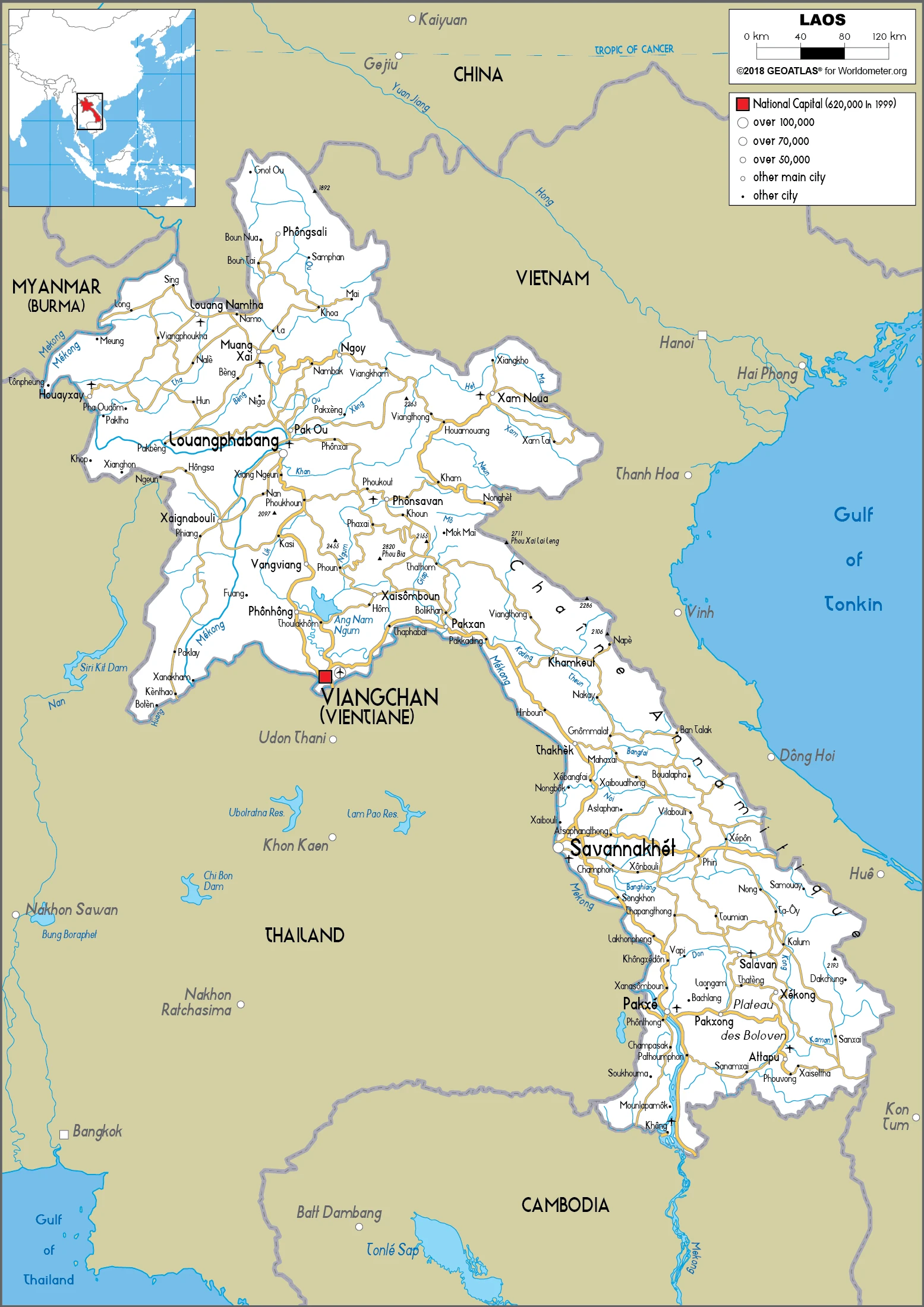
Laos Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Laos, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Laos, Southeast Asia (19 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Vientiane (Viangchan), bordering countries like Burma, Cambodia, China, Thailand, Vietnam, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Southeastern Asian state.
Quick links: Google maps Laos, Vientiane (Viangchan) Google maps, Driving Directions Laos, Printable Road Map.

About Laos in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Laos
- The conventional long form of the name: Lao Peoples Democratic Republic
- Local long form: Sathalanalat Paxathipatai Paxaxon Lao
- Local short form: Mueang Lao (unofficial)
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: name means Land of the Lao people.
- The legal system in Laos: civil law system similar in form to the French system.
- Climate: Monsoon rains SeptemberMay. The rest of the year is hot and dry.
- The national symbols are elephant; national colors: red, white, blue.
