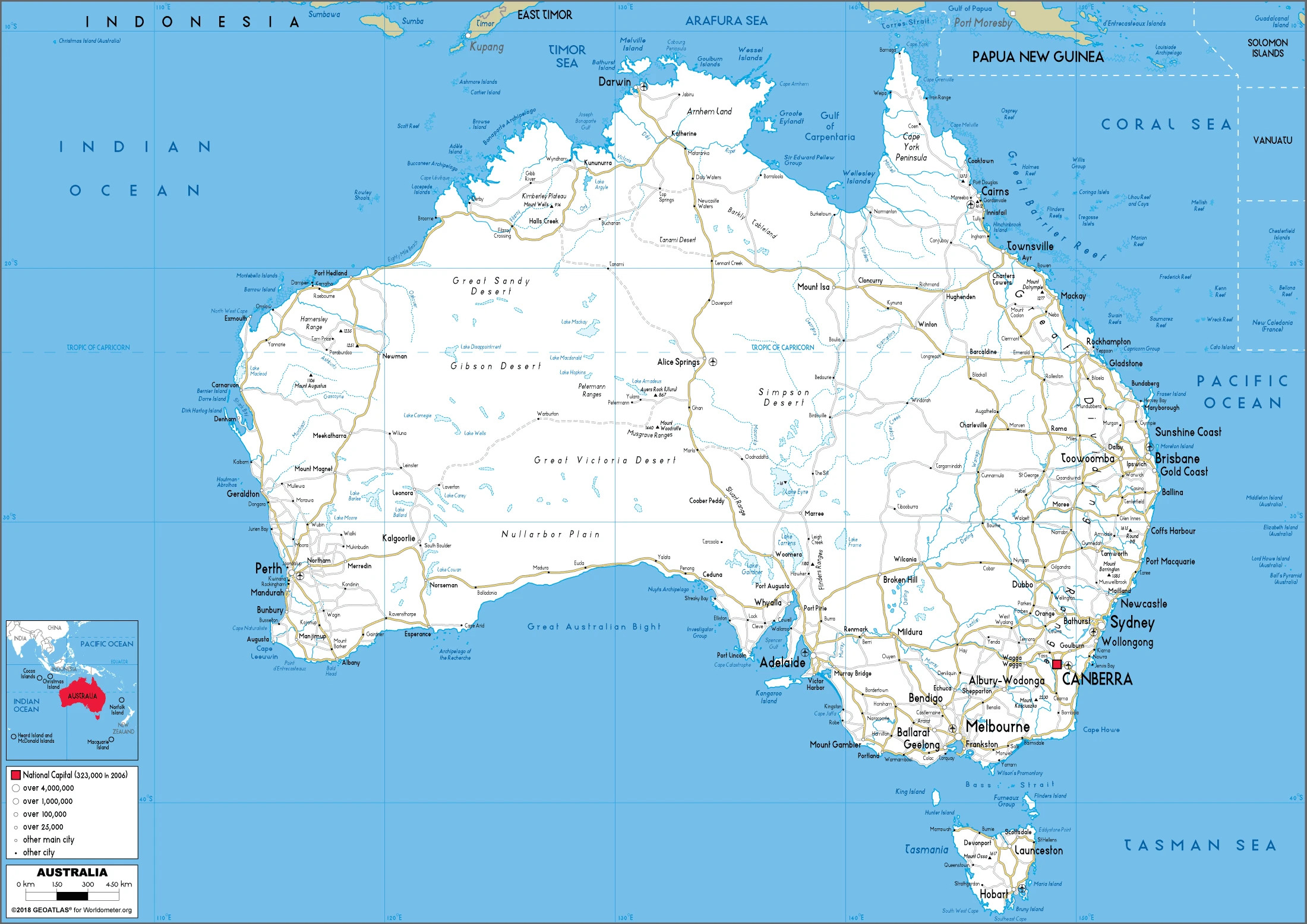
Australia Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Australia, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Australia, Oceania (27 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Canberra, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this Oceanian state.
Quick links: Google Maps Australia, Canberra Google maps, Driving Directions Australia, Printable Road Map.

About Australia in a nutshell
- Australia has the most endemic mammals and reptiles in the world. Species include marsupials such as the kangaroo and wombat, the egg-laying platypus, and the freshwater crocodile.
- Conventional short form of the name: Australia
- The conventional long form of the name: Commonwealth of Australia
- Etymology: the name Australia derives from the Latin australis meaning southern; the Australian landmass was long referred to as Terra Australis or the Southern Land.
- The legal system in Australia: common law system based on the English model.
