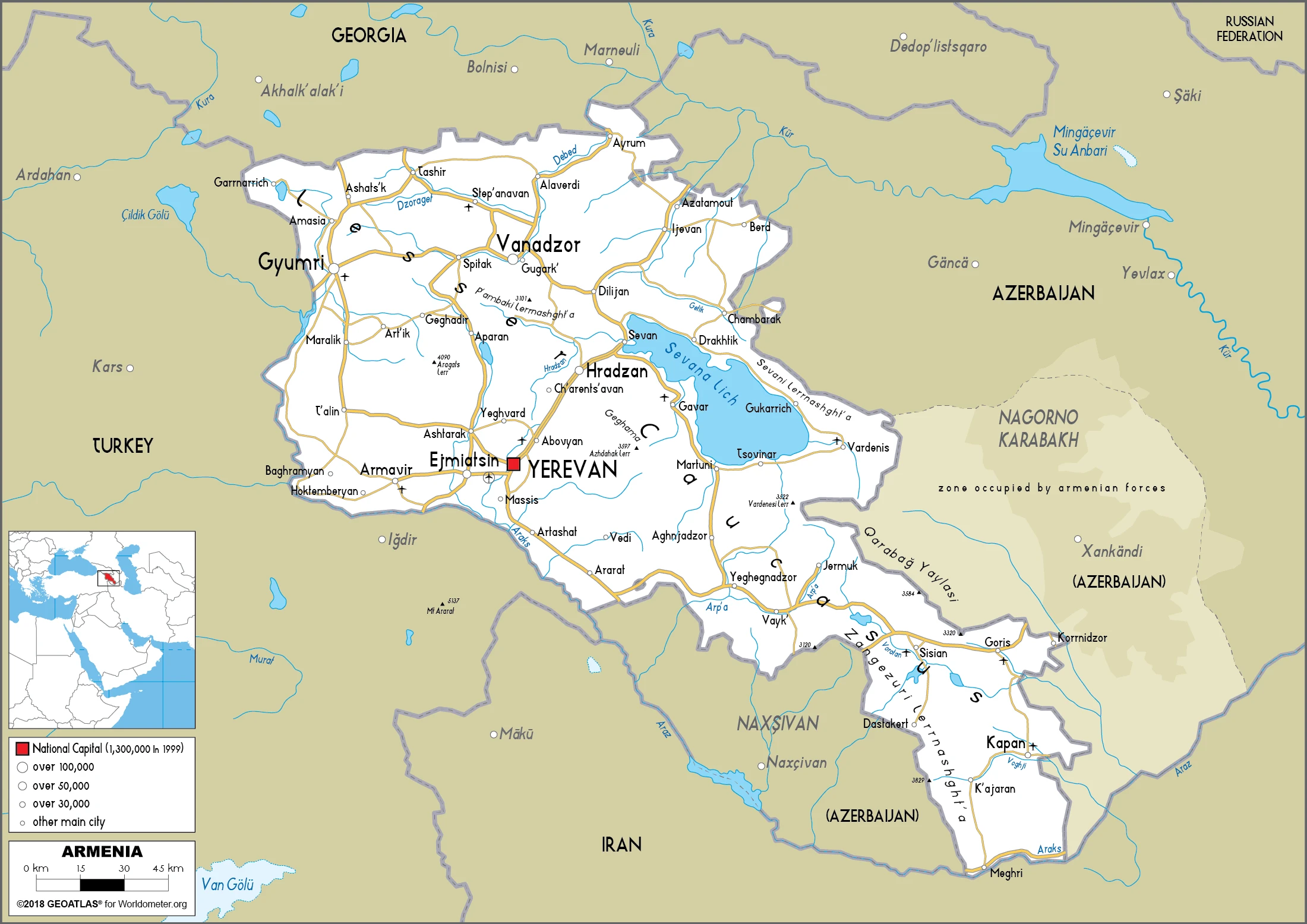
Armenia Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Armenia, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Armenia, Asia (22 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Yerevan, bordering countries like Azerbaijan, Georgia, Iran, Turkey, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Asian state.