- Internet TLD: .la
Occupying mountain ranges and plateaus with an average altitude of 1500-2500 m, the landlocked state has long maintained its isolation. Laos is a real tourist jewel in the crown of Southeast Asia, with an almost complete lack of tourist infrastructure, a traditional rural lifestyle, ethnic groups unfamiliar with the urban lifestyle, and unique wildlife that makes it a rare attraction. During the Vietnam War, Laos was the most bombed region globally. It is still home to some of Southeast Asia’s most pristine mountainous monsoon forests despite the devastation. Half of the country’s land area is covered by ancient forests and 30% by planted forests. Laos boasts two World Heritage sites. Starting from Luang Prabang, which blends European colonial architecture with local traditions, the Mekong leaves Laos’ capital, Vientiane, and meanders for 500 kilometers through traditional villages to the Thai border. The temple complex of Wat Phou, with its two Mekong-front towns and the Champasak culture of the harmonious union of man and nature, is a monument to Khmer culture. The Mekong River splits into two branches from the Cambodian capital and reaches the South China Sea south of Ho Chi Minh City in Vietnam.
Three small Laotian kingdoms were unified under French control in 1899.
Background
Modern-day Laos has its roots in the ancient Lao kingdom of Lan Xang, established in the 14th century under King FA NGUM. For 300 years, Lan Xang had influence reaching into present-day Cambodia and Thailand and overall of what is now Laos. After centuries of gradual decline, Laos came under the domination of Siam (Thailand) from the late 18th century until the late 19th century, when it became part of French Indochina. The Franco-Siamese Treaty of 1907 defined the current Lao border with Thailand. In 1975, the communist Pathet Lao took control of the government, ending a six-century-old monarchy and instituting a strict socialist regime closely aligned to Vietnam. A gradual, limited return to private enterprise and the liberalization of foreign investment laws began in 1988. Laos became a member of ASEAN in 1997 and the WTO in 2013. In the 2010s, the country benefited from direct foreign investment, particularly in the natural resource and industry sectors. The construction of several large hydropower dams and expanding mining activities have also boosted the economy. Laos has retained its official commitment to communism. It maintains close ties with its two communist neighbors, Vietnam and China, both of which continue to exert substantial political and economic influence. China, for example, is providing 70% of the funding for a $5.9 billion 400-km railway line between the Chinese border and the capital Vientiane, which is set for completion in 2021. Laos is financing the remaining 30% with loans from China. At the same time, Laos has expanded its economic reliance on the West and other Asian countries, such as Japan, Malaysia, Singapore, Taiwan, and Thailand.
Geography
Largely forested mountains, broadening in the north to a plateau. Lowlands along the Mekong Valley.
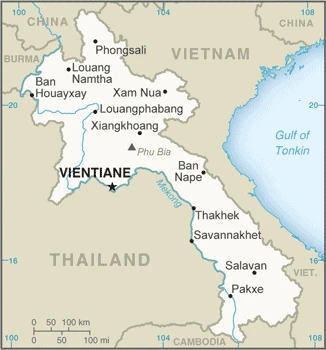
A French colony before 1953, Laos lies landlocked in southeast Asia. Heavily bombed during the Vietnam War, it fell in 1975 to communist insurgents, whose regime remains in power.
This state is located in Southeastern Asia, northeast of Thailand, West of Vietnam, under the coordinates of 18 00 N, 105 00 E, covering an area of 236,800 sq km with a coastline of 0 km (landlocked country). Laos is About twice the size of Pennsylvania, slightly larger than Utah.
Laos has 5,274 km of land boundaries in total and borders with (5 nations): Burma 238 km, Cambodia 555 km, China 475 km, Thailand 1845 km, Vietnam 2161 km.
Primarily rugged mountains, some plains, and plateaus, with Phu Bia 2,817 m as the highest point of Laos, while Mekong River 70 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 710 m throughout the country. With a total of 236,800 sq km, Laos has 230,800 sq km of land and 6,000 sq km water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Mekong (shared with China, Burma, Thailand, Cambodia, and Vietnam) – 4,350 km. The significant watersheds for Laos are Pacific Ocean drainage: Mekong (805,604 sq km).
landlocked; most of the country is mountainous and thickly forested; the Mekong River forms a large part of the western boundary with Thailand
The climate in Laos is as follows: Tropical monsoon, rainy season (May to November), dry season (December to April).
When you visit Laos, the natural hazards shall be considered: Floods, droughts.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Laos: degree of risk: very high (2020), bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, typhoid fever, dengue fever, and malaria.
Current environmental issues affecting the Lao or Laotian people: unexploded ordnance; deforestation; soil erosion; loss of biodiversity; water pollution, most of the population does not have access to potable water.
Google maps Laos
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Vientiane (Viangchan) found under the coordinates 17 58 N, 102 36 E, applying the time zone UTC+7 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Vientiane is the capital of Laos, and it is the largest city in Southeast Asia. It is populated mainly by Laotians, but there are also many people living from all over the world. Vientiane had seen many changes over its history, such as when French soldiers burned it in 1893.
Laos became independent on 19 July 1949 (from France by the Franco-Lao General Convention); 22 October 1953 (Franco-Lao Treaty recognizes complete independence), and its national holiday is Republic Day (National Day), 2 December (1975).
