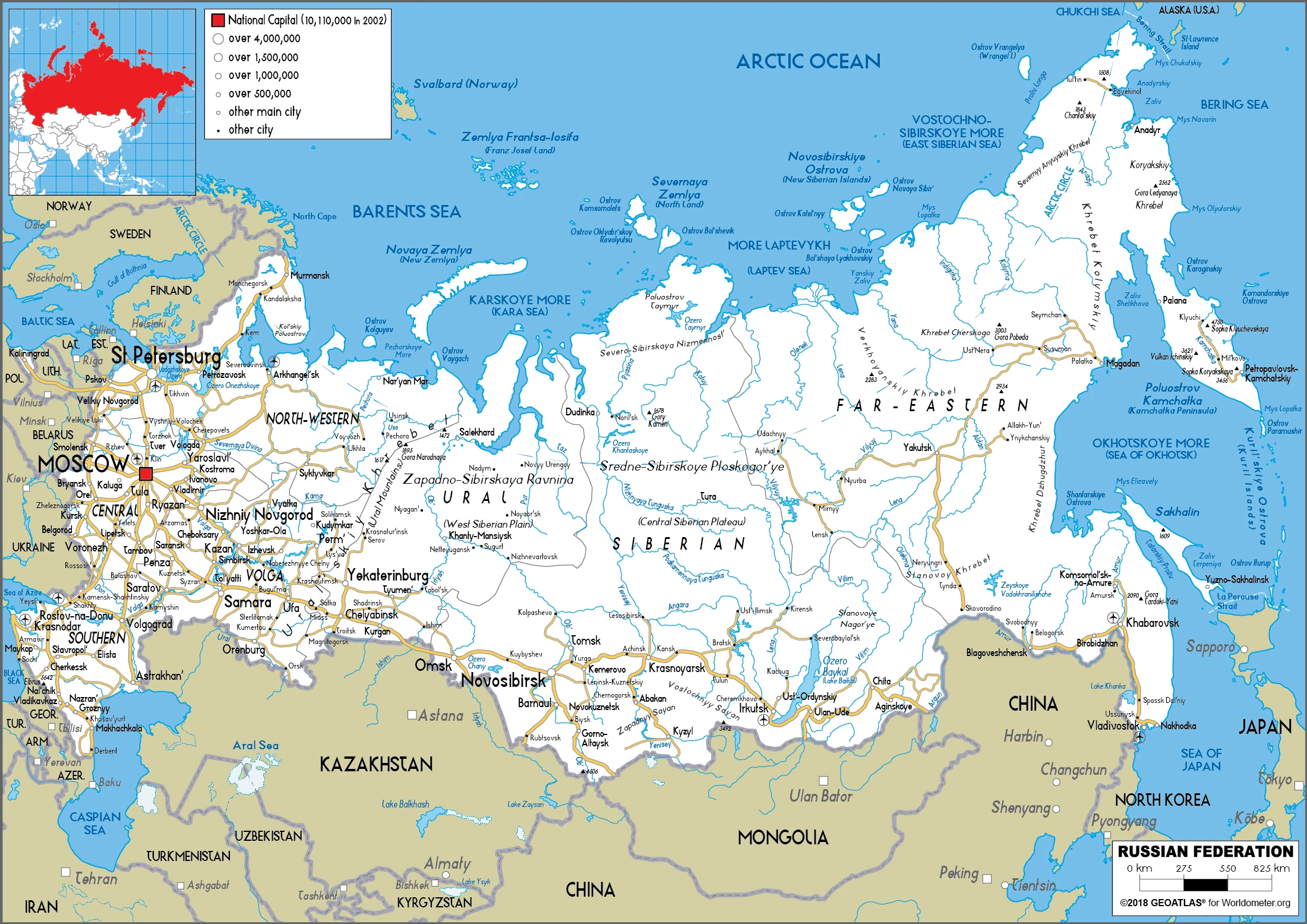
Russia Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Russia, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Russia, Asia (22 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Moscow, bordering countries like Azerbaijan, Belarus, China, Estonia, Finland, Georgia, Kazakhstan, North Korea, Latvia, Lithuania, Mongolia, Norway, Poland, Ukraine, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Asian state.
Quick links: Google Maps Russia, Moscow Google maps, Driving Directions Russia, Printable Road Map.

About Russia in a nutshell
- Conventional short form of the name: Russia
- The conventional long form of the name: Russian Federation
- Local long form: Rossiyskaya Federatsiya
- Local short form: Rossiya
- Former name(s): Russian Empire, Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
- Etymology: Russian lands were generally referred to as Muscovy until PETER I officially declared the Russian Empire in 1721; the new name sought to invoke the patrimony of the medieval eastern European Rus state centered on Kyiv in present-day Ukraine; the Rus were a Varangian (eastern Viking) elite that imposed their rule and eventually their name on their Slavic subjects.
