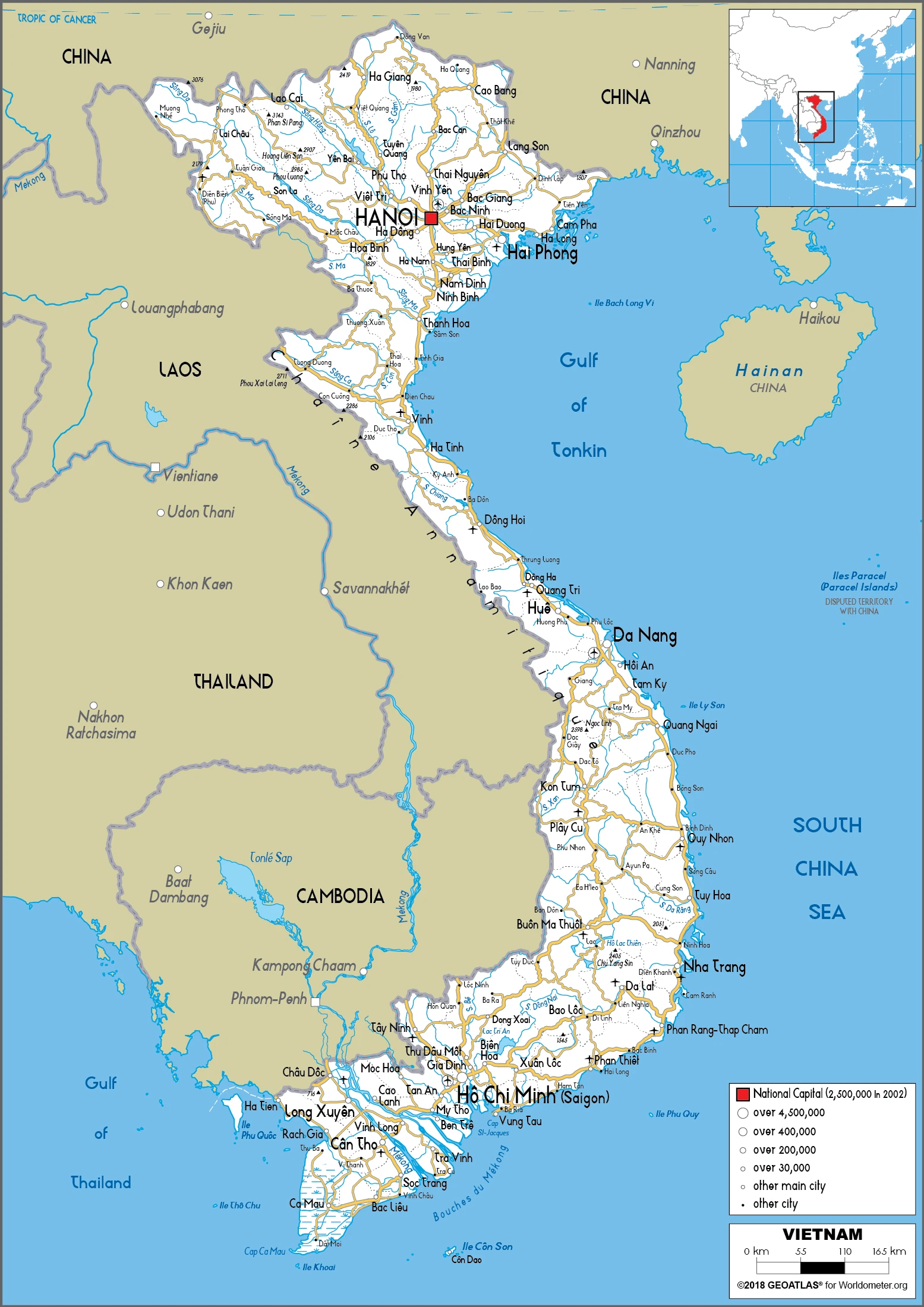
Vietnam Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Vietnam, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Vietnam, Southeast Asia (19 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Hanoi (Ha Noi), bordering countries like Cambodia, China, Laos, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Southeastern Asian state.
Quick links: Google Maps Vietnam, Hanoi (Ha Noi) Google maps, Driving Directions Vietnam, Printable Road Map.

About Vietnam in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Vietnam
- The conventional long form of the name: Socialist Republic of Vietnam
- Local long form: Cong Hoa Xa Hoi Chu Nghia Viet Nam
- Local short form: Viet Nam
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: Viet nam translates as Viet south, where Viet is an ethnic self identification dating to a second century B.C. kingdom and nam refers to its location in relation to other Viet kingdoms.
- The legal system in Vietnam: civil law system.
- Climate: Cool winters in north south is tropical, with even temperatures.
- The national symbols are yellow, five-pointed star on red field; lotus blossom; national colors: red, yellow.