Administrative divisions: 17 provinces (khoueng, singular and plural) and 1 prefecture (kampheng nakhon); Attapu, Bokeo, Bolikhamxai, Champasak, Houaphan, Khammouan, Louangnamtha, Louangphabang, Oudomxai, Phongsali, Salavan, Savannakhet, Viangchan (Vientiane), Viangchan, Xaignabouli, Xaisomboun, Xekong, Xiangkhouang.
People and society
There are over 60 ethnic groups. Lowland Laotians (Lao Loum) live along the Mekong River and are rice farmers. Upland and highland Laotians (Lao Theung and Lao Soung) traditionally employ environmentally damaging slash-and-burn farming and grow illegal cash crops (notably opium). Government efforts to reform these practices are resisted.
The population in Laos is 7,574,356 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 1.46% (2021 estimate) change. That means Laos is the No. 101 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 24 years median age (23.7 years for males and 23.7 years for women), Laos ranks No. 170 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Lao(s) or Laotian(s) (noun) or Lao or Laotian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Lao 53.2%, Khmou 11%, Hmong 9.2%, Phouthay 3.4%, Tai 3.1%, Makong 2.5%, Katong 2.2%, Lue 2%, Akha 1.8%, other 11.6% (2015 estimate). Note: the Laos Government officially recognizes 49 ethnic groups, but the total number of ethnic groups is well over 200.
They speak Lao (official language), French, English, various ethnic languages and practice the following religions: Buddhist 64.7%, Christian 1.7%, none 31.4%, other stated 2.1% (2015 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Laos: The most densely populated area is in and around the capital city of Vientiane. Large communities are primarily found along the Mekong River along the southwestern border. Overall density is considered one of the lowest in Southeast Asia. In Laos, we are talking about 36.9% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 694,000 Vientiane (capital city) (2021).
Industry
One of the worlds least developed nations. Poor infrastructure. Gold, copper, electricity, timber, garments, and coffee are exported. Levels of foreign investment are rising.
The government of Laos, one of the few remaining one-party communist states, began decentralizing control and encouraging private enterprise in 1986. Economic growth averaged more than 6% per year in the period 1988-2008, and Laos growth has more recently been amongst the fastest in Asia, averaging more than 7% per year for most of the last decade.,
Nevertheless, Laos remains a country with an underdeveloped infrastructure, particularly in rural areas. It has a basic but improving road system and limited external and internal land-line telecommunications. Electricity is available to 83% of the population. Agriculture, dominated by rice cultivation in lowland areas, accounts for about 20% of GDP and 73% of total employment. Recently, the country has faced a persistent current account deficit, falling foreign currency reserves, and growing public debt. Laos’ economy is heavily dependent on capital-intensive natural resource exports.
The economy has benefited from high-profile foreign direct investment in hydropower dams along the Mekong River, copper and gold mining, logging, and construction, although some projects in these industries have drawn criticism for their environmental impacts., Laos gained Normal Trade Relations status with the US in 2004. It applied for Generalized System of Preferences trade benefits in 2013 after being admitted to the World Trade Organization earlier. Laos held the chairmanship of ASEAN in 2016. Laos is in the process of implementing a value-added tax system. The government appears committed to raising the country’s profile among foreign investors and has developed special economic zones replete with generous tax incentives. Still, a limited labor pool, a small domestic market, and corruption remain impediments to investment. Laos also has ongoing problems with the business environment, including onerous registration requirements, a gap between legislation and implementation, and unclear or conflicting regulations.
Laos is rich in the following natural resources: Timber, hydropower, gypsum, tin, gold, gemstones.
The main industrial sectors are typically mining (copper, tin, gold, gypsum), timber, electric power, agricultural processing, rubber, construction, garments, cement, tourism.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in electricity, copper, rubber, gold, flavored water (2019), partnering with these nations: Thailand 36%, China 28%, Vietnam 16% (2019). The export trade resulted in $6.99 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Laos’s position of 116.
Land use in Laos: 67.9% (2018 estimate) forest, 21.5% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 6.2% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 10.6% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.7% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 3.7% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 3,100 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Laos are rice, roots/tubers nes, cassava, sugar cane, vegetables, bananas, maize, watermelons, coffee, taro.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, cars, cattle, iron structures, steel products (2019), partnering with the following nations: Thailand 53%, China 26%, Vietnam 10% (2019) in a sum value of $7.52 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $7.56 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Laos 121.
Laos Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Laos, Southeastern Asia, northeast of Thailand, West of Vietnam. We published some basic information about its capital Vientiane (Viangchan), and the Lao or Laotian nation.
Are you interested in visiting Laos and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Laos below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Laos
Did you know about Laos?
The country of Laos is not as well known as other countries in the region, but it has many interesting facts. It is one of the most heavily bombed countries in the world. The Lao Civil War raged on and off from 1964 to 1975. There are a lot of unexploded bombs from this time. The US dropped an average of one million bombs every eight hours during that period!
After virtually visiting Laos, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Burma, Cambodia, China, Thailand, Vietnam.
If you liked our Google map and Laos information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.