of English common law, French civil law, and Islamic sharia law.
- Climate: Summers are very hot and dry. Winters are cooler, with some rain and occasional frost at night.
- The national symbols are golden falcon; national colors: green, white, red, black.
- Internet TLD: .kw
The site of the tales of the Arabian Nights, the adventures of Sinbad, the Persian Gulf has been inhabited for thousands of years. From here, around the bay, the Persians and Arabs, the seafaring merchant peoples, set out to explore the markets of Asia and Africa and populated the East African coast. The archaeological site of Qal’at al-Bahrain is full of character: an artificial mound in which cultures from several eras have been superimposed, from 2300 BC to the 16th century AD. A Portuguese fortress was built on the 12 m high, 300 m x 600 m mounds. Here was the capital of the ancient Dilmun civilization, known until now only from Sumerian documents. The bay has always been a symbol of wealth and splendor. The discovery of oil and gas in the 20th century, which soon became indispensable throughout the world, has enabled the citizens of the Gulf countries to amass tremendous wealth. The ‘indigenous’ aristocracy, descendants of nomadic Bedouin Arabs, which has created an extremely high standard of living, tax-free, free healthcare and education, has a strange problem: unemployment. Few countries in the world can claim to have only one in five of their people: Kuwait, Qatar, Bahrain, and the United Arab Emirates have Asian migrant workers to thank for this strange record.
Background
The AL-SABAH dynasty has ruled Kuwait since the 18th century. The threat of Ottoman invasion in 1899 prompted Amir Mubarak AL-SABAH to seek protection from Britain, ceding foreign and defense responsibility to Britain until 1961 when the country attained its independence. Kuwait was attacked and overrun by Iraq in August 1990. Following several weeks of aerial bombardment, a US-led UN coalition began a ground assault in February 1991 that liberated Kuwait in four days. In 1992, the Amir reconstituted the parliament that he had dissolved in 1986. Amid the 2010-11 uprisings and protests across the Arab world, stateless Arabs, known as Bidoon, staged small protests in early 2011 demanding citizenship, jobs, and other benefits available to Kuwaiti nationals.
Other demographic groups, notably Islamists and Kuwaitis from tribal backgrounds, soon joined the growing protest movements, culminating in late 2011 with the prime minister’s resignation amidst allegations of corruption. Demonstrations were renewed in late 2012 in response to an Amiri decree amending the electoral law that lessened the voting power of the tribal blocs. An opposition coalition of Sunni Islamists, tribal populists, and some liberals largely boycotted legislative elections in 2012 and 2013, which ushered in a legislature more amenable to the government’s agenda. Faced with the prospect of painful subsidy cuts, oppositionists and independents actively participated in the November 2016 election, winning nearly half of the seats. Still, a cohesive opposition alliance largely ceased with the 2016 election, and the opposition became increasingly factionalized. Since coming to power in 2006, the Amir has dissolved the National Assembly on seven occasions (the Constitutional Court annulled the Assembly elections in June 2012 and again in June 2013) and shuffled the cabinet over a dozen times, usually citing political stagnation and gridlock between the legislature and the government.
Geography
The terrain is a low-lying desert. The lowest land is in the north. Cultivation is only possible along the coast.
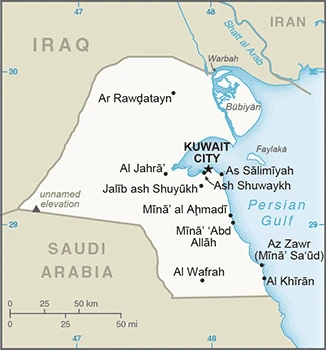
Kuwait lies at the northwest tip of the Gulf, dwarfed by its neighbors Iraq, Iran, and Saudi Arabia. It was a British protectorate until 1961, when complete independence was granted.
This state is located in the Middle East, bordering the Persian Gulf, between Iraq and Saudi Arabia, under the coordinates of 29 30 N, 45 45 E, covering an area of 17,818 sq km with a coastline of 499 km. Kuwait is Slightly smaller than New Jersey.
Kuwait has 475 km of land boundaries in total, and bordering with (2 nations): Iraq 254 km, Saudi Arabia 221 km.
Flat to slightly undulating desert plain, with 3.6 Km w. Of al-salmi border post 300 m as the highest point of Kuwait, while Persian Gulf 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 108 m throughout the country. With a total of 17,818 sq km, Kuwait has 17,818 sq km of land and 0 sq km water surface area.
The significant watersheds for Kuwait are the Indian Ocean drainage: (Persian Gulf), Tigris, and Euphrates (918,044 sq km).
Strategic location at the head of the Persian Gulf.
The climate in Kuwait is as follows: Desert, intensely hot summers, short, cool winters.
When you visit Kuwait, the natural hazards shall be considered: Sudden cloudbursts are common from October to April and bring heavy rain, damaging roads, and houses; sandstorms and dust storms occur throughout the year but are most common between March and August.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Kuwait: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Kuwaiti people: limited natural fresh water resources; some of the world’s most extensive and most sophisticated desalination facilities provide much of the water; air and water pollution; desertification; loss of biodiversity.
Google Maps Kuwait
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Kuwait City found under the coordinates 29 22 N, 47 58 E, applying the time zone UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Kuwait City is the capital of Kuwait, located in the north-central part of the country. The city was founded on 25 July 1765 by Sheikh Al Mubarak Al Sabah I and given its current name to honor his achievements. Kuwait consists of Ras el Ain, a narrow peninsula jutting out into the Persian Gulf, and Al Jahra Island, three natural islands off Kuwait’s northern coast. The city has an estimated population of 2 million people.
