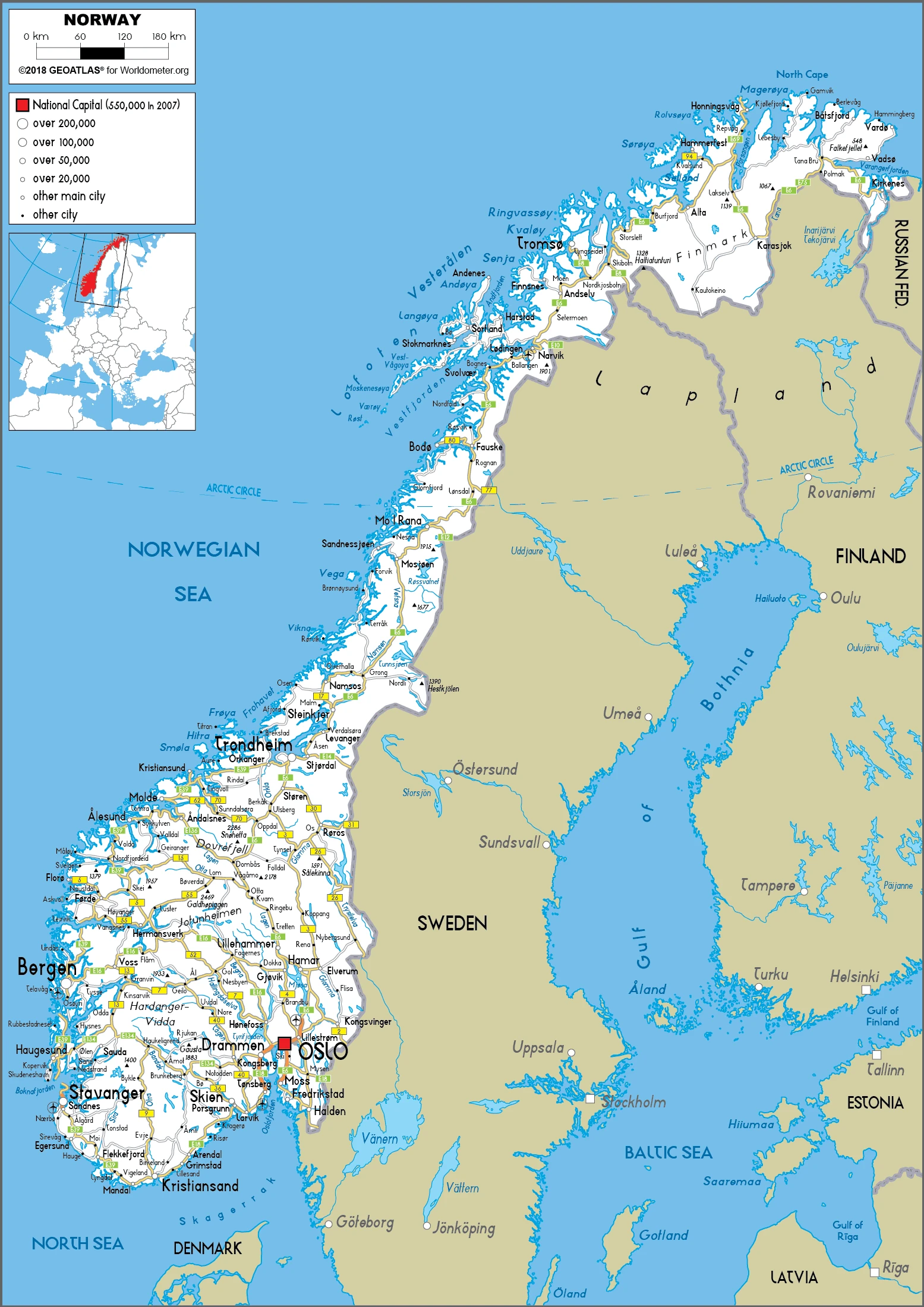
Norway Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Norway, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Norway, Europe (47 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Oslo, bordering countries like Finland, Sweden, Russia, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this European state.
Quick links: Google Maps Norway, Oslo Google maps, Driving Directions Norway, Printable Road Map.

About Norway in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Norway
- The conventional long form of the name: Kingdom of Norway
- Local long form: Kongeriket Norge
- Local short form: Norge
- Former name(s): N/A
- Etymology: derives from the Old Norse words nordr and vegr, meaning northern way, and refers to the long coastline of western Norway.