- Climate: The west and south are semi-arid with hot summers. The arid interior can reach 120°F (50°C) in the central desert areas. The north is hot throughout the year, and humid during the summer monsoon. East, southeast, and south west coastal areas are temperate.
- The national symbols are Commonwealth Star (seven-pointed Star of Federation), golden wattle tree (Acacia pycnantha Benth), kangaroo, emu; national colors: green, gold.
- Internet TLD: .au
Australia is the only continent with only one country occupying its landmass; five countries on Earth are larger. Located in the center of the vast Australia-Indian coeval plate, the land has been left out of the global mountain-building process of recent geological history. It has been in a state of glacial doldrums for centuries – certainly in terms of earthquakes and volcanic activity.
The Southern Drylands is also the lowest continent. As a result of erosion, its highest point rises to just under 2,000 meters above sea level, and only 7% of its territory is higher than 600 meters. The Great Dividing Range on the eastern edge of the continent is a narrow, rainfall-rich coastal strip, which “separates” the continent, leaving two-thirds of Australia desert and semi-desert. Settlement of the continent may have begun from the Malay Archipelago around 40-50,000 years ago. Its indigenous inhabitants, representatives of the Vedic-Australia Grand Race, now number only 200 000; 92% of Australia’s population is descended from European ancestors.
Australia is a paradise for researchers in geology, zoology, botany, and a tourist paradise. The real attractions here are not historical monuments but nature. Just take a look at the UNESCO World Heritage List: 15 of the 17 sites in Australia are primarily natural heritage sites, including desert, savannah, and rainforest national parks, as well as the largest coral reef and sand island on Earth.
Background
Aboriginal Australians arrived on the continent at least 60,000 years ago and developed complex hunter-gatherer societies and oral histories. Dutch navigators led by Abel TASMAN were the first Europeans to land in Australia in 1606, and they mapped the western and northern coasts. They named the continent New Holland but made no attempts to settle it permanently. In 1770, English captain James COOK sailed to the east coast of Australia, named it New South Wales, and claimed it for Great Britain. In 1788 and 1825, Great Britain established New South Wales and Tasmania as penal colonies. Great Britain and Ireland sent more than 150,000 convicts to Australia before ending the practice in 1868. As Europeans began settling areas away from the coasts, they came into more direct contact with Aboriginal Australians.
Europeans also cleared land for agriculture, impacting Aboriginal Australians ways of life. Along with disease and a policy in the 1900s that forcefully removed Aboriginal children from their parents, these issues reduced the Aboriginal Australian population from more than 700,000 pre-European contacts to a low of 74,000 in 1933. Four additional colonies were established in Australia in the mid-1800s: Western Australia (1829), South Australia (1836), Victoria (1851), and Queensland (1859). Gold rushes beginning in the 1850s brought thousands of new immigrants to New South Wales and Victoria, helping to reorient Australia away from its penal colony roots. In the second half of the 1800s, the colonies were all gradually granted self-government, and in 1901, they federated and became the Commonwealth of Australia.
Australia contributed more than 400,000 troops to allied efforts during World War I, and Australian troops played a significant role in defeating Japanese troops in the Pacific in World War II. Australia severed most constitutional links with the UK in 1942, and in 1951 signed the Australia, New Zealand, and US (ANZUS) Treaty, cementing its military alliance with the US. Australia’s post-war economy boomed, and by the 1970s, racial policies that prevented most non-whites from immigrating to Australia were removed, significantly increasing Asian immigration to the country. Australia has become an internationally competitive, advanced market economy due to economic reforms adopted in the 1980s and proximity to East and Southeast Asia. In the early 2000s, Australian politics became unstable with frequent attempts to oust party leaders, including five prime minister changes between 2010 and 2018. As a result, both major parties instituted rules to make it harder to remove a party leader.
Geography
Located between the Indian and Pacific oceans, Australia has a variety of landscapes, including tropical rainforests, the arid plateaus, ridges, and vast deserts of the “red center,”
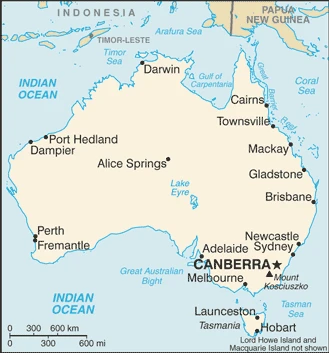
An island continent in its own right, Australia is the worlds sixth-largest country. European settlement began over 200 years ago. Most Australians now live in cities along the coast.
This state is located in Oceania, a continent between the Indian Ocean and the South Pacific Ocean, under the coordinates of 27 00 S, 133 00 E, covering an area of 7,741,220 sq km with a coastline of 25,760 km. Australia is slightly smaller than the US contiguous 48 states.