Quick links: Google Maps Armenia, Yerevan Google maps, Driving Directions Armenia, Printable Road Map.

About Armenia in a nutshell
- In the 4th century, Armenia became the first country to adopt Christianity as its state religion.
- Conventional short form of the name: Armenia
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of Armenia
- Local long form: Hayastani Hanrapetutyun,
- Local short form: Hayastan
- Former name(s): Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic, Armenian Republic
- Etymology: the etymology of the country’s name remains obscure; according to tradition, the country is named after Hayk, the legendary patriarch of the Armenians and the great-great-grandson of Noah; Hayks descendant, Aram, purportedly is the source of the name Armenia.
- The legal system in Armenia: civil law system.
- Climate: Continental climate, with little rainfall in the lowlands. The winters are often bitterly cold.
- The national symbols are Mount Ararat, eagle, lion; national colors: red, blue, orange.
- Internet TLD: .am
Of the two former Soviet republics, Armenia and Azerbaijan, Armenia, a small landlocked country, occupies the slopes of the Lesser Caucasus. The fertile Ararat Valley is the country’s breadbasket. Nearly three times the size of Azerbaijan, the country is predominantly Muslim. It straddles the southeastern slopes of the Caucasus and the broad valley of the Kura River, which flows into the Caspian Sea. From 1200 BC, the region was populated by Indo-European peoples, ruled by Greeks and Romans, and then invaded by Mongol, Turkish and Persian conquerors. During World War I, the Turks displaced 1.75 million Armenians. However, Nagorno-Karabakh and Nakhichevan, predominantly inhabited by Armenians, to Azerbaijan became a source of further conflict. All three of Armenia’s World Heritage Sites contain medieval ecclesiastical monuments: the Byzantine monasteries of Hagbat and Sanahin, the churches of Echmiadzin with its archaeological site of Zvartnoc, and the gateway to the upper Azat River valley: the monastery of Geghard.
Background
Armenia prides itself on being the first nation to adopt Christianity (early 4th century) formally. Despite periods of autonomy, Armenia came under the sway of various empires over the centuries, including the Roman, Byzantine, Arab, Persian, and Ottoman. During World War I in the western portion of Armenia, the Ottoman Empire instituted a policy of forced resettlement coupled with other harsh practices that resulted in at least 1 million Armenian deaths – actions widely recognized as constituting genocide. The Ottomans ceded the eastern area of Armenia to Russia in 1828. This portion declared its independence in 1918 but was conquered by the Soviet Red Army in 1920.
Armenia remains involved in the protracted Nagorno-Karabakh struggle with Azerbaijan. Nagorno-Karabakh was a primarily ethnic Armenian region that Moscow recognized in 1923 as an autonomous oblast within Soviet Azerbaijan. In the late Soviet period, a separatist movement developed to end Azerbaijani control over the region. Fighting over Nagorno-Karabakh began in 1988 and escalated after Armenia and Azerbaijan attained independence from the Soviet Union in 1991. By the time a ceasefire took effect in May 1994, separatists, with Armenian support, controlled Nagorno Karabakh and seven surrounding Azerbaijani territories. Following a Second Nagorno-Karabakh War in September-November 2020, Azerbaijan recaptured much of its lost territory a quarter-century earlier. Under a ceasefire agreement, Armenia returned the remaining territories to Azerbaijan.
Turkey closed the common border with Armenia in 1993 in support of Azerbaijan in its conflict over control of Nagorno-Karabakh and surrounding areas, further hampering Armenian economic growth. In 2009, Armenia and Turkey signed Protocols normalizing relations between the two countries, but neither country ratified the Protocols, and Armenia officially withdrew from the Protocols in March 2018. In 2015, Armenia joined the Eurasian Economic Union alongside Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. In November 2017, Armenia signed a Comprehensive and Enhanced Partnership Agreement (CEPA) with the E.U. In spring 2018, Serzh SARGSIAN of the Republican Party of Armenia (RPA) stepped down, and Civil Contract party leader Nikol PASHINYAN became prime minister.
