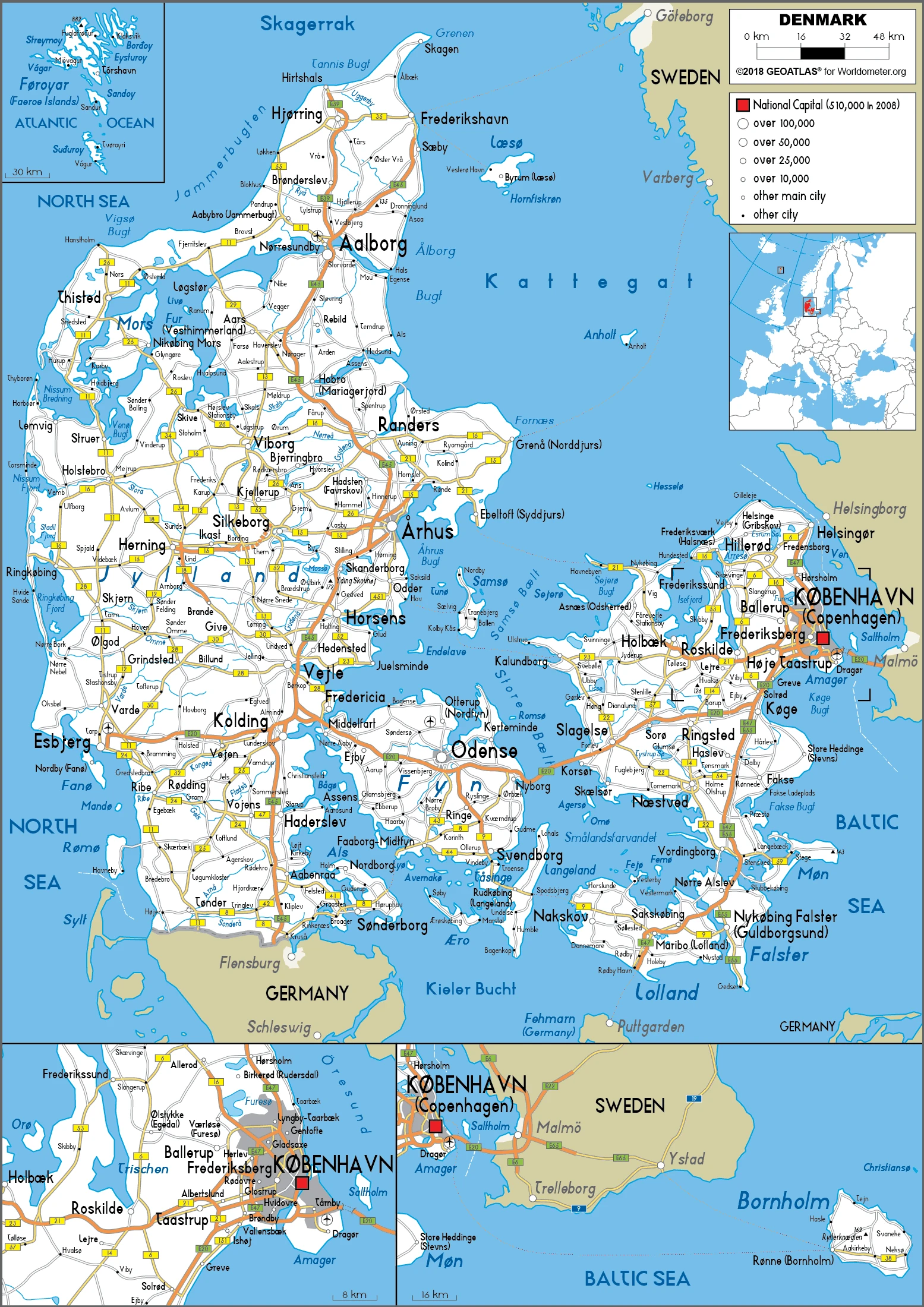
Denmark Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Denmark, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Denmark, Europe (47 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Copenhagen, bordering countries like Germany, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this European state.
