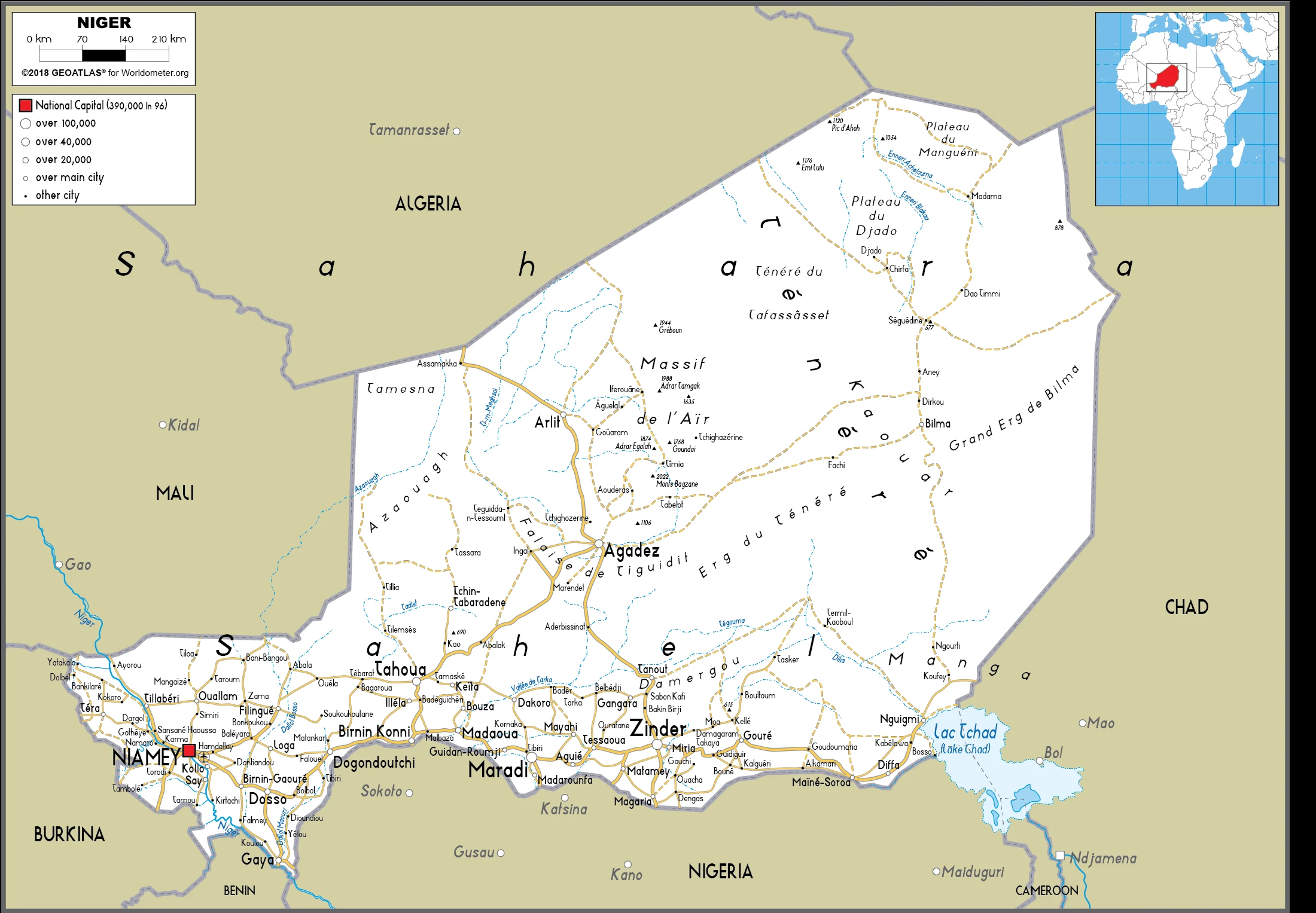
Niger Google Maps is a site/tool that offers a wide range of map views (topographic, satellite, street view) and navigation options, with little effort on your part, yet efficiently. If you need to plan a trip to a new place like Niger, Google maps are available on desktop, mobile, or tablet. This Google maps and information page is dedicated to Niger, Africa (54 countries), showing its location, country facts, details about its capital city Niamey, bordering countries like Algeria, Benin, Burkina Faso, Chad, Libya, Mali, Nigeria, and plenty of other information which may be interesting when you visit this African state.
Quick links: Google Maps Niger, Niamey Google maps, Driving Directions Niger, Printable Road Map.
