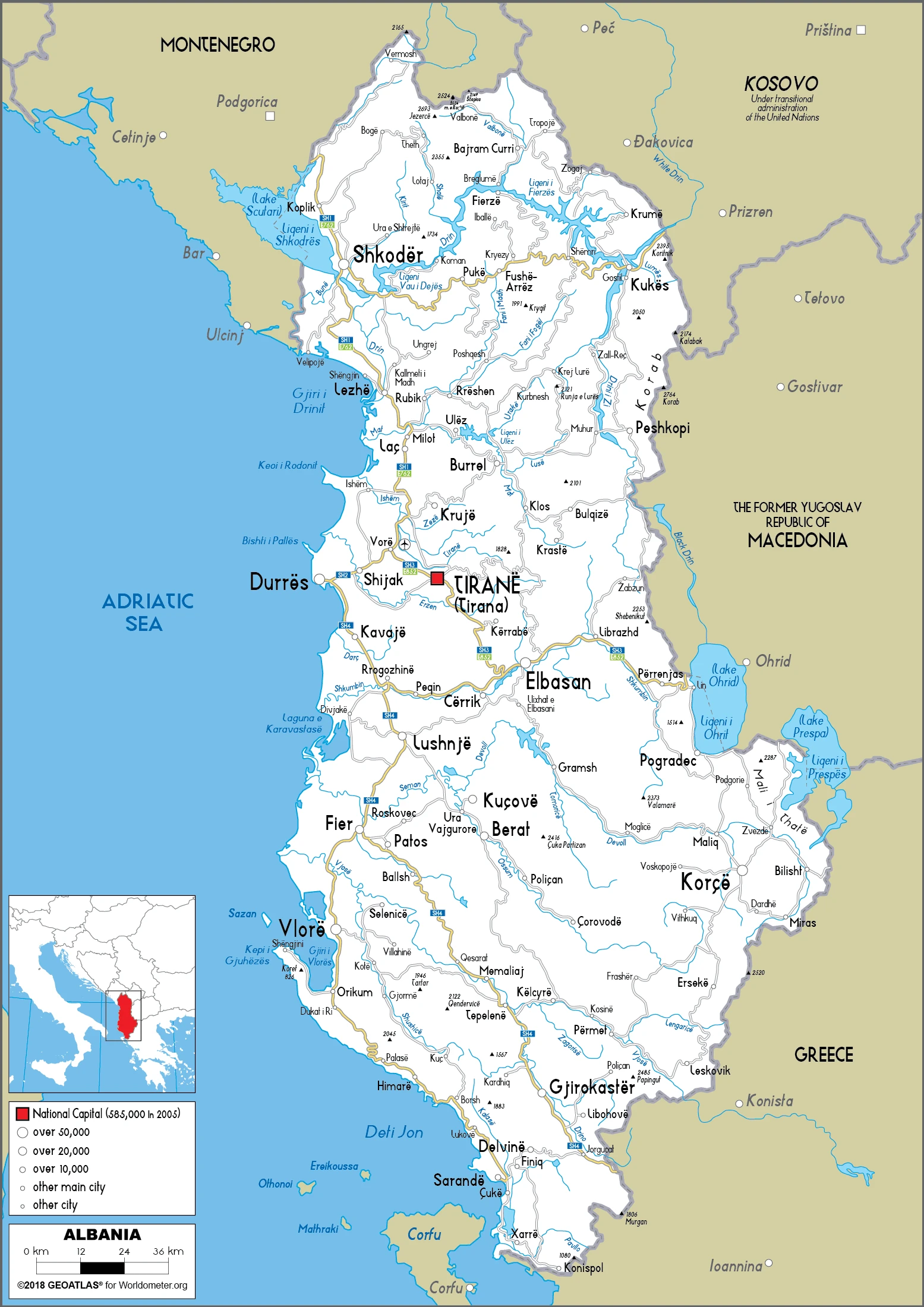
Albania Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Albania, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Albania, Europe (47 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Tirana (Tirane), bordering countries like Greece, Kosovo, Macedonia, Montenegro, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this European state.