- The legal system in Russia: civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts.
- Climate: Ranges from steppes in the south through humid continental in much of European Russia, subarctic in Siberia to tundra climate in the polar north, winters vary from cool along Black Sea coast to frigid in Siberia, summers vary from warm in the steppes to cool along Arctic coast.
- The national symbols are bear, double-headed eagle; national colors: white, blue, red.
- Internet TLD: .ru
Russia’s natural world heritage includes the Sikhote Aliny, the Altai, Lake Baikal, Vrangel Island, the Uvs Nuur Lake basin and the volcanoes of Kamchatka in the Asian part of the country, the Komi Forest and the Western Caucasus, and the 15 cultural heritages of the Russian principalities and empires that have played a decisive role in the history of the Eastern European states for more than a millennium. The Solovetsky Islands and the Derbent of Dagestan have monuments dating back to antiquity; Novgorod from the 9th century, Vladimir and Suzdal from the 12th-13th centuries, and the Moscow Kremlin and Red Square from the 14th century are the dominant centers of Russian history. Sergeyev’s Posad, Ferapontov’s monastery complex, the Church of the Resurrection in Kolomenskoye, the tower of the Kazan Kremlin building from the time of the Tatar Golden Horde, and the buildings of the Novodevichy Convent in Moscow have survived exceptionally intact. The wooden churches on Kizhi Island in Lake Onyega are 18th-century masterpieces of Russian wooden architecture. At the same time, the ancient, rebuilt Yaroslavl and 18th-century St Petersburg are the finest examples of Russian urban planning reform. The World Heritage Sites include the Struve land survey network and the Kur land with Lithuania.
Background
Founded in the 12th century, the Principality of Muscovy emerged from over 200 years of Mongol domination (13th-15th centuries) and gradually conquered and absorbed surrounding principalities. In the early 17th century, a new ROMANOV Dynasty continued this expansion policy across Siberia to the Pacific. Under PETER I (ruled 1682-1725), hegemony was extended to the Baltic Sea, and the country was renamed the Russian Empire. During the 19th century, more territorial acquisitions were made in Europe and Asia. Defeat in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904-05 contributed to the Revolution of 1905, which resulted in forming a parliament and other reforms. Devastating defeats and food shortages in World War I led to widespread rioting in the major cities of the Russian Empire and the overthrow in 1917 of the ROMANOV Dynasty.
The communists under Vladimir LENIN seized power soon after and formed the USSR. The brutal rule of Iosif STALIN (1928-53) strengthened communist rule and Russian dominance of the Soviet Union at the cost of tens of millions of lives. After defeating Germany in World War II as part of an alliance with the US (1939-1945), the USSR expanded its territory and influence in Eastern Europe and emerged as a global power. The USSR was the principal adversary of the US during the Cold War (1947-1991). The Soviet economy and society stagnated in the decades following Stalin’s rule until General Secretary Mikhail GORBACHEV (1985-91) introduced glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring) in an attempt to modernize communism. Still, his initiatives inadvertently released forces that, by December 1991, led to the dissolution of the USSR into Russia and 14 other independent states. Following economic and political turmoil during President Boris Yeltsin’s term (1991-99), Russia shifted toward a centralized authoritarian state under President Vladimir PUTIN (2000-2008, 2012-present), in which the regime seeks to legitimize its rule through managed elections, populist appeals, a foreign policy focused on enhancing the country’s geopolitical influence, and commodity-based economic growth. Russia faces a largely subdued rebel movement in Chechnya and other surrounding regions, although violence still occurs throughout the North Caucasus.
Geography
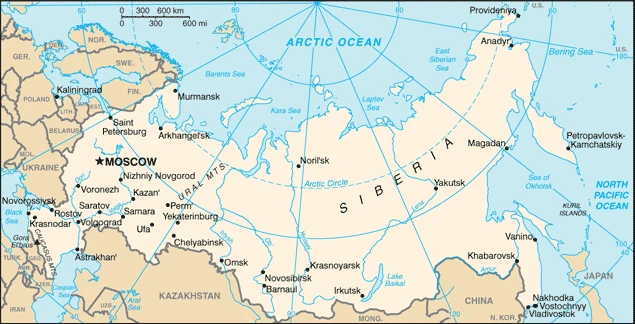
The Russian Federation was the core of the old Soviet Union, which broke up in 1991. Russia is still the world’s largest state. Its diversity is a source of both strength and problems.