About Niger in a nutshell

- Conventional short form of the name: Niger
- The conventional long form of the name: Republic of Niger
- Local long form: Republique du Niger
- Local short form: Niger
- Etymology: named for the Niger River that passes through the southwest of the country; from a native term Ni Gir meaning River Gir.
- The legal system in Niger: mixed legal system of civil law, based on French civil law, Islamic law, and customary law.
- Climate: High temperatures persist for most of the year at around 95°F (35°C). The north is virtually rainless.
- The national symbols are zebu; national colors: orange, white, green.
- Internet TLD: .ne
The Sahara dominates Two-thirds of the Sahel. The Muslim state, inhabited by desert nomads, Tuaregs, Fulani, and Hausa, is regularly hit by drought. During Cure Salae, the most colorful and most prominent festival in West Africa, nomads gather on the salt flats every September to wait for the redemptive rains. One of the festival’s highlights is the wodabé people’s festival of gerewol: a beauty contest of tall, slender, and exceptionally handsome men with elegant, painted faces, accompanied by music and dance, lasts for hours, to the delight of judges chosen from among the women. Niger boasts two World Natural Heritage Sites. The Air and Ténéré reserves are the largest protected areas in Africa. The black, needle-pointed volcanic cliffs of the Ayr Mountains of Switzerland, with their unique wildlife, are home to hot springs and magnificent waterfalls. 500 km to the northeast is the ‘desert of deserts’, the Ténéré, with the most beautiful dunes in the Sahara. Salt is distilled in the area and transported by camel caravans of Tuaregs to the towns’ markets. On the south-western border of the country, the ‘W’ National Park is named after the Tapoa, a tributary of the Niger, which forms the riverbed of the Tapoa. The protected area, which straddles the borders of four countries – Niger, Benin, Nigeria, and Burkina Faso – is a habitat for the typical fauna of the grassy and wooded savannah.
Niger comes from the Tuareg word neghirren, which means “flowing water”.
Background
Present-day Niger originated from the nomadic peoples of the Saharan north and the agriculturalists of the south. The Taureg kingdom of Takeda was one of the largest kingdoms in the north and played a prominent role in regional trade in the 14th century. In the south, the primary ethnic groups were the Songhai-Zarma in the west, the Hausa in the center, and the Kanuri in the east. When European colonizers arrived in the 19th century, the region was an assemblage of disparate local kingdoms. In the late 19th century, the British and French agreed to partition the middle regions of the Niger River, and France began its conquest of what would become the colony of Niger. France experienced determined local resistance – particularly during the Tuareg uprising (1916-1917) – but established a colonial administration in 1922. Following independence from France in 1960, the country experienced single-party or military rule until 1991, when political pressure forced General Ali SAIBOU to allow multiparty elections. Political infighting and democratic backsliding led to coups in 1996 and 1999. In December of that year, military officers restored democratic rule and held elections that brought Mamadou TANDJA to power.
TANDJA was reelected in 2004 and spearheaded a 2009 constitutional amendment allowing him to extend his presidential term. In February 2010, military officers led another coup that deposed TANDJA. ISSOUFOU Mahamadou was elected in April 2011 and reelected in early 2016. In February 2021, BAZOUM Mohammed won the presidential election, marking Nigers first transition from one democratically elected president to another. Niger is one of the poorest countries in the world, with minimal government services and insufficient funds to develop its resource base. It is ranked last in the world on the UN Development Programmes Human Development Index. The largely agrarian and subsistence-based economy is frequently disrupted by extended droughts common to the Sahel region of Africa. The Nigerien government continues its attempts to diversify the economy through increased oil production and mining projects. In addition, Niger is facing increased security concerns on its borders from various external threats, including insecurity in Libya, spillover from the conflict and terrorism in Mali, and violent extremism in northeastern Nigeria.
Geography
The north and northeast regions are part of the Sahara. The Air Mountains in the center rise high above the desert. Savanna lies to the south.
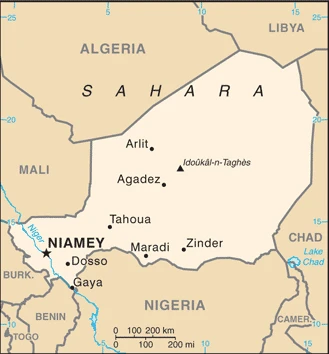
Niger lies in west Africa, upstream from Nigeria on the Niger River. One of the worlds poorest states was ruled by one-party or military regimes until multipartyism was allowed in 1992.