Geography
Rugged and mountainous, with expanses of semidesert and a large lake in the east: Sevana Lich.
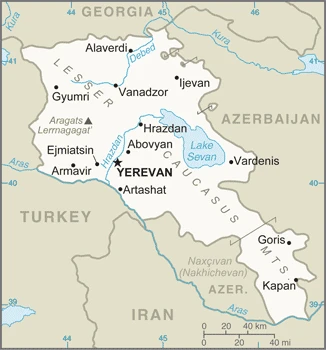
The smallest of the former USSRs republics, Armenia, lies landlocked in the Lesser Caucasus Mountains. After 1988, a confrontation with Azerbaijan dominated national life.
This state is located in Southwestern Asia, between Turkey (to the west) and Azerbaijan, under the coordinates of 40 00 N, 45 00 E, covering an area of 29,743 sq km with a coastline of 0 km (landlocked country). Armenia is Slightly smaller than Maryland.
Armenia has 1,570 km of land boundaries in total and borders with (4 nations): Azerbaijan 996 km, Georgia 219 km, Iran 44 km, Turkey 311 km.
Armenian Highland with mountains, little forest land, fast-flowing rivers, good soil in Aras River valley, with Aragats Lerrnagagat 4,090 m, as the highest point of Armenia, while Debed River 400 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 1,792 m throughout the country. With a total of 29,743 sq km, Armenia has 28,203 sq km of land and a 1,540 sq km water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Lake Sevan – 1,360 sq km (a freshwater lake), no saltwater lake, while the major rivers are: none.
Landlocked in the Lesser Caucasus Mountains, Sevana Lich (Lake Sevan) is the largest lake in this mountain range.
The climate in Armenia is as follows: Highland continental, hot summers, cold winters.
When you visit Armenia, the natural hazards shall be considered: Occasionally severe earthquakes; droughts.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Armenia: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Armenian people: soil pollution from toxic chemicals such as DDT; deforestation; pollution of Hrazdan and Aras Rivers; the draining of Sevana Lich (Lake Sevan), a result of its use as a source for hydropower, threatens drinking water supplies; restart of Metsamor nuclear power plant despite its location in a seismically active zone.
Google Maps Armenia
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Yerevan found under the coordinates 40 10 N, 44 30 E, applying the time zone UTC+4 (9 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Yerevan is the capital and largest city in Armenia. It is also an industrial hub, home to many manufacturing plants, including a now-defunct Soviet aircraft factory named Zvartnots.
Armenia became independent on 21 September 1991 (from the Soviet Union); notable earlier dates: 321 B.C. (the Kingdom of Armenia established under the Orontid Dynasty), A.D. 884 (the Armenian Kingdom reestablished under the Bagratid Dynasty); 1198 (the Cilician Kingdom established); 28 May 1918 (the Democratic Republic of Armenia declared), and its national holiday is Independence Day, 21 September (1991).
Administrative divisions: 11 provinces (marzer, singular – marz); Aragatsotn, Ararat, Armavir, Gegharkunik, Kotayk, Lorri, Shirak, Syunik, Tavush, Vayots Dzor, Yerevan.
People and society
Christianity is the dominant religion, but minority groups are well integrated. War with Azerbaijan over the enclave of Nagorno Karabakh forced 350,000 Armenians living in Azerbaijan to return home, many to live in poverty. There are close and significant ties to the 11-million-strong Armenian diaspora.
The population in Armenia is 3,011,609 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of -0.35% (2021 estimate) change. That means Armenia is the No. 138 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 36.6 years median age (35.1 years for males and 35.1 years for women), Armenia ranks No. 78 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Armenian(s) (noun) or Armenian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Armenian 98.1%, Yezidi (Kurd) 1.2%, other 0.7% (2011 estimate).