This state is located in North Asia bordering the Arctic Ocean, extending from Europe (the portion west of the Urals) to the North Pacific Ocean, under the coordinates of 60 00 N, 100 00 E, covering an area of 17,098,242 sq km with a coastline of 37,653 km. Russia is Approximately 1.8 times the size of the US.
Russia has 22,407 km of land boundaries in total and bordering with (14 nations): Azerbaijan 338 km, Belarus 1312 km, China (southeast) 4133 km and China (south) 46 km, Estonia 324 km, Finland 1309 km, Georgia 894 km, Kazakhstan 7644 km, North Korea 18 km, Latvia 332 km, Lithuania (Kaliningrad Oblast) 261 km, Mongolia 3452 km, Norway 191 km, Poland (Kaliningrad Oblast) 209 km, Ukraine 1944 km.
Broad plain with low hills west of Urals, vast coniferous forest and tundra in Siberia, uplands, and mountains along southern border regions, with Gora Elbrus (highest point in Europe) 5,642 m, as the highest point of Russia, while the Caspian Sea -28 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 600 m throughout the country. With 17,098,242 sq km, Russia has 16,377,742 sq km of land and 720,500 sq km of water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Lake Baikal – 31,500 sq km; Lake Ladoga – 18,130 sq km; Lake Onega – 9,720 sq km; Lake Khanka (shared with China) – 5,010 sq km; Lake Peipus – 4,300 sq km; Ozero Vygozero – 1,250 sq km; Ozero Beloye – 1,120 sq km (freshwater lake), Caspian Sea (shared with Iran, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, and Kazakhstan) – 374,000 sq km; Ozero Malyye Chany – 2,500 sq km; Kurshskiy Zaliv/Kursiu Marios (shared with Lithuania) – 1,620 sq km (saltwater lake) while the major rivers are: Yenisey – 5,539 km, Ob – 5,410 km, Amur (shared with China and Mongolia) – 4,444 km, Lena – 4,400 km, Volga – 3,645 km, Kolyma – 2,513 km, Ural (shared with Kazakhstan) – 2,428 km, Dnieper (shared with Ukraine and Belarus) – 2,287 km, Don (shared with Ukraine) – 1,870 km, Pechora – 1,809 km. The significant watersheds for Russia are Arctic Ocean drainage: Kolyma (679,934 sq km), Lena (2,306,743 sq km), Ob (2,972,493 sq km), Pechora (289,532 sq km), Yenisei (2,554,388 sq km) Atlantic Ocean drainage: (Black Sea) Don (458,694 sq km), Dnieper (533,966 sq km) Pacific Ocean drainage: Amur (1,929,955 sq km) Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: (Caspian Sea basin) Volga (1,410,951 sq km).
The climate in Russia is as follows: Ranges from steppes in the south through humid continental in much of European Russia, subarctic in Siberia to tundra climate in the polar north, winters vary from cool along Black Sea coast to frigid in Siberia, summers vary from warm in the steppes to cool along Arctic coast.
When you visit Russia, the natural hazards shall be considered: Permafrost over much of Siberia is a significant impediment to development. Volcanic activity in the Kuril Islands. Volcanoes and earthquakes on the Kamchatka peninsula. Spring floods and summer/autumn forest fires throughout Siberia and parts of European Russia volcanism. Significant volcanic activity on the Kamchatka peninsula and Kuril islands; the peninsula alone is home to some 29 historically active volcanoes, with dozens more in the Kuril Islands; Kliuchevskoi (4,835 m), which erupted in 2007 and 2010, is Kamchatka’s most active volcano; Avachinsky and Koryaksky volcanoes, which pose a threat to the city of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, have been deemed decade volcanoes by the international association of volcanology and chemistry of the interior of the earth, worthy of study due to their tumultuous history and proximity to human populations; other notable historically active volcanoes include Bezymianny, Chikurachki, Ebeko, Gorely, Grozny, Karymsky, Ketoi, Kronotsky, Ksudach, Medvezhia, Mutnovsky, Sarychev Peak, Shiveluch, Tiatia, Tolbachik, and Zheltovsky.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Russia: degree of risk: intermediate (2020), bacterial diarrhea, Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever, tick-borne encephalitis.
Current environmental issues affecting the Russian people: air pollution from heavy industry, emissions of coal-fired electric plants and transportation in major cities; industrial, municipal, and agricultural pollution of inland waterways and seacoasts; deforestation; soil erosion; soil contamination from improper application of agricultural chemicals; nuclear waste disposal; scattered areas of sometimes intense radioactive contamination; groundwater contamination from toxic waste; urban solid waste management; abandoned stocks of obsolete pesticides.