Quick links: Google Maps Albania, Tirana (Tirane) Google maps, Driving Directions Albania, Printable Road Map.

About Albania in a nutshell
- The Albanians name for their country, Shqipërisë, means “Land of the Eagles”.
- Conventional short form of the name: Albania
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of Albania
- Local long form: Republika e Shqiperise
- Local short form: Shqiperia
- Former name(s): Peoples Socialist Republic of Albania
- Etymology: the English-language country name seems to be derived from the ancient Illyrian tribe of the Albani; the native name Shqiperia is derived from the Albanian word Shqiponje (Eagle) and is popularly interpreted to mean Land of the Eagles.
- The legal system in Albania: civil law system except in the northern rural areas where customary law known as the Code of Leke is still present.
- Climate: Mediterranean coastal climate, with warm summers and cool winters. Mountains receive heavy rains or snows in winter.
- The national symbols are black double-headed eagle; national colors: red, black.
- Internet TLD: .al
Much of the small country is dominated by the high mountainous terrain of Albania, which is more than 1000 m high and heavily dissected by rivers. In front of the mountain ranges is the flat coastal belt of Low Albania, 20-30 km wide. The climate of the coastal areas is typically the Mediterranean, while the inland mountain areas are particularly exposed to the influence of the land in winter. Albania has a history of invasions and uprisings. The Roman conquest of the land of the Illyrians was followed by Byzantine conquest, then Slavic, Bulgarian, Serbian, Venetian rule, and then for a long time by the Turkish Empire.
After independence in 1912, Austro-Hungarian and Italian invaders arrived. From 1946 until the first free elections in 1992, it was a communist republic, since then a democracy. The previously closed country opened its doors to tourists. In addition to the stunning natural environment, which is in many places unspoiled, there are two World Heritage Sites: the ruins of Butrint, a former Greek colony, Roman city and Byzantine bishopric, and the historic city of Gjirokastra, a rare example of a Turkish imperial city that has survived intact.
Background
Albania declared its independence from the Ottoman Empire in 1912 but was conquered by Italy in 1939 and occupied by Germany in 1943. Communist partisans took over the country in 1944. Albania allied itself first with the USSR (until 1960) and then with China (1978). In the early 1990s, Albania ended 46 years of isolated communist rule and established a multiparty democracy. The transition has proven challenging as successive governments have dealt with high unemployment, widespread corruption, dilapidated infrastructure, powerful organized crime networks, and combative political opponents.
Albania has made progress in its democratic development since it first held multiparty elections in 1991, but deficiencies remain. Most of Albania’s post-communist elections were marred by claims of electoral fraud. However, international observers judged elections to be essentially free and fair since the restoration of political stability following the collapse of pyramid schemes in 1997. Albania joined NATO in April 2009 and, in June 2014, became an EU candidate. Albania, in April 2017, received a European Commission recommendation to open EU accession negotiations following the passage of historic EU-mandated justice reforms in 2016. Although Albania’s economy continues to grow, it has slowed, and the country is still one of the poorest in Europe. A large informal economy and a weak energy and transportation infrastructure remain obstacles.
Geography
Narrow coastal plain. The interior is mostly hills and mountains. Forest and scrub cover over 40% of the land.
Lying at the southeastern end of the Adriatic Sea, Albania was the last east European country to liberalize its economy. The regional strife of the 1990s has left a problematic legacy.
This state is located in Southeastern Europe, bordering the Adriatic Sea and the Ionian Sea, between Greece to the south and Montenegro and Kosovo to the north, under the coordinates of 41 00 N, 20 00 E, covering an area of 28,748 sq km with a coastline of 362 km. Albania is Slightly smaller than Maryland.