- Internet TLD: .vn
Spanning 14 latitudes south of the Tropic of Cancer, Vietnam’s coastline is three-and-a-half times the size of our country and is washed by the waves of the South China Sea. The fertile lowlands of the Mekong Delta in the North and the Red River in the South support a population of more than 80 million people speaking 50 different dialects. Three-quarters of the country is mountainous, with the highest peaks rising to over 3,000m. Among the natural World Heritage sites in the North, the 1,600 karstic island mountains rising from the waters of Ha Long (Dragon) Bay, covered in lush tropical vegetation, are a veritable fairytale. The karstic rocks of Phong Nha-Ke Bang National Park in the central mountainous region of the country bordering Laos are the oldest of their kind in Asia. The park is difficult to access and has a unique fauna, with two new mammal species discovered in the last 15 years. The oldest World Heritage Site is the religious, political, and cultural capital of the Champa Hindu kingdom, My Son, which flourished between the 4th and 13th centuries. The ancient port city of Ho An is an excellent example of a Southeast Asian trading city from the 15th to the 19th centuries. The imperial city of Hui was the seat of the Nguyen dynasty from 1802 to 1945 and the capital of the first reunified Vietnam.
Intense US bombing and defoliant spraying in the 1962-1975 Vietnam War has scarred the landscape.
Background
Ancient Vietnam was centered on the Red River Valley and was under Han Chinese rule until approximately the 10th century. The Ly Dynasty (11th-13th century) ruled the first independent Vietnamese state, known as Dai Viet, and established their capital at Thang Long (Hanoi). Under the Tran Dynasty (13th-15th century), Dai Viet forces led by one of Vietnam’s national heroes, TRAN Hang Dao, fought off Mongol invaders in 1279. Following a brief Chinese occupation in the early 1400s, the leader of Vietnamese resistance, Le Thai To, made himself emperor and established the Le Dynasty, which lasted until the late 18th century, although not without decades of political turmoil, civil war, and division. During this period, Dai Viet expanded southward to the Central Highlands and Mekong Delta, reaching the approximate boundaries of modern-day Vietnam by the 1750s. Dai Viet suffered other civil wars and division in the latter half of the 18th century but was reunited and renamed Vietnam under Emperor NGUYEN Phuc Anh (aka Gia Long) in 1802.
The Nguyen Dynasty would be the last Vietnamese dynasty before the conquest by France, which began in 1858 and was completed by 1884. Vietnam became part of French Indochina in 1887. It declared independence after World War II, but France continued to rule until its 1954 defeat by communist forces under Ho Chi MINH. Under the Geneva Accords of 1954, Vietnam was divided into the communist North and anti-communist South. US economic and military aid to South Vietnam grew through the 1960s to bolster the Government, but US armed forces were withdrawn following a cease-fire agreement in 1973. Two years later, North Vietnamese forces overran the South reuniting the country under communist rule. Despite the return of peace, the country experienced little economic growth for over a decade because of conservative leadership policies, the persecution and mass exodus of individuals – many of them successful South Vietnamese merchants – and growing international isolation. However, since the enactment of the Vietnams doi moi (renovation) policy in 1986, Vietnamese authorities have committed to increased economic liberalization and enacted structural reforms needed to modernize the economy and produce more competitive export-driven industries.
Since its implementation, the economy has seen strong growth, particularly in agricultural and industrial production, construction, exports, and foreign investment. Increased tourism has also become a key component of economic growth. Nevertheless, the Communist Party maintains tight political and social control of the country. The country faces considerable challenges, including rising income inequality, corruption, inadequate social welfare, and a poor human rights record. Despite some tensions with Beijing, particularly over rival claims in the South China Sea, China remains Vietnam’s most important bilateral relationship and is its largest trading partner.
Geography
A heavily forested mountain range separates the northern Red River delta lowlands from the Mekong Delta in the South.
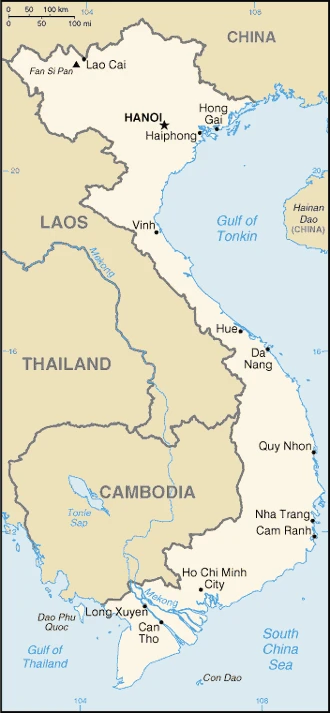
French rule of Vietnam ended in 1954. Divided at 17°N, the US-backed South fought the Communist North. Reunified after the Norths 1975 victory, it is run as a single-party state.
