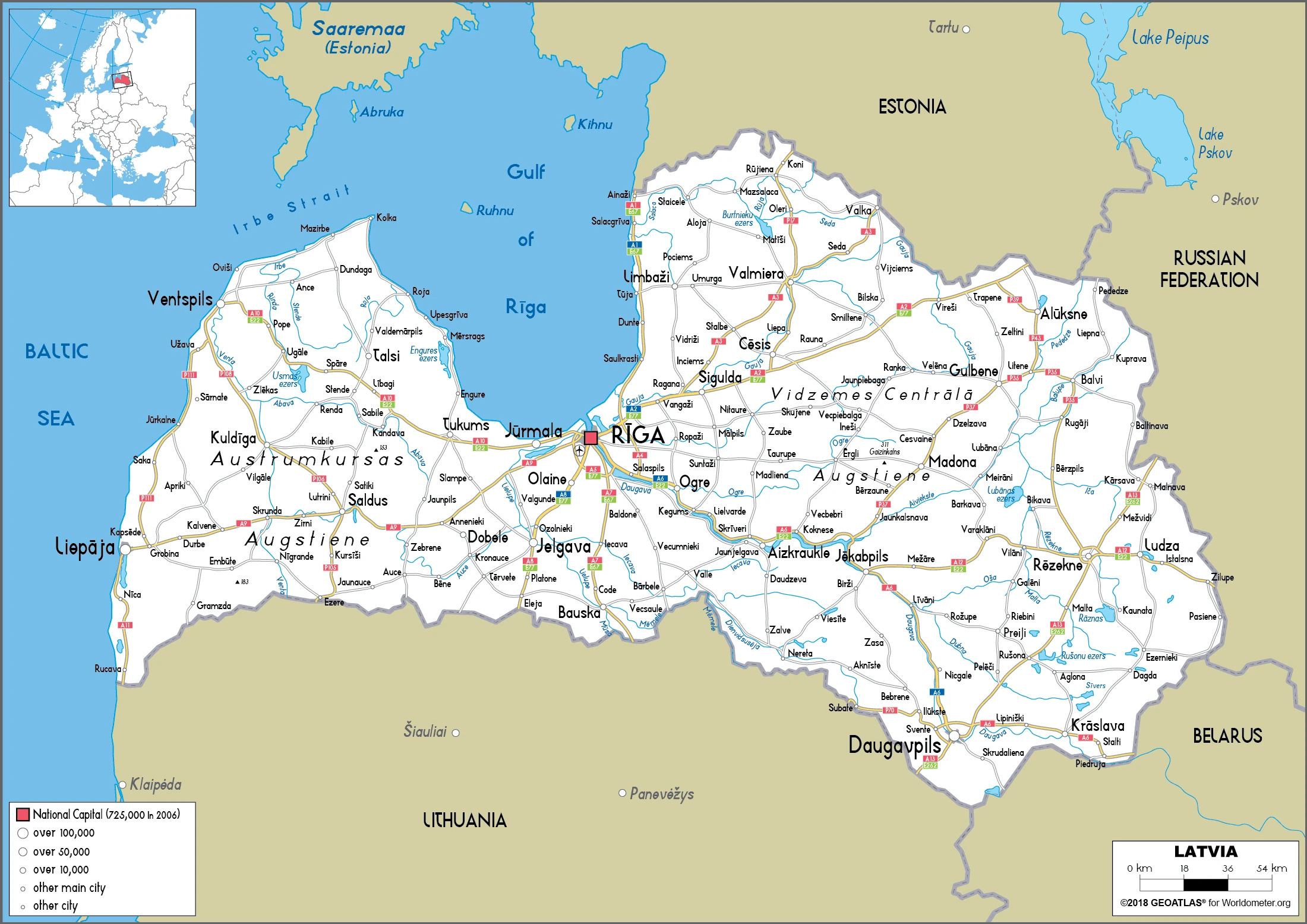
Latvia Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Latvia, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Latvia, Europe (47 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Riga, bordering countries like Belarus, Estonia, Lithuania, Russia, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this European state.
Quick links: Google maps Latvia, Riga Google maps, Driving Directions Latvia, Printable Road Map.

About Latvia in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Latvia
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of Latvia
- Local long form: Latvijas Republika
- Local short form: Latvija
- Former name(s): Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic
- Etymology: the name Latvia originates from the ancient Latgalians, one of four eastern Baltic tribes that formed the ethnic core of the Latvian people (ca. 8th-12th centuries A.D.).
- The legal system in Latvia: civil law system with traces of socialist legal traditions and practices.
- Climate: Temperate, with warm summers and cold winters. There is steady rainfall throughout the year.
- The national symbols are white wagtail (bird); national colors: maroon, white.