Albania has 691 km of land boundaries in total, and bordering with (4 nations): Greece 212 km, Kosovo 112 km, Macedonia 181 km, Montenegro 186 km.
Mostly mountains and hills, small plains along the coast, with Maja e Korabit (Golem Korab) 2,764 m as the highest point of Albania, while the Adriatic Sea 0 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 708 m throughout the country. With a total of 28,748 sq km, Albania has 27,398 sq km of land and a 1,350 sq km water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Lake Scutari (shared with Montenegro) – 400 sq km (a freshwater lake), N/A (saltwater lake), while the major rivers are: N/A. The significant watersheds for Albania are Atlantic Ocean drainage: (Black Sea) Danube (795,656 sq km).
Strategic location along the Strait of Otranto (links Adriatic Sea to the Ionian Sea and the Mediterranean Sea).
The climate in Albania is as follows: Mild temperate, cool, cloudy, wet winters, hot, clear, dry summers. The interior is more relaxed and wetter.
When you visit Albania, the natural hazards shall be considered: Destructive earthquakes, tsunamis along the southwestern coast; floods; drought.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Albania: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Albanian people: deforestation; soil erosion; water pollution from industrial and domestic effluents; air pollution from industrial and power plants; loss of biodiversity due to lack of resources for sound environmental management.
Google Maps Albania
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Tirana (Tirane) found under the coordinates 41 19 N, 19 49 E, applying the time zone UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October.
The ancient capital of Albania, Tirana, is a beautiful city that offers every traveler its many art galleries, monuments, and restaurants.
Albania became independent on 28 November 1912 (from the Ottoman Empire), and its national holiday is Independence Day, 28 November (1912), also known as Flag Day.
Administrative divisions: 12 counties (qarqe, singular – qark); Berat, Diber, Durres, Elbasan, Fier, Gjirokaster, Korce, Kukes, Lezhe, Shkoder, Tirane, Vlore.
People and society
The pace of economic reform remains a significant issue. Albania’s application for EU membership reached candidate status in 2014. Mosques and churches have reopened in what was once the worlds only officially atheist state. The Greek minority in the south suffers much discrimination.
The population in Albania is 3,088,385 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 0.24% (2021 estimate) change. That means Albania is the No. 136 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 34.3 years median age (32.9 years for males and 32.9 years for women), Albania ranks No. 91 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Albanian(s) (noun) or Albanian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Albanian 82.6%, Greek 0.9%, other 1% (including Vlach, Romani, Macedonian, Montenegrin, and Egyptian), unspecified 15.5% (2011 estimate). Note: data represent population by ethnic and cultural affiliation.
They speak Albanian 98.8% (official language – derived from Tosk dialect), Greek 0.5%, other 0.6% (including Macedonian, Romani, Vlach, Turkish, Italian, and Serbo-Croatian), unspecified 0.1% (2011 estimate) languages and practice the following religions: Muslim 56.7%, Roman Catholic 10%, Orthodox 6.8%, atheist 2.5%, Bektashi (a Sufi order) 2.1%, other 5.7%, unspecified 16.2% (2011 estimate) note: all mosques and churches were closed in 1967 and religious observances prohibited; in November 1990, Albania began allowing the private religious practice.
We can conclude the following about the population in Albania: A fairly even distribution, with somewhat higher concentrations of people in the western and central parts of the country. In Albania, we are talking about 63% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 503,000 Tirana (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Oil and natural gas reserves can offset rudimentary infrastructure and a lack of foreign investment. Organized crime problem.