Kuwait became independent on 19 June 1961 (from the UK), and its national holiday is National Day, 25 February (1950).
Administrative divisions: 6 governorates (muhafazat, singular – muhafazah); Al Ahmadi, Al Asimah, Al Farwaniyah, Al Jahra, Hawalli, Mubarak al Kabir.
People and society
Oil-rich monarchy, ruled by the al-Sabah family. It is a conservative Sunni Muslim society, but women are relatively free. Nonetheless, Islamic traditionalists blocked a 1999 decree giving women the vote for six years in parliament. Immigrant workers from other Arab states, India, and Pakistan, now outnumber native citizens. US-led forces rescued Kuwait after the 1990 Iraqi invasion and later used it as a launchpad for the 2003 invasion to oust Saddam Hussein.
The population in Kuwait is 3,032,065 (July 2021 estimate). Note: Kuwait’s Public Authority for Civil Information estimates the country’s total population to be 4,420,110 for 2019, with non-Kuwaitis accounting for nearly 70% of the population, with an average of 1.2% (2021 estimate) change. That means Kuwait is the No. 137 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 29.7 years median age (30.7 years for males and 30.7 years for women), Kuwait ranks No. 127 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Kuwaiti(s) (noun) or Kuwaiti (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Kuwaiti 30.4%, other Arab 27.4%, Asian 40.3%, African 1%, other 0.9% (includes European, North American, South American, and Australian) (2018 estimate).
They speak Arabic (official language), English widely spoken languages and practice the following religions: Muslim (official) 74.6%, Christian 18.2%, other and unspecified 7.2% (2013 estimate) note: data represent the total population; about 69% of the population consists of immigrants.
We can conclude the following about the population in Kuwait: Densest settlement is along the Persian Gulf, particularly in Kuwait city and on Bubiyan Island. Significant population threads extend south and west along highways that radiate from the capital, particularly in the country’s southern half. In Kuwait, we are talking about 100% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 3.177 million, Kuwait (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Oil and natural gas dominate the economy. Skilled workforce, raw materials, and food are imported. High standard of living. Financial services: stock market lost 40% of its value in 2008.
Kuwait is geographically tiny but wealthy, relatively open, with about 102 billion barrels – more than 6% of world reserves. Kuwaiti officials plan to increase production to 4 million barrels of oil equivalent per day by 2020. Petroleum accounts for over half of GDP, 92% of export revenues, and 90% government income. With world oil prices declining, Kuwait realized a budget deficit in 2015 for the first time more than a decade; in 2016, the deficit grew to 16.5% of GDP. Kuwaiti authorities announced cuts to fuel subsidies in August 2016, provoking outrage among the public and National Assembly, and the Amir dissolved the government for the seventh time in ten years. In 2017 the deficit was reduced to 7.2% of GDP, and the government raised $8 billion by issuing international bonds.
Despite Kuwait’s dependence on oil, the government has cushioned itself against the impact of lower oil prices by saving annually at least 10% of government revenue in the Fund for Future Generations. Kuwait has failed to diversify its economy or bolster the private sector because of a poor business climate, a large public sector that employs about 74% of citizens, and an abusive relationship between the National Assembly and the executive branch that has stymied most economic reforms. The Kuwaiti Government has made little progress on its long-term economic development plan first passed in 2010. While the government planned to spend up to $104 billion over four years to diversify the economy, attract more investment, and boost private sector participation, many projects did not materialize because of an uncertain political situation or delays in awarding contracts. To increase non-oil revenues, the Kuwaiti Government in August 2017 approved draft bills supporting a Gulf Cooperation Council-wide value added tax scheduled to take effect in 2018.
Kuwait is rich in the following natural resources: Petroleum, fish, shrimp, natural gas.
The main industrial sectors are petroleum, petrochemicals, cement, shipbuilding and repair, water desalination, food processing, construction materials.
The country’s export sectors are robust in crude petroleum, refined petroleum, aircraft, natural gas, industrial hydrocarbon products (2019), partnering with these nations: China 20%, South Korea 16%, India 15%, Japan 10%, Taiwan 6%, Vietnam 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $72.83 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Kuwait’s position of 49.
Land use in Kuwait: 0.4% (2018 estimate) forest, 91.1% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 0.6% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 8.5% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.3% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 7.6% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 105 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Kuwait are eggs, dates, tomatoes, cucumbers, poultry, milk, mutton, potatoes, vegetables, eggplants.
The country typically needs to import: cars, broadcasting equipment, natural gas, packaged medicines, jewelry (2019), partnering with the following nations: China 14%, United Arab Emirates 12%, United States 10%, Saudi Arabia 6%, Japan 6%, Germany 5%, India 5% (2019) in a sum value of $59.65 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $68.2 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Kuwait 52.
Kuwait Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Kuwait, the Middle East, bordering the Persian Gulf, between Iraq and Saudi Arabia. We published some basic information about its capital Kuwait City and the Kuwaiti nation.
Are you interested in visiting Kuwait and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Kuwait below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Kuwait
Did you know about Kuwait?
Kuwait is situated between Iraq and Saudi Arabia. It’s a small country with just 2.7 million people, making it the 44th most populous globally. Kuwait had its emirate until 1961, when they signed an agreement to share power with Iraq. They joined the United Nations in 1963, but they have never been recognized as an independent state and are still considered part of Iraq.
After virtually visiting Kuwait, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Iraq, Saudi Arabia.
If you liked our Google map and Kuwait information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.