- The legal system in Norway: mixed legal system of civil, common, and customary law; Supreme Court can advise on legislative acts.
- Climate: Mild coastal climate. The weather is more extreme inland, with warmer summers and cold, snowy winters.
- The national symbols are a lion, and the national colors are red, white, and blue.
- Internet TLD: .no
Norway has a tradition of rustic stave churches as well as modern structures. This land is technologically advanced, with exports like oil and hydroelectric energy. It also has beautiful landscapes with steep and jagged fjords and rivers full of fish, glaciers, mountains, and meadows.
Norway has been a developing country, but it is one of the richest today, and prices are high. As a result, Swedes are often in Norway and working menial jobs for money to enjoy the changes in Norway.
Around a third of Europe’s northernmost or saga, stretching 13 degrees of latitude, lies beyond the Arctic Circle. The Svalbard Islands, or Spttzbergs, at 80 degrees north latitude, are under the north Norwegian jurisdiction. The land of the country, which lies between the North Sea, the Norwegian Sea, and the Arctic Ocean, is dominated by the glacially carved, crystalline rocks of the Skandl-Nav mountain range.
Ice-age glaciers once stretched to the Sea, carving deep valleys into the hard rock. Today, the lower parts of these valleys are covered by seawater – fjords sometimes extend hundreds of kilometers inland. Norway’s ice-capped coastline is more than 25 000 kilometers long.
Most of the world’s wilderness sites are also associated with fjords and coastlines. Geiranger and Naeroy Fjords are the most spectacular fjords on the World Natural Heritage list. Thousands of rock paintings found on the shores of the Alta fjord near the Arctic Circle prove that the coastline was inhabited as early as 4200 BC.
The tiny culture of the Vegaoyan or Vega Islands, covering only 70 km2 of land, was inhabited in the Stone Age, and its fishing villages, warehouses, piers, farmland, and marker booms preserve a 1500-year-old tradition of fishing and farming. The 12th-century bell-tower church of Urnes, on the banks of the Sogne fjord, has Celtic, Viking, and Romanesque features, and Bergen (Bryggen) was an important port for the Hanseatic League between the 14th and 16th centuries, its colorful wooden houses surviving several fires.
The town of Roros, nestling in the Scandinavian Mountains, has a mining connection: the inhabitants of this typical wooden-hut settlement mined copper here from the 17th century until 1977, when it was abandoned in 333 years. The port town of Hammerfest, near Cape North, is not only the northernmost town in Europe but also the northernmost on Earth: in 1816, under the direction of astronomer FGW Struve, it was here that the first accurate meridian arc length measurements in modern cartography were taken, all the way to the Black Sea. The World Heritage List includes the markings of 34 basepoints of the original network, which today covers the territories of ten states.
Near Narvik, mainland Norway is only 4 miles (7 km) wide.
Background
Two centuries of Viking raids into Europe tapered off following the adoption of Christianity by King Olav TRYGGVASON in 994. Conversion of the Norwegian kingdom occurred over the next several decades. In 1397, Norway was absorbed into a union with Denmark that lasted more than four centuries. In 1814, Norwegians resisted the cession of their country to Sweden and adopted a new constitution. Sweden then invaded Norway but agreed to let Norway keep its constitution in return for accepting the union under a Swedish king. Rising nationalism throughout the 19th century led to a 1905 referendum granting Norway independence. Although Norway remained neutral in World War I, it suffered heavy losses to its shipping. Norway proclaimed its neutrality at the outset of World War II but was nonetheless occupied for five years by Nazi Germany (1940-45). In 1949, Norway abandoned neutrality and became a member of NATO. The Discovery of oil and gas in adjacent waters in the late 1960s boosted Norway’s economic fortunes. In referenda held in 1972 and 1994, Norway rejected joining the EU. Key domestic issues include immigration and integration of ethnic minorities, maintaining the country’s extensive social safety net with an aging population, and preserving economic competitiveness.
Geography
The western coast is indented with numerous fjords and features tens of thousands of islands. Mountains and plateaus cover most of the country.