Albania, a formerly closed, centrally-planned state, is a developing country with a modern open-market economy. Albania managed to weather the first waves of the global financial crisis, but the crisis’s harmful effects caused a significant economic slowdown. Since 2014, Albania’s economy has steadily improved, and economic growth reached 3.8% in 2017. However, close trade, remittance, and banking sector ties with Greece and Italy make Albania vulnerable to spillover effects of possible debt crises and weak euro-zone growth. Remittances, a significant catalyst for economic growth, declined from 12-15% of GDP before the 2008 financial crisis to 5.8% of GDP in 2015, mostly from Albanians residing in Greece and Italy. The agricultural sector, which accounts for more than 40% of employment but less than one-quarter of GDP, is limited primarily to small family operations and subsistence farming because of a lack of modern equipment, unclear property rights, and the prevalence of small, inefficient plots of land. Complex tax codes and licensing requirements, a weak judicial system, endemic corruption, poor enforcement of contracts and property issues, and antiquated infrastructure contribute to Albania’s poor business environment making attracting foreign investment difficult.
Since 2015, Albania has launched an ambitious program to increase tax compliance and bring more businesses into the formal economy. In July 2016, Albania passed constitutional amendments reforming the judicial system to strengthen law and reduce entrenched corruption. Albania’s electricity supply is uneven despite upgraded transmission capacities with neighboring countries. However, the government has recently taken steps to stem non-technical losses and upgrade the distribution grid. Better enforcement of electricity contracts has improved the sector’s financial viability, decreasing its reliance on budget support. Also, with help from international donors, the government is taking steps to improve the poor road and rail networks, a long-standing barrier to sustained economic growth. Inward foreign direct investment has increased significantly in recent years as the government has embarked on an ambitious program to improve the business climate through fiscal and legislative reforms. The government is focused on simplifying licensing requirements and tax codes, and it entered into a new arrangement with the IMF for additional financial and technical support. Albania’s three-year IMF program, an extended fund facility arrangement, was successfully concluded in February 2017. The Albanian government has strengthened tax collection amid moderate public wage and pension increases to reduce its budget deficit. The country faces high public debt, exceeding its former statutory limit of 60% of GDP in 2013 and reaching 72% in 2016.
Albania is rich in the following natural resources: Petroleum, natural gas, coal, bauxite, chromite, copper, iron ore, nickel, salt, timber, hydropower, arable land.
The main industrial sectors are food, footwear, apparel, and clothing; lumber, oil, cement, chemicals, mining, basic metals, hydropower.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in leather footwear and parts, crude petroleum, iron alloys, clothing, electricity, perfumes (2019), partnering with these nations: Italy 45%, Spain 8%, Germany 6%, Greece 5%, France 4%, China 4% (2019). The export trade resulted in $3.47 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Albania’s position of 141.
Land use in Albania: 28.8% (2018 estimate) forest, 28.2% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 22.3% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 42.8% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 3% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 17.4% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 3,537 sq km (2014).
The main agro-industrial products of Albania are milk, maize, tomatoes, potatoes, watermelons, wheat, grapes, cucumbers, onions, apples.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, cars, tanned hides, packaged medical supplies, footwear parts (2019), partnering with the following nations: Italy 28%, Greece 12%, China 11%, Turkey 9%, Germany 5% (2019) in a sum value of $5.67 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $6.93 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $6.85 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Albania 134.
Albania Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Albania, Southeastern Europe, bordering the Adriatic Sea and the Ionian Sea, between Greece to the south and Montenegro and Kosovo to the north. We published some basic information about its capital Tirana (Tirane), and the Albanian nation.
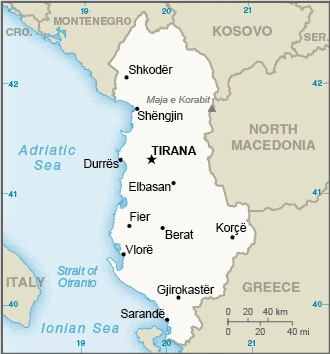
Are you interested in visiting Albania and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Albania below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Albania
Did you know about Albania?
Albania is one of only four countries globally that is not a member of NATO but is still considered a “partner for peace.” Although they are not members, Albania has contributed troops to NATO-led international missions.
After virtually visiting Albania, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Greece, Kosovo, Macedonia, Montenegro.
If you liked our Google map and Albania information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.