Quick links: Google Maps Denmark, Copenhagen Google maps, Driving Directions Denmark, Printable Road Map.

About Denmark in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Denmark
- The conventional long form of the name: Kingdom of Denmark
- Local long form: Kongeriget Danmark
- Local short form: Danmark
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: the name derives from the words Dane(s) and mark; the latter refers to a march (borderland) or forest.
- The legal system in Denmark: civil law; judicial review of legislative acts.
- Climate: Damp, temperate with mild summers and cold, wet winters. Rainfall is moderate.
- The national symbols are lion, and mute swan, while the national colors: are red, and white.
- Internet TLD: .dk
Copenhagen, Denmark’s capital, has added a few side trips that you can take in a day or two. Copenhagen got its name from the word københavn, meaning “merchants’ harbor.” This city grew in size because of its location on the Øresund, guarding the entrance to the Baltic. Copenhagen has become the largest Scandinavian city, home to 1.7 million people. Copenhagen is easily accessible by the Øresund Bridge, which provides transport between Denmark and Sweden. With a population of 1 million people, Copenhagen is one of Northern Europe’s most prominent domestic markets, larger than Stockholm and equal in size to Berlin, Hamburg, and Amsterdam.
The Kingdom of Denmark, which occupies the Jutland peninsula between Norway and Sweden, and the archipelago to its east, is strategically located between the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. It has controlled the Straits of Skagerrak and Kattegat, the gateways to the Baltic Sea, for almost 1,500 years – until the mid-17th century, it even controlled the southern part of the Scandinavian peninsula. Today, Denmark is the only state on Earth with a much larger external territory than its own: Greenland, the largest island on the planet, geologically part of the North American continent, is about 50 times larger than the mainland.
For centuries, the inhabitants of this flat land covered with glacial sediments have made their living from agriculture and the sea. The southernmost country in northern Europe is still the breadbasket of Scandinavia. Visitors to Denmark can visit three World Heritage Sites. Jelling’s tumuli and its rune-inscribed stones are relics of pagan Nordic culture. At the same time, the other rune and its church are reminiscent of mid-10th century Christian Denmark Roskilde’s cathedral, built in the 12th and 13th centuries, is Scandinavia’s first Gothic church built of brick. From here, the architectural technique spread throughout northern Europe. From the 15th century, it also served as a mausoleum for the Danish royal family, with side chapels only being built in the 19th century. Kronborg Castle rises at an important strategic point on the banks of the Oresund Strait near Helsingor (Elsinore). The Renaissance castle, built in the second half of the 16th century and later fortified with cannons, symbolizes the Danish people. It has played an essential role in the history of northern Europe for three centuries, and from the island of Sjaelland, it still overlooks the Swedish coast, just 4 km away, intact. But its world fame is not due to this but as the setting for Shakespeare’s Hamlet.
Denmark is Europes oldest kingdom the monarchy dates back to the 10th century.
Background
Once the seat of Viking raiders and later a significant north European power, Denmark has evolved into a modern, prosperous nation participating in the general political and economic integration of Europe. It joined NATO in 1949 and the EEC (now the EU) in 1973. However, the country has opted out of some aspects of the EU’s Maastricht Treaty, including the European Economic and Monetary Union, European defense cooperation, and certain justice and home affairs issues.
Geography
Fertile farmland covers two-thirds of the terrain, which is among the flattest. About 100 islands are inhabited.
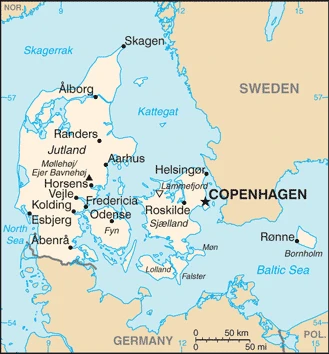
Denmark occupies the Jutland peninsula and over 400 islands in southern Scandinavia. Greenland and the Faeroe Islands are self-governing associated territories.