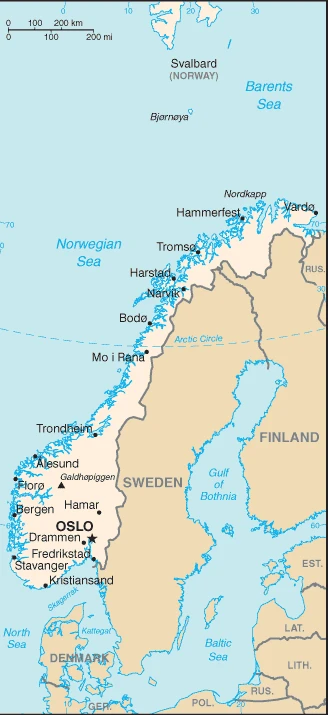
The Kingdom of Norway traces the rugged western coast of Scandinavia. Settlements are primarily restricted to southern and coastal areas. Vast oil and natural gas revenues bring prosperity.
This state is located in Northern Europe, bordering the North Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, west of Sweden, under the coordinates of 62 00 N, 10 00 E, covering an area of 323,802 sq km with a coastline of 25,148 km. Norway is slightly larger than twice the size of Georgia; slightly larger than New Mexico.
Norway has 2,566 km of land boundaries in total and borders (3 nations): Finland 709 km, Sweden 1666 km, Russia 191 km.
Glaciated, primarily high plateaus and rugged mountains broken by fertile valleys, small, scattered plains, coastline deeply indented by fjords, arctic tundra in the north, with Galdhopiggen 2,469 m as the highest point of Norway, while Norwegian Sea 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 460 m throughout the country. With a total of 323,802 sq km, Norway has 304,282 sq km of land and 19,520 sq km of water surface area.
About two-thirds of mountains; some 50,000 islands off its much-indented coastline; strategic location adjacent to sea lanes and air routes in the North Atlantic; one of the most rugged and longest coastlines globally.
The climate in Norway is as follows: Temperate along the coast, modified by North Atlantic current, colder interior with increased precipitation and colder summers, rainy year-round on the west coast.
When you visit Norway, the natural hazards shall be considered: Rockslides, avalanches volcanism: Beerenberg (2,227 m) on Jan Mayen island in the Norwegian Sea is the country’s only active volcano.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Norway: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Norwegian people: water pollution; acid rain damaging forests and adversely affecting lakes, threatening fish stocks; air pollution from vehicle emissions.
Google Maps Norway
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Oslo found under the coordinates 59 55 N, 10 45 E, applying the time zone UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October.
It is known for its grand buildings, such as The Nobel Peace Center, The Royal Palace, The Oslo Cathedral, and Holmenkollen Ski Jump, and many more that the city has as popular attractions with tourists.
Norway became independent on 7 June 1905 (declared the union with Sweden dissolved); 26 October 1905 (Sweden agreed to the repeal of the union); notable earlier dates: ca. 872 (traditional unification of petty Norwegian kingdoms by HARALD Fairhair); 1397 (Kalmar Union of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden); 1524 (Denmark-Norway); 17 May 1814 (Norwegian constitution adopted); 4 November 1814 (Sweden-Norway union confirmed), and its national holiday is Constitution Day, 17 May (1814).
Administrative divisions: 18 counties (fylker, singular – fylke); Akershus, Aust-Agder, Buskerud, Finnmark, Hedmark, Hordaland, More og Romsdal, Nordland, Oppland, Oslo, Ostfold, Rogaland, Sogn og Fjordane, Telemark, Troms, Trondelag, Vest-Agder, Vestfold.
People and society
Relatively homogeneous, but has welcomed refugees from Iraq, Somalia, Bosnia, Sri Lanka, and elsewhere. Strong family tradition, but divorce is common. Fair-minded consensus promotes female equality, boosted by the generous childcare provision. Wealth is more evenly distributed than in most countries. Voted against joining the EU in 1994.a
The population in Norway is 5,509,591 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 0.8% (2021 estimate) change. That means Norway is No. 117 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 39.5 years median age (38.8 years for males and 38.8 years for women), Norway ranks No. 57 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Norwegian(s) (noun) or Norwegian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Norwegian 81.5% (includes about 60,000 Sami), other European 8.9%, other 9.6% (2021 estimate).