Google Maps Russia
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Moscow found under the coordinates 55 45 N, 37 36 E, applying the time zone UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: does not observe daylight savings time.
Moscow is Russia’s capital and the country’s largest city. It has a population of around 14 million people, which makes it the 12th most populous city in the world. The city is considered one of Russia’s most important political, economic, scientific, cultural, and educational centers. Many people from all over the world come to Moscow to study the Russian language or other subjects related to Russia. It is home to many buildings, monuments, museums, and theatres.
Russia became independent on 25 December 1991 (from the Soviet Union; Russian SFSR renamed Russian Federation); notable earlier dates: 1157 (Principality of Vladimir-Suzdal created); 16 January 1547 (Tsardom of Muscovy established); 22 October 1721 (Russian Empire proclaimed); 30 December 1922 (the Soviet Union established), and its national holiday is Russia Day, 12 June (1990).
Administrative divisions: 46 provinces (oblasti, singular – oblast), 21 republics (respubliki, singular – respublika), 4 autonomous okrugs (avtonomnyye okrugi, singular – avtonomnyy okrug), 9 krays (kraya, singular – kray), 2 federal cities (goroda, singular – gorod), and 1 autonomous oblast (avtonomnaya oblast), oblasts: Amur (Blagoveshchensk), Arkhangelsk, Astrakhan, Belgorod, Bryansk, Chelyabinsk, Irkutsk, Ivanovo, Kaliningrad, Kaluga, Kemerovo, Kirov, Kostroma, Kurgan, Kursk, Leningrad, Lipetsk, Magadan, Moscow, Murmansk, Nizhniy Novgorod, Novgorod, Novosibirsk, Omsk, Orenburg, Orel, Penza, Pskov, Rostov, Ryazan, Sakhalin (Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk), Samara, Saratov, Smolensk, Sverdlovsk (Yekaterinburg), Tambov, Tomsk, Tula, Tver, Tyumen, Ulyanovsk, Vladimir, Volgograd, Vologda, Voronezh, Yaroslavl, republics: Adygeya (Maykop), Altay (Gorno-Altaysk), Bashkortostan (Ufa), Buryatiya (Ulan-Ude), Chechnya (Groznyy), Chuvashiya (Cheboksary), Dagestan (Makhachkala), Ingushetiya (Magas), Kabardino-Balkariya (Nalchik), Kalmykiya (Elista), Karachayevo-Cherkesiya (Cherkessk), Kareliya (Petrozavodsk), Khakasiya (Abakan), Komi (Syktyvkar), Mariy-El (Yoshkar-Ola), Mordoviya (Saransk), North Ossetia (Vladikavkaz), Sakha Yakutiya (Yakutsk), Tatarstan (Kazan), Tyva (Kyzyl), Udmurtiya (Izhevsk), autonomous okrugs: Chukotka (Anadyr), Khanty-Mansi-Yugra (Khanty-Mansiysk), Nenets (Naryan-Mar), Yamalo-Nenets (Salekhard), krays: Altay (Barnaul), Kamchatka (Petropavlovsk-Kamchatskiy), Khabarovsk, Krasnodar, Krasnoyarsk, Perm, Primorskiy Maritime (Vladivostok), Stavropol, Zabaykalsk Transbaikal (Chita), federal cities: Moscow Moskva, Saint Petersburg Sankt-Peterburg autonomous oblast: Yevreyskaya Jewish (Birobidzhan) note 1: administrative divisions have the same names as their administrative centers (exceptions have the administrative center name following in parentheses) note 2: the United States does not recognize Russias annexation of Ukraines Autonomous Republic of Crimea and the municipality of Sevastopol, nor their redesignation as the Republic of Crimea and the Federal City of Sevastopol.
People and society
The population in Russia is 142,320,790 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of -0.2% (2021 estimate) change. That means Russia is the No. 9 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 40.3 years median age (37.5 years for males and 37.5 years for women), Russia ranks No. 52 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Russian(s) (noun) or Russian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Russian 77.7%, Tatar 3.7%, Ukrainian 1.4%, Bashkir 1.1%, Chuvash 1%, Chechen 1%, other 10.2%, unspecified 3.9% (2010 estimate). Note: nearly 200 national and ethnic groups are represented in Russia’s 2010 census.
They speak Russian (official language) 85.7%, Tatar 3.2%, Chechen 1%, other 10.1% languages and practice the following religions: Russian Orthodox 15-20%, Muslim 10-15%, other Christian 2% (2006 estimate) note: estimates are of practicing worshipers; Russia has large populations of non-practicing believers and non-believers, a legacy of over seven decades of official atheism under Soviet rule; Russia officially recognizes Orthodox Christianity, Islam, Judaism, and Buddhism as the country’s traditional religions.