This state is located in Northern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea and the North Sea, on a peninsula north of Germany (Jutland). Also includes several major islands (Sjaelland, Fyn, and Bornholm). under the coordinates of 56 00 N, 10 00 E, covering an area of 43,094 sq km with a coastline of 7,314 km. Denmark is slightly less than twice the size of Massachusetts, about two-thirds the size of West Virginia.
Denmark has 140 km of land boundaries and borders with (1 nation): Germany, 140 km.
Low and flat to gently rolling plains, with Mollehoj/Ejer Bavnehoj 171 m as the highest point of Denmark, while Lammefjord -7 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation of 34 m throughout the country. With 43,094 sq km, Denmark has 42,434 sq km of land and 660 sq km of water surface area.
Composed of the Jutland Peninsula and a group of more than 400 islands (Danish Archipelago), it controls Danish Straits (Skagerrak and Kattegat), linking the Baltic and North Seas; about one-quarter of the population lives in greater Copenhagen.
The climate in Denmark is as follows: Temperate, humid and overcast, with mild, windy winters and cool summers.
When you visit Denmark, the natural hazards shall be considered: Flooding is a threat in some areas of the country (e.G., Parts of Jutland, along the southern coast of the island of Lolland) protected from the sea by a system of dikes.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Denmark: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Danish people: air pollution, principally from vehicle and power plant emissions; nitrogen and phosphorus pollution of the North Sea; drinking and surface water becoming polluted from animal wastes and pesticides; much of the country’s household and industrial waste is recycled.
Google Maps Denmark
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Copenhagen found under the coordinates 55 40 N, 12 35 E, applying the time zone UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October.
Copenhagen is the capital of Denmark and one of the most beautiful cities in Europe. It was a major tourist destination throughout the 18th and 19th centuries but has since fallen off in popularity as its beauty became more widely known. Many people are rediscovering this gem, with many coming for its stunning scenery and peaceful atmosphere.
Denmark became independent on ca. 965 (unified and Christianized under HARALD I Gormsson); 5 June 1849 (became a parliamentary constitutional monarchy), and its national holiday is Constitution Day, 5 June (1849).
Administrative divisions: metropolitan Denmark – 5 regions (regioner, singular – region); Hovedstaden (Capital), Midtjylland (Central Jutland), Nordjylland (North Jutland), Sjaelland (Zealand), Syddanmark (Southern Denmark).
People and society
Income distribution is the most even in the West. Danish liberalism is challenged over immigration: cultural clashes have arisen with immigrant minorities. Almost all women now work; Denmark is a world leader in childcare provision. Marriage is becoming less common, even for couples with children.
The population in Denmark is 5,894,687 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 0.44% (2021 estimate) change. That means Denmark is the No. 113 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 42 years median age (40.9 years for males and 40.9 years for women), Denmark ranks No. 38 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Dane(s) (noun) or Danish (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Danish (includes Greenlandic (who are predominantly Inuit) and Faroese) 86.3%, Turkish 1.1%, other 12.6% (largest groups are Polish, Syrian, German, Iraqi, and Romanian) (2018 estimate). Note: data represent population by ancestry.
They speak Danish, Faroese, Greenlandic (an Inuit dialect), German (small minority); languages and practice the following religions: Evangelical Lutheran (official) 74.7%, Muslim 5.5%, other/none/unspecified (denominations of less than 1% each in descending order of size include Roman Catholic, Jehovahs Witness, Serbian Orthodox Christian, Jewish, Baptist, Buddhist, Church of Jesus Christ, Pentecostal, and nondenominational Christian) 19.8% (2019 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Denmark: With excellent access to the north sea, Skagerrak, Kattegat, and the Baltic sea, population centers tend to be along with coastal areas, particularly in Copenhagen and the eastern side of the country’s mainland. In Denmark, we are talking about 88.2% (2021) of the total population living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 1.359 million, Copenhagen (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Natural gas and oil reserves. Skilled workforce key to high-tech industrial success. Pork, bacon, and dairy products are exported. Opted not to join the euro, though its currency is pegged.