- Internet TLD: .lv
Latvia is a “transitional” state among the Baltic republics regarding territory, geography, history, and population. “A small, flat and marshy filling in a sandwich of neighbors”, say the cartographers. Like that of its northern neighbor, its surface is shaped by the ice sheet that extends down from Scandinavia: an uneven, undulating plain, the highest point, Gaizina Kalns, rises to 311 m. The Gulf of Riga, with its sandy coastline, penetrates deep into the country’s body. About 40% of its territory is covered by forest, while the eastern part is dotted with lakes, marshes, and swamps. The climate is moderately cool, and the Gulf of Riga freezes over in winter. Like their Lithuanian neighbors, the Latvians are ancient Baltic people who occupied the area in the 2nd millennium BC. Their history is similar to that of the Estonians. The capital Riga, situated at the mouth of the Daugava River, 15 km from the gulf, was one of the centers of the Hanseatic League between the 13th and 15th centuries. The city continued to be an important economic and commercial center in the 19th century, with neoclassical wooden houses built around the medieval core – the most beautiful Art Nouveau buildings in Europe are to be found in Riga. The old town is a World Heritage Site, as are the bases of the Struve survey network.
In Latvia, life expectancy for men is ten years less than for women.
Background
Several eastern Baltic tribes merged in medieval times to form the ethnic core of the Latvian people (ca. 8th-12th centuries A.D.). The region subsequently came under Germans, Poles, Swedes, and finally, Russians. A Latvian republic emerged following World War I, but the USSR annexed it in 1940 – an action never recognized by the US and many other countries. Latvia reestablished its independence in 1991 following the breakup of the Soviet Union. However, the last Russian troops left in 1994, the status of the Russian minority (some 26% of the population) remains of concern to Moscow. Latvia acceded to both NATO and the EU in the spring of 2004. It joined the eurozone in 2014 and the OECD in 2016. A dual citizenship law was adopted in 2013, easing naturalization for non-citizen children.
Geography
A flat coastal plain that the Gulf of Riga deeply indents. Poor drainage creates many bogs and swamps in the forested interior.
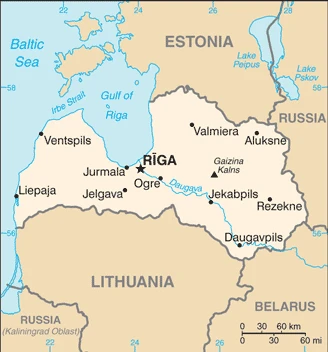
Latvia lies on the east coast of the Baltic Sea. Like its Baltic neighbors, it regained independence from Moscow in 1991 and joined the EU and NATO in 2004.
This state is located in Eastern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, between Estonia and Lithuania, under the coordinates of 57 00 N, 25 00 E, covering an area of 64,589 sq km with a coastline of 498 km. Latvia is Slightly larger than West Virginia.
Latvia has 1,370 km of land boundaries in total and borders with (4 nations): Belarus 161 km, Estonia 333 km, Lithuania 544 km, Russia 332 km.
Low plain, with Gaizina Kalns 312 m as the highest point of Latvia, while Baltic Sea 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 87 m throughout the country. With a total of 64,589 sq km, Latvia has 62,249 sq km of land and 2,340 sq km water surface area.
Most of the country comprises fertile low-lying plains with some hills in the east.
The climate in Latvia is as follows: Maritime, wet, moderate winters.
When you visit Latvia, the natural hazards shall be considered: Many agricultural fields can become waterlogged and require drainage.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Latvia: degree of risk: intermediate (2020), N/A, tickborne encephalitis.
Current environmental issues affecting the Latvian people: while land, water, and air pollution are evident, Latvias environment has benefited from a shift to service industries after the country regained independence; improvements have occurred in drinking water quality, sewage treatment, household, and hazardous waste management, as well as reduction of air pollution; concerns include nature protection and the management of water resources and the protection of the Baltic Sea.
Google maps Latvia
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Riga found under the coordinates 56 57 N, 24 06 E, applying the time zone UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October.
Riga is the capital of Latvia and the largest city in the Baltic States. Founded by the Livonian Brothers of the Sword in 1201, it is the oldest city in Northern Europe. It is well known for its Baroque architecture and 19th-century neoclassical buildings. More recently, Riga has experienced rapid growth, with its population increasing from about 200,000 people to nearly 900,000 people between 1991 and 2008.
Latvia became independent on 18 November 1918 (from Soviet Russia); 4 May 1990 (declared from the Soviet Union); 6 September 1991 (recognized by the Soviet Union), and its national holiday is Independence Day (Republic of Latvia Proclamation Day), 18 November (1918).
Administrative divisions: 36 municipalities (novadi, singular – novads) and 7 state cities (valstpilsetu pasvaldibas, singular valstspilsetas pasvaldiba) municipalities: Adazi, Aizkraukle, Aluksne, Augsdaugava, Balvi, Bauska, Cesis, Dienvidkurzeme, Dobele, Gulbene, Jekabpils, Jelgava, Kekava, Kraslava, Kuldiga, Limbazi, Livani, Ludza, Madona, Marupe, Ogre, Olaine, Preili, Rezekne, Ropazi, Salaspils, Saldus, Saulkrasti, Sigulda, Smiltene, Talsi, Tukums, Valka, Valmiera, Varaklani, Ventspils cities: Daugavpils, Jelgava, Jurmala, Liepaja, Rezekne, Riga, Ventspils.