This state is located in Southeastern Asia, bordering the Gulf of Thailand, Gulf of Tonkin, and the South China Sea, as well as China, Laos, and Cambodia, under the coordinates of 16 10 N, 107 50 E, covering an area of 331,210 sq km with a coastline of 3,444 km (excludes islands). Vietnam is About three times the size of Tennessee, slightly larger than New Mexico.
Vietnam has 4,616 km of land boundaries and borders (3 nations): Cambodia 1158 km, China 1297 km, Laos 2161 km.
Low, flat delta in south and north, central highlands, hilly, mountainous in far north and northwest, with Fan si pan 3,144 m as the highest point of Vietnam, while the South China Sea 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 398 m throughout the country. With a total of 331,210 sq km, Vietnam has 310,070 sq km of land and 21,140 sq km of water surface area.
The principal rivers are Mekong (shared with Burma, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia, and China) – 4,350 km, Pearl (shared with China) – 2,200 km, and Red (shared with China) – 1,149 km. The significant watersheds for Vietnam are Pacific Ocean drainage: Mekong (805,604 sq km).
The climate in Vietnam is as follows: Tropical in the South, monsoonal in the North with the hot, rainy season (May to September), and a warm, dry season (October to March).
When you visit Vietnam, the natural hazards shall be considered: Occasional typhoons (May to January) with extensive flooding, especially in the Mekong river delta.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Vietnam: degree of risk: very high (2020), bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, typhoid fever, dengue fever, malaria, and Japanese encephalitis.
Current environmental issues affecting the Vietnamese people: logging and slash-and-burn agricultural practices contribute to deforestation and soil degradation; water pollution and overfishing threaten marine life populations; groundwater contamination limits potable water supply; air pollution; growing urban industrialization and population migration are rapidly degrading the environment in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City.
Google Maps Vietnam
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Hanoi (Ha Noi) found under the coordinates 21 02 N, 105 51 E, applying the time zone UTC+7 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Nowadays, Hanoi is a modern city with many places to visit and explore. It’s famous for its delicious food and old architectural heritage. Hanoi is also home to many beautiful attractions, including the Ho Chi Minh Mausoleum, The Botanical Gardens, and The Temple of Literature. Its location is about halfway between Cham Island in the South, and Ninh Binh Province, in the North.
Vietnam became independent on 2 September 1945 (from France), and its national holiday is Independence Day (National Day), 2 September (1945).
Administrative divisions: 58 provinces (tinh, singular, and plural) and 5 municipalities (thanh pho, singular, and plural) provinces: An Giang, Bac Giang, Bac Kan, Bac Lieu, Bac Ninh, Ba Ria-Vung Tau, Ben Tre, Binh Dinh, Binh Duong, Binh Phuoc, Binh Thuan, Ca Mau, Cao Bang, Dak Lak, Dak Nong, Dien Bien, Dong Nai, Dong Thap, Gia Lai, Ha Giang, Ha Nam, Ha Tinh, Hai Duong, Hau Giang, Hoa Binh, Hung Yen, Khanh Hoa, Kien Giang, Kon Tum, Lai Chau, Lam Dong, Lang Son, Lao Cai, Long An, Nam Dinh, Nghe An, Ninh Binh, Ninh Thuan, Phu Tho, Phu Yen, Quang Binh, Quang Nam, Quang Ngai, Quang Ninh, Quang Tri, Soc Trang, Son La, Tay Ninh, Thai Binh, Thai Nguyen, Thanh Hoa, Thua Thien-Hue, Tien Giang, Tra Vinh, Tuyen Quang, Vinh Long, Vinh Phuc, Yen Bai municipalities: Can Tho, Da Nang, Ha Noi (Hanoi), Hai Phong, Ho Chi Minh City (Saigon).
People and society
Ethnic Vietnamese dominate; the Chinese minority was viewed as a corrupt bourgeoisie by the victorious Communists after the war. Mountain-based minorities (Montagnards) were also sidelined; tensions persisted over highlands settled by lowlanders. Women play an active role in society. There is no political or press freedom.
The population in Vietnam is 102,789,598 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 1% (2021 estimate) change. That means Vietnam is the No. 16 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 31.9 years median age (30.8 years for males and 30.8 years for women), Vietnam ranks No. 112 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Vietnamese (also singular and plural) (noun) or Vietnamese (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Kinh (Viet) 85.3%, Tay 1.9%, Thai 1.9%, Muong 1.5%, Khmer 1.4%, Mong 1.4%, Nung 1.1%, other 5.5% (2019 estimate). Note: the Vietnamese Government recognizes 54 ethnic groups.