This thoroughly modern market economy features advanced industry with world-leading pharmaceuticals, maritime shipping, renewable energy, and a high-tech agricultural sector. Danes enjoy a high standard of living, and the Danish economy is characterized by extensive government welfare measures and equitable distribution of income. An aging population will be a long-term issue. Denmark’s small open economy is highly dependent on foreign trade, and the government strongly supports trade liberalization. Denmark is a net exporter of food, oil, and gas and enjoys a comfortable balance of payments surplus but depends on imports of raw materials for the manufacturing sector. Denmark is a member of the EU but not the eurozone.
Denmark has negotiated an opt-out with the EU despite previously meeting the criteria to join the European Economic and Monetary Union and must not adopt the euro. Denmark is experiencing a modest economic expansion. The economy grew by 2.0% in 2016 and 2.1% in 2017. The expansion is expected to decline slightly in 2018. According to the national labor survey, unemployment stood at 5.5% in 2017. The labor market was tight in 2017, with corporations experiencing some difficulty finding appropriately-skilled workers to fill billets. The Danish government offers extensive programs to train unemployed persons to work in sectors that need qualified workers.
Denmark maintained a healthy budget surplus for many years up to 2008, but the global financial crisis swung the budget balance into deficit. Since 2014 the balance has shifted between surplus and deficit. In 2017 there was a surplus of 1.0%. The government projects a lower deficit in 2018 and 2019 of 0.7%, and public debt (EMU debt) as a share of GDP is expected to decline to 35.6% in 2018 and 34.8% in 2019. The Danish government plans to address increasing municipal, public housing, and integration spending in 2018.
Denmark is rich in the following natural resources: Petroleum, natural gas, fish, arable land, salt, limestone, chalk, stone, gravel, and sand.
The main industrial sectors are wind turbines, pharmaceuticals, medical equipment, shipbuilding and refurbishment, iron, steel, nonferrous metals, chemicals, food processing, machinery, transportation equipment, textiles and clothing, electronics, construction, furniture, and other wood products.
The country’s export sectors are robust in packaged medicines, electric generators, pork, refined petroleum, and medical cultures/vaccines (2019), partnering with these nations: Germany 14%, United States 11%, Sweden 10%, United Kingdom 7%, Norway 6%, Netherlands 5%, China 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $191.53 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Denmark’s position of 31.
Land use in Denmark: 12.9% (2018 estimate) forest, 23.7% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 58.9% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 63.4% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.1% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 4.4% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 4,350 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Denmark are milk, wheat, barley, potatoes, sugar beet, pork, rye, rapeseed, oats, and poultry.
The country typically needs to import: cars, refined petroleum, packaged medicines, crude petroleum, and broadcasting equipment (2019), partnering with the following nations: Germany at 21%, Sweden at 11%, the Netherlands at 8%, China at 7% (2019) in a sum value of $170.33 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $178.44 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $179.95 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Denmark 32.
Denmark Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Denmark, Northern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea and the North Sea, on a peninsula north of Germany (Jutland). Also includes several major islands (Sjaelland, Fyn, and Bornholm). We published some basic information about its capital Copenhagen, and the Danish nation.
Are you interested in visiting Denmark and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Denmark below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Denmark
Did you know about Denmark?
Denmark is a very cool country that we don’t know much about. They have one of Europe’s highest living standards and some of the world’s most stringent environmental laws. The average Dane wastes around 170 liters of food per year, enough to feed 10 people.
Denmark is governed as a parliamentary democracy within the framework of a constitutional monarchy, and the government consists of a Prime Minister and Cabinet.
Denmark is a Scandinavian country and is the happiest country in the world. It is also ranked as having one of the best work-life balances in the world. A big reason for this is that Danes don’t usually work more than 37 hours a week, and there are plenty of long, paid holidays.
After virtually visiting Denmark, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries, Germany and Sweden.
If you liked our Google map and Denmark information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.