This state is located in Western Africa, southeast of Algeria, under the coordinates of 16 00 N, 8 00 E, covering an area of 1.267 million sq km with a coastline of 0 km (landlocked country). Niger is Slightly less than twice the size of Texas.
Niger has 5,834 km of land boundaries in total and borders (7 nations): Algeria 951 km, Benin 277 km, Burkina Faso 622 km, Chad 1196 km, Libya 342 km, Mali 838 km, Nigeria 1608 km.
Predominately desert plains and dunes, flat to rolling plains in the south, hills in the north, with Idoukal-n-Taghes 2,022 m as the highest point of Niger, while Niger River 200 m as the lowest point, causing a mean elevation at 474 m throughout the country. With 1.267 million sq km, Niger has 1,266,700 sq km of land and 300 sq km of water surface area.
Major water bodies in the country: Lake Chad (endorheic lake shared with Chad, Nigeria, and Cameroon) – 10,360-25,900 sq km (a freshwater lake), N/A (saltwater lake), while the major rivers are: Niger (shared with Guinea, Mali, and Nigeria) – 4,200 km. The significant watersheds for Niger are Atlantic Ocean drainage: Niger (2,261,741 sq km), Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: and Lake Chad (2,497,738 sq km).
Landlocked; one of the hottest countries in the world; northern four-fifths is desert, southern one-fifth is savanna, suitable for livestock and limited agriculture.
The climate in Niger is as follows: Desert, mostly hot, dry, dusty, tropical in the extreme south.
When you visit Niger, the natural hazards shall be considered: Recurring droughts.
The following major health-threatening issues shall be considered when visiting Niger: degree of risk: very high (2020), bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, typhoid fever, malaria, dengue fever, schistosomiasis, rabies, meningococcal meningitis.
Current environmental issues affecting the Nigerien people: overgrazing; soil erosion; deforestation; desertification; contaminated water; inadequate potable water; wildlife populations (such as elephant, hippopotamus, giraffe, and lion) threatened because of poaching and habitat destruction.
Google Maps Niger
The capital and other divisions
Capital city: Niamey found under the coordinates 13 31 N, 2 07 E, applying the time zone UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time), using the following daylight saving time: none.
Niamey is the capital of Niger, located in the northwest corner of the country. The city was established by French colonists in 1887 and became the capital of Niger upon independence from France. The city was subjected to severe flooding incidents in 2012. More than a third of the Nigerien industry takes place in Niamey, making it the country’s fastest-growing city. The city has a population that grows by 10% annually.
Niger became independent on 3 August 1960 (from France), and its national holiday is Republic Day, 18 December (1958).
Administrative divisions: 7 regions (regions, singular – region) and 1 capital district (communaute urbaine); Agadez, Diffa, Dosso, Maradi, Niamey, Tahoua, Tillaberi, Zinder.
People and society
Tuareg nomads in the north feel excluded from politics and the benefits of their areas uranium resources. An early 1990s rebellion reignited briefly in 2007-2009. In the south, egalitarianism and a sense of community help to combat economic difficulties. Almost the entire urban population lives in slum conditions. Two-thirds of the population is under 25. Women have limited rights and restricted access to education. The army seized power briefly in 2010.
The population in Niger is 23,605,767 (July 2021 estimate), with an average of 3.65% (2021 estimate) change. That means Niger is the No. 56 in the world’s populated rank list. With an average of 14.8 years median age (14.5 years for males and 14.5 years for women), Niger ranks No. 227 on the globe’s median age rank list.
The people living in this country are the Nigerien(s) (noun) or Nigerien (adjective) and belong mainly to the following ethnic groups: Hausa 53.1%, Zarma/Songhai 21.2%, Tuareg 11%, Fulani (Peuhl) 6.5%, Kanuri 5.9%, Gurma 0.8%, Arab 0.4%, Tubu 0.4%, other/unavailable 0.9% (2006 estimate).
They speak French (official language), Hausa, and Djerma languages and practice the following religions: Muslim 99.3%, Christian 0.3%, animist 0.2%, none 0.1% (2012 estimate).
We can conclude the following about the population in Niger: The majority of the populace is located in the southernmost extreme of the country along the border with Nigeria and Benin, as shown in this population distribution map. In Niger, we are talking about 16.8% (2021) of the total population is living in cities, and most of them reside in the following municipalities: 1.336 million, Niamey (capital city) (2021).
Industry
Vast uranium deposits. Frequent droughts and food shortages. Banditry. Expansion of Sahara. Oil potential.