They speak Armenian (official language) 97.9%, Kurdish (spoken by Yezidi minority) 1%, other 1% languages and practice the following religions: Armenian Apostolic 92.6%, Evangelical 1%, other 2.4%, none 1.1%, unspecified 2.9% (2011 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Armenia: Most of the population is located in the northern half of the country. The capital of Yerevan is home to more than five times as many people as Gyumri, the second-largest city in the country. In Armenia, we are talking about 63.4% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 1.089 million, Yerevan (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Overseas remittances and agriculture each account for a sixth of GDP. The main products are wine, tobacco, potatoes, and fruit. Well-developed machine-building and manufacturing include textiles and bottling of mineral water.
Under the old Soviet central planning system, Armenia developed a modern industrial sector, supplying machine tools, textiles, and other manufactured goods to sister republics in exchange for raw materials and energy. Armenia has since switched to small-scale agriculture and away from the large agro-industrial complexes of the Soviet era. Armenia has only two open trade borders – Iran and Georgia – because its borders with Azerbaijan and Turkey have been closed since 1991 and 1993, respectively, as a result of Armenia’s ongoing conflict with Azerbaijan over the separatist Nagorno-Karabakh region., Armenia joined the World Trade Organization in January 2003. In recent years, the government has improved tax and customs administration, but anti-corruption measures have been largely ineffective.
Armenia will need to pursue additional economic reforms and strengthen the rule of law to raise its economic growth and improve economic competitiveness and employment opportunities, especially given its economic isolation from Turkey and Azerbaijan. Armenia’s geographic isolation, a narrow export base, and pervasive monopolies in important business sectors have made it particularly vulnerable to volatility in the global commodity markets and the economic challenges in Russia. Armenia is mainly dependent on Russian commercial and governmental support, as most key Armenian infrastructure is Russian-owned and managed, especially in the energy sector. Remittances from expatriates working in Russia are equivalent to about 12-14% of GDP. Armenia joined the Russia-led Eurasian Economic Union in January 2015 but has remained interested in pursuing closer ties with the E.U., signing a Comprehensive and Enhanced Partnership Agreement with the E.U. in November 2017. Armenia’s rising government debt is leading Yerevan to tighten its fiscal policies the amount is approaching the debt to GDP ratio threshold set by national legislation.
Armenia is rich in the following natural resources: Small deposits of gold, copper, molybdenum, zinc, bauxite.
The main industrial sectors are typically brandy, mining, diamond processing, metal-cutting machine tools, forging and pressing machines, electric motors, knitted wear, hosiery, shoes, silk fabric, chemicals, trucks, instruments, microelectronics, jewelry, software, food processing.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in copper ore, gold, tobacco, liquors, iron alloys (2019), partnering with these nations: Russia 22%, Switzerland 20%, China 7%, Bulgaria 6%, Iraq 5%, Serbia 5%, Netherlands 5%, Germany 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $3.82 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Armenia’s position of 137.
Land use in Armenia: 9.1% (2018 estimate) forest, 31.2% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 15.8% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 59.7% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 1.9% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 42% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 2,740 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Armenia are milk, potatoes, grapes, vegetables, tomatoes, watermelons, wheat, apples, cabbages, barley.
The country typically needs to import: natural gas, cars, refined petroleum, broadcasting equipment, diamonds (2019), partnering with the following nations: Russia 29%, China 10%, Georgia 8%, Iran 6%, Turkey 5% (2019) in a sum value of $5 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $7.47 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $6.61 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Armenia 139.
Armenia Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Armenia, Southwestern Asia, between Turkey (to the west) and Azerbaijan. We published some basic information about its capital Yerevan, and the Armenian nation.
Are you interested in visiting Armenia and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Armenia below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Armenia
Did you know about Armenia?
Armenia is a country at the crossroads of Europe and Asia. Armenia is known for its cultural heritage and is home to 4 World Heritage sites. Yerevan’s capital is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities globally. Armenia has gone through many transitions over the centuries, with different empires dominating the region’s culture.
After virtually visiting Armenia, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Azerbaijan, Georgia, Iran, Turkey.
If you liked our Google map and Armenia information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.