They speak Vietnamese (official language), English (increasingly favored as a second language), some French, Chinese, and Khmer, mountain area languages (Mon-Khmer and Malayo-Polynesian) languages and practice the following religions: Catholic 6.1%, Buddhist 5.8%, Protestant 1%, other 0.8%, none 86.3% (2009 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Vietnam: Though it has one of the highest population densities in the world, the population is not evenly dispersed. Clustering is heaviest along the south china sea and gulf of Tonkin, with the Mekong delta (in the South) and the red river valley (in the North) having the largest concentrations of people. In Vietnam, we talk about 38.1% (2021) of the total population lives in cities. Most of them reside in the following municipalities: 8.838 million, Ho Chi Minh City, 4.875 million, Hanoi (capital city), 1.703 million, Can Tho, 1.341 million, Hai Phong, 1.157 million, Da Nang, 1.046 million, Bien Hoa (2021).
Industry
Liberal economic policy (doi moi) from 1986: now one of the fastest-growing economies. Major rice exporter. Cheap labor. Strong manufacturing: textiles, electrical goods. Diverse resource base.
Vietnam is a densely populated developing country transitioning since 1986 from the rigidities of a centrally planned, highly agrarian economy to a more industrial and market-based economy, and it has raised incomes substantially. Vietnam exceeded its 2017 GDP growth target of 6.7% with a growth of 6.8%, primarily due to unexpected increases in domestic demand and strong manufacturing exports. Vietnam has a young population, stable political system, commitment to sustainable growth, relatively low inflation, stable currency, strong FDI inflows, and a strong manufacturing sector. In addition, the country is committed to continuing its global economic integration. Vietnam joined the WTO in January 2007 and concluded several free trade agreements in 2015-16, including the EU-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (which the EU has not yet ratified), the Korean Free Trade Agreement, and the Eurasian Economic Union Free Trade Agreement. In 2017, Vietnam successfully chaired the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Conference with its key priorities, including inclusive growth, innovation, strengthening small and medium enterprises, food security, and climate change.
Seeking to diversify its opportunities, Vietnam also signed the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for the Transpacific Partnership in 2018 and continued to pursue the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership. To continue its trajectory of strong economic growth, the Government acknowledges the need to spark a second wave of reforms, including reforming state-owned enterprises, reducing red tape, increasing business sector transparency, reducing the level of non-performing loans in the banking sector and increasing financial sector transparency. Vietnams public debt to GDP ratio is nearing the government-mandated ceiling of 65%. In 2016, Vietnam canceled its civilian nuclear energy development program, citing public concerns about safety and the program’s high cost; it faces growing pressure on energy infrastructure. Overall, the country’s infrastructure fails to meet the needs of an expanding middle class. Vietnam has demonstrated a commitment to sustainable growth over the last several years. Still, despite the recent speed-up in economic growth, the Government remains cautious about the risk of external shocks.
Vietnam is rich in the following natural resources: Antimony, phosphates, coal, manganese, rare earth elements, bauxite, chromate, offshore oil and gas deposits, timber, hydropower, and arable land.
The main industrial sectors are food processing, garments, shoes, and machine-building; mining, coal, steel; cement, chemical fertilizer, glass, tires, oil, and mobile phones.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in broadcasting equipment, telephones, integrated circuits, footwear, and furniture (2019), partnering with these nations: the United States 23%, China 14%, Japan 8%, South Korea 7% (2019). The export trade resulted in $280.83 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Vietnam’s position of 24.
Land use in Vietnam: 45% (2018 estimate) forest, 20.2% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 20.6% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 34.8% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 12.1% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 2.1% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 46,000 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Vietnam are rice, vegetables, sugar cane, cassava, maize, pork, fruit, bananas, coffee, and coconuts.
The country typically needs to import: integrated circuits, telephones, refined petroleum, textiles, and semiconductors (2019), partnering with the following nations: China, 35%, South Korea, 18%, Japan, 6% (2019) in a sum value of $261.68 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $245.63 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate) $217.684 billion (2017 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Vietnam 22.
Vietnam Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Vietnam, Southeastern Asia, bordering the Gulf of Thailand, Gulf of Tonkin, the South China Sea, and China, Laos, and Cambodia. We published some basic information about its capital Hanoi (Ha Noi), and the Vietnamese nation.
Are you interested in visiting Vietnam and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Vietnam below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Vietnam
Did you know about Vietnam?
The Vietnamese culture is rich and diverse, with many influences from surrounding countries. It isn’t easy to pinpoint what is considered traditional Vietnamese food because they use so many aspects of cuisine to create their dishes. They also love to experiment with new ingredients and combinations not typically found in other Asian countries.
Did you know that they have an official calendar called the Tai-Lung year in Vietnam, which is made up of twelve lunar months? The Vietnamese think that it’s a new person when each year starts.
After virtually visiting Vietnam, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Cambodia, China, and Laos.
If you liked our Google map and Vietnam information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.