People and society
Latvians make up just under two-thirds of the population and are mostly Lutheran. The state has officially favored them since 1991 over the predominantly Orthodox Christian Russian minority. Latvian was declared the only official language in 2000 and has been used exclusively in schools since 2004. This discrimination has strained relations with neighboring Russia. Women enjoy full equality. The divorce rate is high.
The population in Latvia is 1,862,687 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of -1.1% (2021 estimate) change. That means Latvia is the No. 153 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 44.4 years median age (40.5 years for males and 40.5 years for women), Latvia ranks No. 16 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Latvian(s) (noun) or Latvian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Latvian 62.7%, Russian 24.5%, Belarusian 3.1%, Ukrainian 2.2%, Polish 2%, Lithuanian 1.1%, other 1.8%, unspecified 2.6% (2021 estimate).
They speak Latvian (official language) 56.3%, Russian 33.8%, other 0.6% (includes Polish, Ukrainian, and Belarusian), unspecified 9.4% languages and practice the following religions: Lutheran 36.2%, Roman Catholic 19.5%, Orthodox 19.1%, other Christian 1.6%, other 0.1%, unspecified/none 23.5% (2017 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Latvia: The largest concentration of people is found in and around the port and capital city of Riga. Small agglomerations are scattered throughout the country. In Latvia, we are talking about 68.4% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 628,000 Riga (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Service-led economy. After fast growth, the global credit crunch brought Latvia to the verge of bankruptcy in 2008: banks were bailed out, stringent austerity measures were imposed. The worst recession in the EU ensued. Back to fastest growth in EU in 20122013. Adopted euro in 2014.
Latvia is a small, open economy with exports contributing more than half of GDP. Due to its geographical location, transit services are highly-developed, along with timber and wood-processing, agriculture and food products, and manufacturing of machinery and electronics industries. Corruption impedes attracting foreign direct investment, and Latvia’s low birth rate and decreasing population are significant challenges to its long-term economic vitality. Latvia’s economy experienced GDP growth of more than 10% per year during 2006-2007 but entered a severe recession in 2008 due to an unsustainable current account deficit and significant debt exposure amid the slowing world economy. Triggered by the collapse of the second-largest bank, GDP plunged by more than 14% in 2009 and, despite solid growth since 2011, the economy took until 2017 to return to pre-crisis levels in real terms. Substantial investment and consumption, the latter stoked by rising wages, helped the economy grow by more than 4% in 2017, while inflation rose to 3%.
Continued gains in competitiveness and investment will be vital to maintaining economic growth, especially in light of unfavorable demographic trends, including the emigration of skilled workers and one of the highest levels of income inequality in the EU. In the wake of the 2008-09 crisis, the IMF, EU, and other international donors provided substantial financial assistance to Latvia as part of an agreement to defend the currency peg to the euro in exchange for the government’s commitment to stringent austerity measures. The IMF/EU program successfully concluded in December 2011, although the austerity measures imposed enormous social costs. The majority of companies, banks, and real estate have been privatized, although the state still holds sizable stakes in a few large enterprises, including 80% ownership of the Latvian national airline. Latvia officially joined the World Trade Organization in February 1999 and the EU in May 2004. Latvia also joined the eurozone in 2014 and the OECD in 2016.
Latvia is rich in the following natural resources: peat, limestone, dolomite, amber, hydropower, timber, arable land.
The main industrial sectors are typically processed foods, processed wood products, textiles, processed metals, pharmaceuticals, railroad cars, synthetic fibers, electronics.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in lumber, broadcasting equipment, whiskey, and other hard liquors, wheat, packaged medicines (2019), partnering with these nations: Lithuania 16%, Estonia 10%, Russia 9%, Germany 7%, Sweden 6%, United Kingdom 6% (2019). The export trade resulted in $20.23 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Latvia’s position of 81.
Land use in Latvia: 54.1% (2018 estimate) forest, 16.7% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 18.6% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 29.2% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.1% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 10.5% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 12 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Latvia are wheat, milk, rapeseed, barley, oats, potatoes, rye, beans, pork, poultry.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, broadcasting equipment, cars, packaged medicines, aircraft (2019), partnering with the following nations: Russia 21%, Lithuania 14%, Germany 9%, Poland 7%, Estonia 7% (2019) in a sum value of $19.84 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $20.79 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $21.38 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Latvia 85.
Latvia Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Latvia, Eastern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, between Estonia and Lithuania. We published some basic information about its capital Riga, and the Latvian nation.
Are you interested in visiting Latvia and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Latvia below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Latvia
Did you know about Latvia?
The Latvian language is one of 18 languages that belong to the Indo-European language family. Latvians can speak Russian fluently due to Latvia being occupied by Russia during World War II and later occupations by the Soviet Union.
After virtually visiting Latvia, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Belarus, Estonia, Lithuania, Russia.
If you liked our Google map and Latvia information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.