Mostly low plateau with deserts, fertile plain in the southeast with Mount Kosciuszko 2,228 m as the highest point of Australia, while Lake Eyre -15 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 330 m throughout the country. With a total of 7,741,220 sq km, Australia has 7,682,300 sq km of land and 58,920 sq km water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Lake Alexandrina – 570 sq km (freshwater lake), Lake Eyre – 9,690 sq km; Lake Torrens (ephemeral) – 5,780 sq km; Lake Gairdner – 4,470 sq km; Lake Mackay (ephemeral) – 3,494 sq km; Lake Frome – 2,410 sq km; Lake Amadeus (ephemeral) – 1,032 sq km (saltwater lake) while the major rivers are: River Murray – 2,508 km, Darling River – 1,545 km, Murrumbidgee River – 1,485 km, Lachlan River – 1,339 km, Cooper Creek – 1,113 km, Flinders River – 1,004 km. The significant watersheds for Australia are Indian Ocean drainage: (Great Australian Bight) Murray-Darling (1,050,116 sq km) Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: Lake Eyre (1,212,198 sq km).
World’s smallest continent but a sixth-largest country; the largest country in Oceania, the largest country entirely in the Southern Hemisphere, and the largest country without land borders.
The climate in Australia is as follows: Generally arid to semiarid, temperate in south and east, tropical in north.
When you visit Australia, the natural hazards shall be considered: Cyclones along the coast; severe droughts; forest fires, volcanism: volcanic activity on Heard and McDonald Islands.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Australia: none.
Current environmental issues affecting the Australian people: soil erosion from overgrazing, deforestation, industrial development, urbanization, and poor farming practices; limited natural freshwater resources; soil salinity rising due to the use of poor quality water; drought, desertification; clearing for agricultural purposes threatens the natural habitat of many unique animal and plant species; disruption of the fragile ecosystem has resulted in significant floral extinctions; the Great Barrier Reef off the northeast coast, the largest coral reef in the world, is threatened by increased shipping and its popularity as a tourist site; overfishing, pollution, and invasive species are also problems.
Google Maps Australia
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Canberra found under the coordinates 35 16 S, 149 08 E, applying the time zone UTC+10 (15 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: +1hr, begins first Sunday in October; ends first Sunday in April.
Canberra is a city in Australia’s southeast. It’s home to the nation’s highest concentration of technological innovation, with many start-ups and tech giants.
Australia became independent on 1 January 1901 (from the federation of UK colonies), and its national holiday is Australia Day (commemorates the arrival of the First Fleet of Australian settlers), 26 January (1788); ANZAC Day (commemorates the anniversary of the landing of troops of the Australian and New Zealand Army Corps during World War I at Gallipoli, Turkey), 25 April (1915).
Administrative divisions: 6 states and 2 territories*; Australian Capital Territory, New South Wales, Northern Territory, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria, Western Australia.
People and society
The first settlers arrived in Australia at least 100,000 years ago. Today, the Aborigines make up around 2% of the population. European colonization began in 1788 and was dominated by British and Irish immigrants convicts. White-only immigration drives brought many Europeans to Australia, but since the 1960s, multiculturalism has been encouraged, and most new settlers are Asian; Cantonese has overtaken Italian as the second most widely spoken language. Wealth disparities are small, but Aborigines, the exception in an otherwise integrated society, are marginalized: their average life expectancy is around ten years less than other Australians. Illegal immigration is a critical political divide; Liberal-National government policies aim to turn back asylum seekers or process and resettle them offshore.
The population in Australia is 25,809,973 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 1.31% (2021 estimate) change. That means Australia is the No. 55 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 37.5 years median age (36.5 years for males and 36.5 years for women), Australia ranks No. 69 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Australian(s) (noun) or Australian (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: English 25.9%, Australian 25.4%, Irish 7.5%, Scottish 6.4%, Italian 3.3%, German 3.2%, Chinese 3.1%, Indian 1.4%, Greek 1.4%, Dutch 1.2%, other 15.8% (includes Australian Aboriginal .5%), unspecified 5.4% (2011 estimate). Note: data represent self-identified ancestry, over a third of respondents reported two ancestries.