They speak Bokmal Norwegian (official language), Nynorsk Norwegian (official language), small Sami- and Finnish-speaking minorities languages and practice the following religions: Church of Norway (Evangelical Lutheran – official) 68.1%, Muslim 3.4%, Roman Catholic 3.1%, other Christian 3.8%, other 9.6%, unspecified 15.4% (2020 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Norway: Most Norwegians live in the south, where the climate is milder, and there is better connectivity to mainland Europe. Population clusters are found along the north sea coast in the southwest and Skaggerak in the southeast. The interior areas of the north remain sparsely populated. In Norway, we are talking about 83.3% (2021) of the total population lives in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 1.056 million, Oslo (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Western Europe’s top oil and natural gas producer: trust fund saves for post-oil future. Metal, chemical, and engineering industries. Generous aid donor. High cost of living.
Norway has a stable economy with a vibrant private sector, a large state sector, and an extensive social safety net. Norway opted out of the EU during a referendum in November 1994. However, as a member of the European Economic Area, Norway partially participates in the EU’s single market and contributes sizably to the EU budget. The country is richly endowed with natural resources such as oil and gas, fish, forests, and minerals. After China, Norway is a leading producer and the world’s second-largest seafood exporter. The government manages the country’s petroleum resources through extensive regulation. According to official national estimates, the petroleum sector provides about 9% of jobs, 12% of GDP, 13% of the state’s revenue, and 37% of exports. Norway is one of the worlds leading petroleum exporters, although oil production is close to 50% below its peak in 2000. Gas production, conversely, has more than doubled since 2000. Although oil production is historically low, it rose in 2016 for the third consecutive year due to the higher production of existing oil fields and new fields.
Norway’s domestic electricity production relies almost entirely on hydropower. In anticipation of eventual declines in oil and gas production, Norway saves state revenue from petroleum sector activities in the world’s largest sovereign wealth fund, valued at over $1 trillion at the end of 2017. To help balance the federal budget each year, the government follows a fiscal rule, which states that spending of revenues from petroleum and fund investments shall correspond to the expected real rate of return on the fund, an amount it estimates is sustainable over time. In February 2017, the government revised the expected rate of return for the fund downward from 4% to 3%. After solid GDP growth in the 2004-2007 period, the economy slowed in 2008 and contracted in 2009 before returning to modest, positive growth from 2010 to 2017. The Norwegian economy has been adjusting to lower energy prices, as demonstrated by labor force participation and employment growth in 2017. GDP growth was about 1.5% in 2017, mainly driven by domestic demand, boosted by the rebound in the labor market and supportive fiscal policies. Economic growth is expected to remain constant or improve slightly in the next few years.
Norway is rich in the following natural resources: Petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, copper, lead, zinc, titanium, pyrites, nickel, fish, timber, and hydropower.
The main industrial sectors are petroleum and gas, shipping, fishing, aquaculture, food processing, shipbuilding, pulp and paper products, metals, chemicals, timber, mining, and textiles.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in crude petroleum, natural gas, fish, refined petroleum, and aluminum (2019), partnering with these nations: United Kingdom 18%, Germany 14%, Netherlands 10%, Sweden 9%, France 6%, United States 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $117.06 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Norway’s position of 37.
Land use in Norway: 27.8% (2018 estimate) forest, 69.5% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 2.2% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 2.7% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 0.5% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 900 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Norway are milk, barley, wheat, potatoes, oats, pork, poultry, beef, eggs, and rye.
The country typically needs to import: cars, refined petroleum, broadcasting equipment, natural gas, and crude petroleum (2019), partnering with the following nations: Sweden 17%, Germany 12%, China 8%, Denmark 7%, United States 6%, United Kingdom 5%, Netherlands 5% (2019) in a sum value of $119.08 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $140.14 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $140.3 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Norway 36.
Norway Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Norway, Northern Europe, bordering the North Sea, and the North Atlantic Ocean, west of Sweden. We published some basic information about its capital Oslo, and the Norwegian nation.
Are you interested in visiting Norway and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Norway below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Norway
Did you know about Norway?
Norway is a Scandinavian, beautiful country with breathtaking scenery located in the northwest region of Europe. The country has several different regions, which have different climates and cultures. Northern Norwegians live in the north of Norway, near the Arctic, while the Southern Norwegians live in the south, near its borders with Sweden and Denmark. It also has an exciting culture, with many history and traditions that you can learn about while visiting.
Did you know that Norway is the happiest country in the world? The people are happy because they have a high GDP, low unemployment, and good public services. One of the reasons they have such a high GDP is their healthy exports.
After virtually visiting Norway, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Finland, Sweden, and Russia.
If you liked our Google map and Norway information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.