We can conclude the following about the population in Russia: Population is heavily concentrated in the westernmost fifth of the country, extending from the baltic sea, south to the Caspian Sea, and eastward parallel to the Kazakh border. Elsewhere, sizeable pockets are isolated and generally found in the south. In Russia, we talk about 74.9% (2021) of the total population lives in cities. Most of them reside in the following municipalities: 12.593 million, Moscow (capital city), 5.504 million, Saint Petersburg, 1.676 million, Novosibirsk, 1.513 million, Yekaterinburg, 1.280 million, Kazan, 1.255 million, Nizhniy Novgorod (2021).
Industry
Since the collapse of the Soviet Union, Russia has undergone significant changes, moving from a centrally planned economy toward a more market-based system. Both economic growth and reform have stalled in recent years. However, Russia remains a predominantly statist economy with a high concentration of wealth in officials’ hands. Economic reforms in the 1990s privatized most industries, with notable exceptions in the energy, transportation, banking, and defense-related sectors. The protection of property rights is still weak, and the state continues to interfere in the free operation of the private sector. Russia is one of the worlds leading producers of oil and natural gas and is also a top exporter of metals such as steel and primary aluminum. Russia is heavily dependent on the movement of world commodity prices as reliance on commodity exports makes it vulnerable to boom and bust cycles that follow the volatile swings in global prices. The economy, which had averaged 7% growth during the 1998-2008 period as oil prices rose rapidly, has seen diminishing growth rates since then due to the exhaustion of Russia’s commodity-based growth model. A combination of falling oil prices, international sanctions, and structural limitations pushed Russia into a deep recession in 2015, with GDP falling by close to 2.8%. The downturn continued through 2016, with GDP contracting another 0.2%, but was reversed in 2017 as world demand picked up. Government support for import substitution has increased recently to diversify the economy away from extractive industries.
Russia is rich in the following natural resources: a broad natural resource base including significant deposits of oil, natural gas, coal, and many strategic minerals, bauxite, reserves of rare earth elements, timber, note, formidable obstacles of climate, terrain, and distance hinder exploitation of natural resources.
The main industrial sectors are typically a complete range of mining and extractive industries producing coal, oil, gas, chemicals, and metals; all forms of machine building from rolling mills to high-performance aircraft and space vehicles; defense industries (including radar, missile production, advanced electronic components), shipbuilding; road and rail transportation equipment; communications equipment; agricultural machinery, tractors, and construction equipment; electric power generating and transmitting equipment; medical and scientific instruments; consumer durables, textiles, foodstuffs, handicrafts.
The country’s export sectors are robust in crude petroleum, refined petroleum, natural gas, coal, wheat, and iron (2019), partnering with these nations: China 14%, Netherlands 10%, Belarus 5%, Germany 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $379.12 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). A global rank of the export values resulted in Russia’s position of 20.
Land use in Russia: 49.4% (2018 estimate) forest, 37.5% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 7.3% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 13.1% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.1% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 5.7% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 43,000 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Russia are wheat, sugar beet, milk, potatoes, barley, sunflower seed, maize, poultry, oats, and soybeans.
The country typically needs to import: cars and vehicle parts, packaged medicines, broadcasting equipment, aircraft, computers (2019), partnering with the following nations: China 20%, Germany 13%, Belarus 6% (2019) in a sum value of $304.68 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $353.25 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $343.58 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Russia 20.
Russia Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Russia, North Asia bordering the Arctic Ocean, extending from Europe (the portion west of the Urals) to the North Pacific Ocean. We published some basic information about its capital Moscow, and the Russian nation.
Are you interested in visiting Russia and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Russia below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Russia
Did you know about Russia?
Russia is the largest country globally (11 percent of the Earth’s land area) and global power. It has over eight time zones, but most of it has standardized Moscow time. With a population of 144 million people, Russia is also one of the most populous countries globally.
The Russian Federation is divided into 85 federal subjects, which all have their governments and laws. Russia was an absolute monarchy for a long time, and then it became a communist state. It is still officially a state socialist republic, but it adopted a new constitution in 1993 that guarantees many personal freedoms like freedom of speech, religion, and assembly.
After virtually visiting Russia, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Azerbaijan, Belarus, China, Estonia, Finland, Georgia, Kazakhstan, North Korea, Latvia, Lithuania, Mongolia, Norway, Poland, and Ukraine.
If you liked our Google map and Russia information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.