Niger is a landlocked, Sub-Saharan nation whose economy centers on subsistence crops, livestock, and some of the world’s largest uranium deposits. Agriculture contributes approximately 40% of GDP and provides a livelihood for over 80% of the population. The UN ranked Niger as the second least developed country in the world in 2016 due to multiple factors such as food insecurity, lack of industry, high population growth, a weak educational sector, and few prospects for work outside of subsistence farming and herding., Since 2011 public debt has increased due to efforts to scale-up public investment, particularly that related to infrastructure and increased security spending. The government relies on foreign donor resources for a significant portion of its fiscal budget.
The economy in recent years has been hurt by terrorist activity near its uranium mines and by instability in Mali and the Diffa region of the country; security concerns have resulted in increased support from regional and international partners on defense. Low uranium prices, demographics, and security expenditures may continue to pressure the government’s finances. The Government of Niger plans to exploit oil, gold, coal, and other mineral resources to sustain future growth. Although Niger has sizable oil reserves, the prolonged drop in oil prices has reduced profitability. Food insecurity and drought remain perennial problems for Niger, and the government plans to invest more in irrigation. Nigers three-year $131 million IMF Extended Credit Facility (ECF) agreement for the years 2012-15 was extended until 2016. In February 2017, the IMF approved a new 3-year $134 million ECF.
In June 2017, The World Banks International Development Association (IDA) granted Niger $1 billion over three years for IDA18, a program to boost the country’s development and alleviate poverty. A $437 million Millennium Challenge Account compact for Niger, commencing in FY18, will focus on large-scale irrigation infrastructure development and community-based, climate-resilient agriculture while promoting sustainable agricultural productivity and sales increases. Formal private sector investment needed for economic diversification and growth remains a challenge, given the country’s limited domestic markets, access to credit, and competitiveness. Although President ISSOUFOU is courting foreign investors, including those from the US, as of April 2017, no US firms were operating in Niger. In November 2017, the National Assembly passed the 2018 Finance Law geared towards raising government revenues and moving away from international support.
Niger is rich in the following natural resources: Uranium, coal, iron ore, tin, phosphates, gold, molybdenum, gypsum, salt, and petroleum.
The main industrial sectors are uranium mining, petroleum, cement, brick, soap, textiles, food processing, chemicals, and slaughterhouses.
The country’s export sectors are particularly strong in gold, sesame seeds, uranium, natural gas, and refined petroleum (2019), partnering with these nations: the United Arab Emirates 54%, China 25%, France 7%, Pakistan 5% (2019). The export trade resulted in $1.39 billion. Note: Data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate). In a global rank of the export, values resulted in Niger’s position of 168.
Land use in Niger: 1% (2018 estimate) forest, 63.9% (2018 estimate) other.
The arable land area is 12.3% (2018 estimate), and the agricultural land is 35.1% (2018 estimate). Land use for permanent crops 0.1% (2018 estimate), permanent pasture 22.7% (2018 estimate). The sum of the area of the irrigated land is 1,000 sq km (2012).
The main agro-industrial products of Niger are millet, cowpeas, sorghum, onions, milk, groundnuts, cassava, cabbages, goat milk, and fruit.
The country typically needs to import: rice, packaged medicines, palm oil, cars, cement (2019), partnering with the following nations: China 19%, France 9%, United Arab Emirates 7%, Côte d’Ivoire 6%, India 6%, Nigeria 5%, Togo 5%, Turkey 5% (2019) in a sum value of $3.4 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2019 estimate) $3.37 billion. Note: data are in current year dollars (2018 estimate). This sum value on the global ranking list of imports resulted in Niger 155.
Niger Driving Directions
In this post, you learned about Niger, Western Africa, and southeast Algeria. We published some basic information about its capital Niamey and the Nigerien nation.
Are you interested in visiting Niger and looking for driving directions? Click here to plan your route, or see a printable road map of Niger below to overview the route network.
Printable map of Niger
Did you know about Niger?
You probably have never heard of Niger, but it is the fifth-largest African country. Niger has 23,6 million people with a great diversity in ethnic groups and languages. The country has just one university and only four hospitals. To make things worse, Niger is the poorest country in the world. It’s estimated that over half the population lives on less than $1 per day, and about 40% are illiterate.
After virtually visiting Niger, you may also be interested in the neighboring countries: Algeria, Benin, Burkina Faso, Chad, Libya, Mali, and Nigeria.
If you liked our Google map and Niger information page,
please share it with others or save the link https://www.drivingdirections.net in your bookmarks.