They speak English 72.7%, Mandarin 2.5%, Arabic 1.4%, Cantonese 1.2%, Vietnamese 1.2%, Italian 1.2%, Greek 1%, other 14.8%, unspecified 6.5% (2016 estimate). Note: data represent language spoken at home languages and practice the following religions: Protestant 23.1% (Anglican 13.3%, Uniting Church 3.7%, Presbyterian and Reformed 2.3%, Baptist 1.5%, Pentecostal 1.1%, Lutheran .7%, other Protestant .5%), Roman Catholic 22.6%, other Christian 4.2%, Muslim 2.6%, Buddhist 2.4%, Orthodox 2.3% (Eastern Orthodox 2.1%, Oriental Orthodox .2%), Hindu 1.9%, other 1.3%, none 30.1%, unspecified 9.6% (2016 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Australia: Population is primarily located on the periphery, with the highest concentration of people residing in the east and southeast secondary population center is located in and around Perth in the west. Of the states and territories, new south wales have, by far, the largest population. The interior, or outback, has a very sparse population. In Australia, we are talking about 86.4% (2021) of the total population is living in cities. Most of them reside in the following municipalities: 5,061 million, Melbourne, 4.992 million, Sydney, 2.439 million, Brisbane, 2.067 million, Perth, 1.345 million, Adelaide, 462,000 Canberra (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Efficient mining and agriculture: particular success in viticulture. Large resource base: coal, iron ore, bauxite, and most other minerals. Protectionism abandoned to open up Australian markets. Concentration on trade with Asia: Chinas rapidly expanding demand for minerals means it has surpassed Japan as Australias major trading partner. The upward trend in Asian visitor arrivals has strengthened tourism. The effects of droughts, floods, and cyclones have dented economic growth in recent years.
Australia is an open market with minimal imports of goods and services. The process of opening up has increased productivity, stimulated growth, and made the economy more flexible and dynamic. Australia plays an active role in the WTO, APEC, the G20, and other trade forums. Australia’s free trade agreement (FTA) with China entered into force in 2015, adding to existing FTAs with the Republic of Korea, Japan, Chile, Malaysia, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, the US, and a regional FTA with ASEAN and New Zealand. Australia continues to negotiate bilateral agreements with Indonesia, more extensive agreements with its Pacific neighbors and the Gulf Cooperation Council countries, and an Asia-wide Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership that includes the 10 ASEAN countries and China, Japan, Korea, New Zealand, and India.
Australia is a significant exporter of natural resources, energy, and food. Australias abundant and diverse natural resources attract high levels of foreign investment and include extensive reserves of coal, iron, copper, gold, natural gas, uranium, and renewable energy sources. A series of significant investments, such as the US$40 billion Gorgon Liquid Natural Gas Project, will significantly expand the resources sector., For nearly two decades until 2017, Australia had benefited from a dramatic surge in its terms of trade. As export prices increased faster than import prices, the economy experienced continuous growth, low unemployment, contained inflation, very low public debt, and a solid and stable financial system. Australia entered 2018 facing a range of growth constraints, principally driven by the sharp fall in global prices of essential export commodities. Demand for resources and energy from Asia and especially China is growing slower, and sharp drops in export prices have impacted growth.
Australia is rich in natural resources: Alumina, coal, iron ore, copper, tin, gold, silver, uranium, nickel, tungsten, rare earth elements, mineral sands, lead, zinc, diamonds, natural gas, petroleum.
The main industrial sectors are mining, industrial and transportation equipment, food processing, chemicals, steel.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in iron ore, coal, natural gas, gold, aluminum oxide (2019), partnering with these nations: China 39%, Japan 15%, South Korea 7%, India 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $299.04 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Australia’s position of 23.
Land use in Australia: 17.42% (2018 estimate) forest, 33.42% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 4.03% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 46.65% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.04% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 42.58% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 25,460 sq km (2014).
The main agro-industrial products of Australia are sugar cane, wheat, barley, milk, rapeseed, beef, cotton, grapes, poultry, potatoes.
The country typically needs to import: refined petroleum, cars, crude petroleum, broadcasting equipment, delivery trucks (2019), partnering with the following nations: China 25%, United States 12%, Japan 7%, Germany 5%, Thailand 5% (2019) in a sum value of $249.07 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2020 estimate) $295.46 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $310.23 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Australia 23.
Australia Driving Directions
You learned about Australia, Oceania, continent between the Indian Ocean and the South Pacific Ocean in this post. We published some basic information about Canberra’s capital and the Australian nation.
Are you interested in visiting Australia and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Australia below for an overview of the route network.
Printable map of Australia
Did you know about Australia?
Australia is a country made up of the Australian continent and the island of Tasmania. It is a country of extremes, with some of the world’s most fertile agricultural land in areas such as the Murray-Darling Basin in the southeast hile. Some parts are arid deserts or rugged mountain ranges. There are six states and two territories in mainland Australia – New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Victoria, Western Australia, and Tasmania – and two large islands off its coast: Tasmania and Papua New Guinea.
After virtually visiting Australia, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: China, Germany, India, Japan, United States, South Korea Thailand.
If you liked our Google map and Australia information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.